Abstract on the topic Periodic system of Mendeleev. "Periodic law and a periodic system of chemical elements d
Chemistry lesson
in grade 9 on the topic:
"Periodic law and periodic system D.I. Inendeeva "
Further: Chemistry Teacher, Biology
Korshunova Svetlana Valerievna
p. Golyshchmanovo 2015
Topic: Periodic Law and Periodic System D.I. Inendeeva
Purpose:To give students an idea of \u200b\u200bthe law of D.I. Imeleeev and on the structure of its periodic system, to identify the significance of this law to develop chemistry and understanding the scientific picture of the world as a whole.
Tasks:Educational.
To form knowledge of the periodic law and the Periodic system of D.I. Imeleeev.
Teach students to work with the periodic system (able to determine the position of the element in the periodic system, the properties of the element depending on its position in the periodic system).
Continue the formation of skills to work with a tutorial, notebook. Developing.
Develop observation, memory (when studying the physical meaning of the periodic law and the graphical display of it).
Develop the ability to compare (for example, a comparison of the properties of the elements depending on their position in the periodic system).
Teach students to summarize and draw conclusions. Educational.
To continue the formation of the worldview of students on the basis of ideas about the meaning of the law of D.I. Imeleeva. Type of lesson: learning a new material
Form of lesson: Working with information text
Methods:1. Perceptual aspect (aspect of perception): Visually - practical methods.
2. Logical aspect (mental operations when applying and assimilating educational material); deductive methods (from total to private); Systematization of knowledge.
3. Gnostic aspect (cognition); Heuristic (partially search) method.
4. Management aspect (degree of independence of the student); Independent training activities. Channels communication: student - literary source; student - student; Pupil - Teacher.
Equipment:system chemical elements D. I. Mendeleev, presentation on the subject of the lesson.
During the classes:
Epigraph on the board."Periodic law does not threaten the future, but only the superstructure and development are promised" (D.I. Imeteleev)
Stages lesson All students have the text in which they must try to find answers to the questions they melt themselves. It is about 15 minutes to work with the text, after which the teacher returns to questions recorded on the board and asks the guys to respond to them. (Appendix) Then the guys are given a task to make a new story, but already on the basis of read. You can only hear only one answer, and the guys offer to supplement it. Continated testing. Intellite independently 5-7 minutes respond to test tasks that are printed in advance and distributed to each to the table. 1. Alkali metals include elements:
a) na; b) Al; c) Ca; d) Li. 2. Sodium Store under the layer:
a) kerosene; b) water; c) sand; d) gasoline. 3. The most active among the elements:
a) li; b) na; c) CS; d) K. 4. Medium characteristic of NaOH solution:
a) acid; b) alkaline; c) neutral. 5. Set compliance:
Alkaline metal
6. Set compliance:Oxide
7. To halogens include:a) CL; b) Mn; c) in; d) re. 8. Choose a medium characteristic of an aqueous solution of HCl:
a) alkaline; b) acid; c) neutral. 9. The classification of the elements of D.I. Indelaev put it:
a) mass; b) density; c) temperature. 10. Please offer:
"D.I. Imeteleev placed elements in order ..." 11. In the list of chemical elements Al, P, Na, C, Cu more:
a) metals; b) non-metals. 12. Small periods are:
a) 1; b) 2; at 5; d) 7. 13. The main subgroup I includes:
a) na; b) Cu; c) k; d) Li. 14. In the main subgroup with a decrease in the sequence number Metal properties:
a) increase; b) weaken; c) do not change. The students who actively worked when checking tests and correctly answered them, high marks are exposed.
Periodic law and periodic system D.I. Mendeleev
Dmitry Mendeleev was born on February 8, 1834 in Tobolsk in the family of the director of the gymnasium and the trustee of popular schools of the Tobolsk province Ivan Pavlovich Mendeleev and Mary Dmitrievna Mendeleev, nee Corneli.
