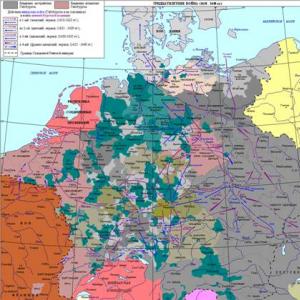
1 Periodization of the history of the ancient China. The main epochs of Chinese history
China has a long and practically continuous history, numbering about six thousand years. Written sources, however, indicate a little less age - 3,600 years. China presented to humanity a lot of inventions, including gunpowder, compass, paper and a typical printing. Until the XIX century, China was one of the most advanced world states and the main cultural center of East Asia. Later, the country survived whole centuries of colonial seizures, but was able to once again become a powerful, independent industrial power.
Short review
It is believed that people in China lived already 7 million years ago. And the first Chinese dynasty - Sia - began to edit another 2700 BC. All subsequent periods are associated with the board in the country of different dynasties, consistently replaced by one another. To facilitate the perception of all Chinese history, use the following periodization based on traditional Haniography:
- Dobimer's China (Xia, Shang, Zhou - up to 221 BC. E.)
- Imperial China (Qin - Qing)
- New China (1911 - Sovr.)
The first emperor Shi Juandy - united China under his power, dividing the new formed empire Qin(221-206 BC) on 36 provinces that managed officials appointed by the emperor. He announced the cessation of all wars, gathered a weapon from subjects and melted, building 12 large monuments. He streamlined measures and weight, introduced the standard writing of the hieroglyphs, organized a hard bureaucratic management system. During the Board of Shi Huangdi, the construction of the Great Wall of China was launched. The road network of 15 meters and a total length of 7,500 km tied a country.
Second in the history of China, the empire called Han(206 BC-220 AD), founded a leav of the average officials of Liu Ban. This period is considered one of the most important periods in China's history, the Chinese themselves themselves took their self-calf from here (Hantsev).
Epochs Tang(618-907) and Sun. (960-1127) is customary to be called a classic period in China's history.
During the period of domination, the Tang was formed a system state exams. They contributed to the upbringing of the educated elite, as a candidate who knew the classic texts well, regardless of social origin was able to take the rank of an official. People of humanitarian exercises are writers, philosophers, scientists - were the people of the privileged class.
The Sun period is considered to be the era of the economic and cultural heyday of China. The number of cities is growing, the increase in the number of urban population continues, Chinese artisans reach heights in the manufacture of products from porcelain, silk, varnish, wood, ivory, etc.
At the beginning of the XIII century to China invaded the United States of Genghis Khan Mongola. They were expelled in the middle of the XIV century after a long struggle. One of the leaders of the uprising came to power - the son of the peasant Zhu Yuanzhan, who founded the state Min.(1368-1644)
Dynasty Qing(1644-1911), created by nomads-conquerors from Manchuria, lined up the last empire, expanding the country as much as possible. By the middle of the 19th century, China's population rose to about 400 million people, but the