In the autumn of 1841, Mitya entered Tobolsk gymnasium. Having finished gymnasium in his hometown, Dmitry Ivanovich entered St. Petersburg in main pedagogical Institute, after the end of which the gold medal went to two years in a scientific business trip abroad. After returning, he was invited to St. Petersburg University. Starting reading lectures in chemistry, Mendeleev did not find nothing that could be recommended to students as tutorial. And he i decided to write a new book - "Fundamentals of Chemistry."The discovery of the periodic law was preceded by 15 years of hard work. By the time of the opening of the periodic law, 63 chemical elements were known, there were about 50 different classifications. Most scientists were compared among themselves only similar elements on the properties, so they could not open the law. Mendeleev compared everything among himself, including non-elements. As main characteristic Atom when building a periodic system was his atomic mass has been adopted.D. I. Mendeleev discovered a periodic change in the properties of elements with a change in the values \u200b\u200bof their atomic masses, comparing unrequisite natural groups of elements among them. At that time, such groups of elements, such as halogens, alkaline and alkaline earth metals, were known. Mendeleev followed and compared the elements of these groups, placing them in ascending order of atomic mass values.All this gave the opportunity to D. I. REMEELEEVA OPERATION TO THE ENGLISH THE LAW Name "the law of periodicity" and formulate as follows: "The properties of simple bodies, as well as the forms and properties of the compounds of elements are in periodic dependence (or, expressing algebraically, form a periodic function) from the value Atomic weights of elements. In accordance with this law, a periodic system of elements ", which objectively reflects the periodic law. The whole range of elements arranged in the order of increasing atomic masses, D. I. Mendeleev splits for periods. Inside each period, the properties of elements (for example, from alkali metal to halogen) are naturally changed. Placing periods so as to highlight similar elements, D. I. Mendeleev created a periodic system of chemical elements. At the same time, a number of elements were fixed atomic masses, and for 29 not open elements, empty places (docking) were left.
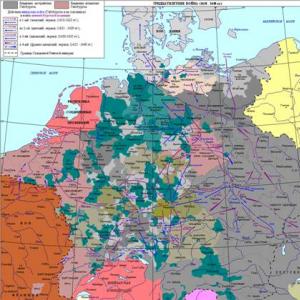
Periodic system of elements is a graphic (tabular) image of a periodic law
The opening date of the law and the creation of the first version of the periodic system is March 1, 1869, over the improvement of the periodic system of elements D. I. Mendeleev worked until the end of his life.Currently, more than 500 options for the image of the periodic system are known; These are various forms of transmission of a periodic law.
In the periodic system horizontally, there are 7 periods (indicated by Roman numbers), of which I, II and III are called small, and IV, V, VI and VII are large. All elements of the periodic system are numbered in the order in which they follow each other. Rooms of elements are called ordinal or atomic numbers.
In the periodic vertical system, eight groups are located (marked with Roman numbers). The number of the group is associated with the degree of oxidation of the elements that appear in the connections. As a rule, the highest positive degree of oxidation of the elements is equal to the number of the group. Exception are fluorine - its oxidation degree is -1; Copper, silver, gold exhibit oxidation degree +1, +2 and +3; From the elements of the VIII group, the degree of oxidation is +8 known only for osmium, ruthenium and xenon.
Each group is divided into two subgroups - the main thing and sidethat in the periodic system is emphasized by the displacement of some to the right, and others left.The properties of elements in subgroups are naturally changed: metal properties and non-metallic weakens are intensified from top to bottom. Obviously, metal properties are most strongly expressed in France, then the cesium; Non-metallic - at fluorine, then at oxygen.
Irkutsk region
Kirensky district
MKOU "Sosh S. Makarovo"
2014 U.G.
Teacher: Kozlova T.I.
Chemistry. 8th grade.
Theme lesson: Periodic system D.I. Mendeleev
The purpose of the lesson: the formation of knowledge about the structure of the periodic system and its role in the global chemical community.
Tasks lesson:
examine the structure of PSH.h.E.
show the significance of PSH.E. when studying chemistry;
get acquainted with modern variants of periodic systems;
prove that psh.h.e. is a great opening of Russian science, in the face of D.I. Mendeleev;
form the skills and skills of using the table, for the extraction of information laid in it;
The basic concepts of the topic: - D.I. Mendeleev
- Periodic system
- periods (small and large)
- Groups (main and side)
- Options PSH.E.:
a) short version
b) half-shaped version
c) long version
Type of lesson: combined
Equipment: Portrait of D.I Mendeleev, Chemistry Textbooks 8kl., 11 CL. (G. Rudzitis); Wall psh.h.E.D.I. Inendeleva; Multimedia training manual for chemistry (8kl).
During the classes:
1. Organizing time.
2. Actualization of knowledge:
Information: by the time of the opening of the Periodic Law (1896.XIX.b) 63 chemical elements were known. After examining their features, D.I. Mendeleev formulated the law.
- Express survey: Word the Periodic Law D.I. Mendeleev
3. We formulate theme lesson, goal, task
The task: continue the offer: "Periodic law became a base for ........."
Therefore, behind the lesson "Periodic law D.I. Mendeleev ", should follow the topic"? "(Call Students)
— ?: Try to designate the tasks and objectives of this lesson.
4. Assimplement of new knowledge:
Working with a textbook test § 36 Task: Fill out a table, responding to the questions assigned (the table is attached, see page 5)
Answer | |
2. The purpose of the creation of PSH.E. | Classification of chemical elements, according to their properties. |
3. What is the structure of psh.hh? | PSH.E. It consists of horizontal series (periods) and vertical columns (groups), whose intersections form cells. Each cell corresponds to a specific chemical element and has no. / N. |
4. Give a description of the periods. | Table seven periods. Distinguish small (1,2,3) periods. They contain no more than 8 chemical elements. Large periods (4,5,6,7) from 18 or more chemical elements. The seventh period is not completed. Until now, it is timeally received information about the opening of new chemical elements. At the moment, 118 chemical elements are open. |
Any period (except first) begins alkaline metal and ends with noble gas. The period number indicates the number of energy levels in the atom. In the period to the left for the right of the metallic properties of H.E. Weaken, and non-metallic - enhanced. |
|
6. Give description groups. | Table 8 groups indicated by Roman numbers. Each group is divided into two subgroups: the main (a) and side (b). Home (a) Subgroup unites H.E. both small and large periods. The side (b) subgroup contains X.E. Only large periods. |
№ the groups indicate the highest valence of X.E., as well as the number of electrons in the external energy level. In the group from above, the metallic properties of H.E., and non-metallic weaken are strengthened. In B-groups, such a pattern is not always respected. |
|
All chemical elements are located in the periodic system in ascending order of atomic scales, but there are exceptions: argon - potassium; cobalt - nickel; Tellur - iodine. |
|
9. Why psh.h.e. is greatopening Russianscience, in the face of D.I. Mendeleev; | Periodic pattern, which can be traced in P.Sh.E. Allows you to predict the properties of not only chemical elements, but also formed by them simple and complex substances. In addition, it allows you to predict the existence of unknown chemical elements: ekabor - Scandium; eCASILITIONS - Germany ekualumin - Galley This table is a triumph of Russian science. Chemical science uses it for 145 years. Therefore, P.Sh.E. The right is considered fundamental. |
Output:
5. Primary checking the correctness of the understanding of the new material, knowledge correction (conversation by Learned issues using multimedia training manual: Chemistry 8kl).
6. Reflection (testing, using multimedia tutorial)
7. Summing up the lesson.
8. D / s § 36 p.125 №4
Theme lesson:
Objectives lesson:
Question | Answer | Know | |
1. Who and when created a periodic system of chemical elements? | |||
2. The purpose of the creation of PSH.E. | |||
3. What is the structure of psh.hh? | |||
4. Give a description of the periods. | |||
5. What information do the periods carry? | |||
6. Give description groups. | |||
7. What information are the groups? | |||
8. What a discrepancy with the periodic law of Mendeleev you saw in PSh.E. | |||
9. Why psh.h.e. is a great opening of Russian science, in the face of D.I. Mendeleev; |
Conclusion: Today I understood at the lesson (a)
Attention! Site Administration Website is not responsible for the content methodological developments, as well as for the compliance of the development of GEF.
Explanatory note
This lesson is mainly conducted high School For studying 8 classes in 1 half of the year.
The relevance of the development of the lesson Based on the use of the Web site's resource, the most unusual periodic system of chemical elements D.I. Mendeleev "is dictated by the requirement of the GEF of the new generation, the use of ICT technologies provided for by the professional standard of the teacher, including the information skills of the teacher.
Practical significance The development of this lesson model is to develop a number of key competencies necessary for the integrity of the studied chemical exchange rate.
Used Web site "The most unusual periodic system of chemical elements D.I. Mendeleev "is an educational product developed by my students in 2013. The main pedagogical task of this resource is the creation of a simple for the user of an interactive model of a periodic system of chemical elements D.I. Mendeleeva.
On the this lesson A variety of forms and methods of work are used, whose goal is to develop from learning skills to analyze, compare, observe, draw conclusions. In the course of the lesson, the teacher sets questions, possible answers to them stand out in the text italics. The lesson material corresponds to the program, is organically connected with previous classes.
The emotional coloring of the lesson enhances not only the use of an interactive periodic system, but also the use of a presentation with various illustrations performed by the student, as well as the demonstration of their own variants of the project "My Mendeleev Table", the inclusion of funny songs of Tom Lerra.
I have a modern office of chemistry in which there is a multimedia computer class. With such a laboratory, there is a laptop on each desktop. This allows you to simplify the work as much as possible in the lesson for students, and for the teacher - to track the progress of the tasks in pairs at each workplace.
Evaluation of students' activity. The number of estimates for the described lesson is minimally: only a student's performance on the opening of the periodic law and individual participants in the lesson, which correctly respond to quizzes, participating in the design of the table at the end of the lesson.
You can check the effectiveness of the learned knowledge in the next lesson when students surrender homework - the project "My Table Mendeleev". The main purpose of creating a project: Show learning, as In fact, the opening of a periodic law could occur (contrary to the established opinion that the Table Dmitry Ivanovich had dreamed of), feel the complexity of the classification of objects.
Main criteria for estimating tables May be like:
- The relevance of the topic ("chemistry" of creating a table, i.e. classification of chemical concepts or substances, biographies of scientists, chemicals laureates Nobel Prize different years, etc.). If the student cannot find objects in the subject of "chemistry" to classify, it can refer to other sources, i.e. classify and compare, for example, city in population and various countries. At the same time, in the "period" there may be a country, and in the "group" there are cities to increase population. Each "element" of the student's table must be called, a digit that denotes the population is denoted by the symbol. For example, the city's table offers the city of Rostov-on-Don. It can be symbol Ro.. If there are several cities, starting with the same letter, then add the following to the capital letter. Suppose there are two cities on the letter "R": Rostov-on-Don and exactly. Then for Rostov-on-Don there will be an option Ro., and for the city of Rivne - RB..
- Registration of work. Work can have a handwriting option, scored in Word or Excel (work 2013). The size of the table I do not limit. But I prefer A4 format. In my table of tables there are, for example, a variant consisting of two watman sheets. Work must be colorful, sometimes contains pictures or photos. Accuracy is welcome.
- Originality of work.
- Annotation to work includes the following parameters: the name of the work, the validity of the principle of the location of the selected "elements". The student can also argue the color palette of its table.
- Presentation of work. Each student protects its project for which I envisage in the program 1 lesson (this does not violate the presentation of software in chemistry, because at the end of the year the program provides for up to 6 lessons allocated to repetition of the course through the study of biographies of various scientists, stories about substances and phenomena).
Assessment of the periodic system of students I give not only me. High school students are involved in the discussion of work, as well as my graduates who can provide practical assistance to eighth graders when making their work.
The course of evaluation of students. I and experts fill in special sheets in which they put the estimates on the criteria specified above three-point scale: "5" - complete compliance with the criterion; "3" - partial compliance with the criterion; "1" - a complete non-compliance with the criterion. Then the points are summed up and ordinary marks are set. For this type of activity, the student can get several estimates. For each point of the criterion or only one - total. I do not exhibit unsatisfactory marks. The whole class takes part in the work.
Provided View creative work It provides for preliminary training, so students receive the task of "creating their system" in advance. In this case, I do not explain the principle of building a system of the original, the guys have to independently understand how Dmitry Ivanovich had elements known at that time, which principles were guided.
Evaluation of the project 8 class "My Mendeleev Table"
|
Criteria |
Assessment of teacher |
Student assessment |
Total assessment |
|
|
Relevance of the topic |
||||
|
Design of work |
||||
|
Originality of work |
||||
|
Annotation to work |
||||
|
Presentation of work |
||||
|
final grade |
The basic concepts used in the lesson
- Atomic mass
- Substance
- Group (main and side subgroup)
- Metals / Nemmetalla
- Oxides (oxide characteristics)
- Period
- Periodicity
- Periodic law
- Radius atom
- Properties of chemical element
- System
- Table
- The physical meaning of the main values \u200b\u200bof the periodic system
- Chemical element
The purpose of the lesson
Examine the periodic law and the structure of the periodic system of chemical elements D.I. Mendeleeva.
Tasks lesson
- Educational:
- Analysis of the database of chemical elements;
- Teach to see the unity of nature and the general laws of its development.
- To form the concept of "frequency".
- Examine the structure of the periodic system of chemical elements D.I. Mendeleeva.
- Developing: Create conditions for development of key competencies: information (extraction of primary information); personal (self-control and self-assessment); informative (ability to structure knowledge, the ability to identify the essential characteristics of objects); communicative (productive group communication).
- Raising: Contribute to the development of intelligent personality resources through independent work from additional literature, Internet technologies; upbringing positive learning motivation, proper self-esteem; The ability to communicate in the team, group, build a dialogue.
Type of lesson
Lesson studying a new material.
Technologies
ICT technology, elements of critical thinking technology, elements of technology based on emotional-shaped perception.
Expected educational results
- Personal: Formation of readiness of students to self-education based on motivation for learning; the formation of readiness for the conscious choice of the further educational trajectory of training through the preparation of the work plan in the lesson; Formation of communicative competence in communication and cooperation with classmates through paired work.
- MetaPered: Formation of the ability to independently determine the goals of their learning and the development of the motive of its cognitive activity through goaling in class; Formation of the ability to conduct a dialogue.
- Subjects: Formation of initial systematic ideas about periodic law and a periodic system of elements D.I. Mendeleev, phenomenon of periodicity.
Forms of education
Individual work of students, work in pairs, front work teacher with class.
Means of education
Dialogue, handout, Task teacher, the experience of interaction with others.
Stages of work
- Organizing time.
- Goaling and motivation.
- Planning activities.
- Actualization of knowledge.
- Generalization and systematization of knowledge.
- Reflection.
- Homework.
During the classes
1. Organizational moment
Mutual greeting teacher and students.
: Personal: self-organization; Communicative - the ability to listen.
2. Goaling and motivation
Teacher's introductory word. With deep antiquity, contemplating the world around and admiring nature, a man wondered: from which, from which substance is the human body surrounding, the man, the universe itself.
Students are invited to consider the following images: seasons of the year, heart cardiogram (you can use the heart layout), the scheme "Building solar system"; Periodic system of chemical elements D.I. Mendeleev ( different types) And answer the question: "What unites all the images represented?" (Periodicity).
Setting goals.What do you think, guys, about what question we will be speaking today (students make assumptions that the speech will go on the periodic system of chemical elements D.I. Mendeleev)? In the notebook, the lesson theme is recorded: "Structure of the Periodic System".
Tasks for students:
- Pick up examples pointing to frequency in nature. ( The movement of cosmic bodies around the center of the Galaxy, the change of day and night).
Invite single words and phrases to the word "frequency" (Periodic Publications). - Who "Author" of the Periodic Law ( DI. Mendeleev)? Can you "create" a periodic system ( the answer to this question will be delayed, it is given to the guys as homework )?
- Bluff-game "Do you believe that ..."
- After graduation, you can award aluminum circle? ( Currently it is impossible. But Dmitry Ivanovich Mendeleev for the discovery of the periodical law was presented with aluminum bowl, because At that time, the cost of aluminum exceeded the price of gold and platinum.)
- Opening D.I. Mendeleev periodic law can be considered a feat? (Dmitry Ivanovich Mendeleev predicted several unknown elements at the time of elements Ekabor (Scandium), Ekaluminum (Gallium), ECASILITIONS (Germany), Ekamarganese (techneti). Well, predicted and predicted. And what is the feat? (It is appropriate to bring to children to kiss the topic of the scholar's feat) The fact is that at the first open element of Gallium (L. Buabodran, France), density was incorrectly defined, and therefore the mass of the element, and D.I. Mendeleev indicated not only the error of the scientist, but also its cause - Insufficient cleaning of the sample Gallium. If Dmitry Ivanovich was mistaken with the calculations, he would have suffered himself, because his name would be poured forever).
Teacher. Guys before studying new topicI would like to "draw" a portrait of a scientist together with you. Determine what qualities must necessarily have a scientist (hereinafter follows the assumptions of students about some of the qualities of the scientist: intellect, enthusiasm, perseverance, perfection, ambition, determination, originality).
Developed Universal Educational Actions: Subject Action: Ability to analyze the proposed pictures, find similarity between them. Personal: the establishment of communication between the purpose of activity and its motive. Regulatory: self-regulation. Cognitive: independent allocation and formulation of the goal; Proof of his point of view. Communicative: the ability to listen and join the dialogue.
3. Planning activities
February 8, 2014 turned 180 years since the birth of the great Russian scientist Dmitry Ivanovich Mendeleev. Now we will see a fragment of the film about the Great Scientist (Next follows a fragment of the video film "Russian da Vinci" or cartoon "Three questions Mendeleev").
March 1, 1869. A young and at that time, a few people famous Russian scholar sent to the chemists around the world, a modest printed sheet, entitled "The experience of a system of elements based on their atomic weight and chemical similarity." Let's plunge into the past and learn a little about how a periodic law was opened. Next, a student's story about different variants of periodic systems (5-7 minutes) using the presentation .
Educatives make records in the notebook: the wording of the periodic law and the date of its opening (on the local network, the teacher shows Website I.section of the websitePeriodic law).
Teacher.Do you think guys, scientists immediately accepted a periodic law? Did you believe in it? To plunge into the epoch a little, let's listen to the excerpt from the poem about the opening of Gallium.
What conclusions should be made from this passage (students suggest that in order to believe in a new law, irrefutable evidence is necessary)?
There are many options for periodic systems. Different objects are subject to classification: flowers, booked elements, food products, etc. All these tables combine certain principles of construction, i.e. structure.
Developed universal learning actions: Regulatory - drawing up a plan and sequence of actions; Cognitive - construction of a logical chain of reasoning; Communicative - the ability to listen and join the dialogue, to accurately express your thoughts.
4. Actualization of knowledge
All the laws apply the comparison criterion - the possibility of predicting the new, foresight of the unknown. Today you have to "open" for yourself the periodic system, i.e. A little to be scientists. To do this, you need to task.
The task.You have a laptop on the desktop with an Internet access, there is an instruction (Appendix 1) to work with the website "The most unusual periodic system of elements D.I. Mendeleev " . Analyze the site interface, draw conclusions; Results Reflect in the instruction card (Appendix 1).
In the absence of a mobile computer class, you can prepare paper cards-instructions. In this case, the teacher conducts work with the student). The task of the student teacher can: 1) sent over the local network; 2) Leave the file in advance on the desktop of each laptop. Students can give response to the teacher using the Paint or Word program, because Another type of feedback between the main (teacher) laptop and the mobile class (student laptops) is not provided.
Table for students does not contain answers. Work is performed in pairs. The task is appropriate to take 10 minutes. Students, the first to meet the task, can show it to everyone on the local network (resolve the student to show a demo).
Developed Universal Educational Actions: Personal: Understanding the causes of success learning activities; Regulatory: finding errors with the correction of them on their own or with a classmate, manifestation of perseverance; Communicative: Assessment of the actions of the partner to fulfill the task, the ability to listen and join the dialogue.
5. Generalization and systematization of knowledge
The teacher checks the work of students and together with them formulates the definition of the phenomenon of periodicity.
Teacher. Is the structure of the periodic system posted on the site from the table form, proposed by D.I. Mendeleev? If so, select similar and distinguishing features of both tables (After clarifying general features, a joint formulation of the phenomenon of periodicity follows).
Periodicity - regular repeatability of changes in phenomena and properties.
Developed Universal Educational Actions: Personal: Understanding the reasons for the success of educational activities; Regulatory: finding errors with correction them yourself or with a classmate; Communicative - the ability to listen and join the dialogue.
6. Reflection
Science Development confirmed the words of Dmitry Ivanovich himself about the development of the law, this phrase learned could prepare at home, guessing the rebus. Answer:"Periodic law the future threatens not by destruction, but only the add-in and development are promised." It is also appropriate to check the knowledge in the lesson using the COR collection (testing of periods and groups).
In conclusion, the lesson sounds the song Tom Lerr.
Developed Universal Educational Actions: Subject: Check your own knowledge on the proposed test; Regulatory awareness of the knowledge gained and ways to achieve success; Communicative - participation in collective discussion.
7. Homework
- §5, perform written tasks after paragraph: 1,4,5;
- In the lesson, we saw different variants of periodic systems. At home I suggest you "create" your periodic system. This work will be performed in the project format. Title: "My Mendeleeva Table". Purpose: learn how to classify objects, analyze their properties, be able to explain the principle of building your system of elements / objects.
Samoenalysis lesson
The lesson showed its effectiveness. Most of the proven homework on creating their system of elements fully complied with the evaluation criteria set forth in theses, i.e. The student consciously created the tables of their system selected elements / objects.
The project "My Table of Mendeleev", which started as an exclusively paper version, gradually acquired a digitized form. So there were presentations, table options in Excel and, finally, the COR - the site "The most unusual periodic system of elements D.I. Mendeleev. " Samples of students are posted on my site, the rubric "student", the sub-service "Work of my students."
Criteria and lesson efficiency indicators: positive emotional background lesson; cooperation of students; The judgments of students regarding the level of their own answers and the possibilities of further self-education.
Subject. Periodic law and periodic system D.I. Mendeleev
Purpose:
To form students in students that the objectively existing relationship between chemical elements and formed substances is subordinated to the periodic law and is reflected in the periodic system; consider the structure of the periodic system, form the concept of periods and groups;
Develop the ability to analyze information and draw conclusions, the skills of using the periodic system to search for information on chemical elements and their properties;
Rail in cognitive interest in the subject.
During the classes
І. Organizing time
ІІ. Actualization of reference knowledge
Conversation
1. What is a classification?
2. Which chemistry scientists have attempted classifying chemical elements? What characteristics did they take as a basis?
3. What groups of chemical elements are familiar to you? Give them a brief description.(Alkaline metals, alkaline earth metals, halogens, inert gases)
ІІІ. Studying a new material
1. History of opening of a periodic law
At the last lesson, we learned that the middle of the XIX century. Knowledge of chemical elements has become enough, and the number of elements has increased so much that there was a natural need for their classification in science. The first attempts to classify elements were insolvent. Predecessors D.I. Iveleeva (I. V. Debereyer, J. A. Newlands, L. Yu. Meyer) did a lot to prepare the opening of the periodic law, but could not comprehend the truth.
They used one of the two approaches to the construction of the system:
1. Combining elements into groups in the similarity of the composition and properties of the substances they have formed.
2. The location of the chemical elements in the order of increasing their atomic mass.
But none nor another approach led to the creation of a system that combines all elements.
The problem of systematization of chemical elements is interested in the young 35-year-old professor of the Pedagogical University D.I. Mendeleeva. In 1869, he worked on creating a textbook for students "Basics of Chemistry." The scientist understood well that in order for students to figure out better in the diversity of the properties of chemical elements, these properties need to be systematized.
By 1869, 63 chemical elements were known, for many of which relative atomic masses were incorrectly defined.
Mendeleev placed chemical elements in the order of increasing their atomic masses and noticed that the properties of the elements are repeated after a certain period - period, Dmitry Ivanovich placed periods of each other, so that the similar elements are located in each other - the periodic system was built on one vertical Elements.
As a result of painstaking work for 15 years to correct the atomic masses and valence of elements, as well as to clarify the place of not yet open chemical elements D.I. Mendeleev opened the law, which called the Periodic law.
The properties of chemical elements, simple substances, as well as the composition and properties of compounds are in periodic dependence on the values \u200b\u200bof atomic masses.
March 1, 1869 (February 18 by the old style) - the date of opening of the periodic law.
Unfortunately, supporters of the Periodic Law first were very small. Opponents - a lot, especially in Germany and England.
The opening of the periodic law is a brilliant sample of the scientific foresight: in 1870, Dmitry Ivanovich predicted the existence of three even-known elements, which called Ekasilicia, Ekalayumin and Ekabor. He managed to properly predict the most important properties of new elements. And in 5 years, in 1875, French scientist P.E. Lekki de Baabodran, who did not know anything about the works of Dmitry Ivanovich, opened a new metal, calling him Gallium. For a number of properties and the method of opening gallium coincided with ekalumin, predicted Mendeleev. But his weight was less than predicted. Despite this, Dmitry Ivanovich sent a letter to France, insisting on his prediction.
The scientist world was stunned by the fact that the prediction of Mendeleev propertiesekaluminia
it turned out so accurate. From this point on, the periodic law begins to be approved in chemistry.
In 1879, L. Nilson opened the scandium in Sweden, in which the predicted Dmitry Ivanovich was embodiedekabor.
.
In 1886, K. Wincler in Germany opened Germany, which turned out to be ECASILITSIME
.
But the genius of Dmitry Ivanovich Mendeleev and its discoveries are not only these predictions!
In four places of the periodic system, D. I. Mendeleev placed elements not in order of increasing atomic masses:
AR - K, CO - NI, TE - I, TH - PA
Back at the end of the 19th century D.I. Mendeleev wrote that, apparently, an atom consists of other smaller particles. After his death in 1907 it was proved that an atom consists of elementary particles. The theory of the structure of the atom confirmed the correctness of Mendeleev, the rearrangement of these elements is not fully justified with the growth of atomic masses.
The graphic image of the periodic law is the periodic system of chemical elements. it short abstract all chemistry of elements and their connections.
2. Structure of the periodic system
There is a long and short table option.
Each element is in a certain cell periodic system.
What information does it carry?(element character, sequence number, element name, simple substance name, relative atomic weight)
Composite parts of the table are periods and groups.
The teacher shows the period in the table and asks students to formulate the definition. Then compare with the definition in the textbook (p. 140).
The period is a horizontal range of chemical elements, which begins with an alkaline metal and ends with an inert element.
The teacher shows a group in the table and asks students to formulate the definition. Then compare with the definition in the textbook (p. 140).
Periods are large and small.
What periods are big? Small?
How do metal properties change in the period from left to right? Strengthen or weaken? Why do you think so?
Metal properties in the period from left to right weaken, therefore, non-metallic enhanced. We learn the reason for this by studying the structure of the atom on the subsequent lessons.
In which element, metal properties are pronounced brighter: ag.- CD? Mg-al?
In which element, non-metallic properties are pronounced:N.? S-Cl?
A group is a vertical stack of elements that contains elements similar by properties. (write to the notebook)
The group is divided on the main(but) and side (in).
The main subgroup includes elements of both small and large periods. In the side and only big. Side subgroups contain only metal elements (transition metals)
Name the elements of the second group, the main subgroup.
Name the elements of the fifth group, a side subarror.
Name the elements of the eighth group, the main subarror. What are their names?
IV. Generalization and systematization of knowledge
V. Education of the results of the lesson, assessing knowledge of students
V. І . Homework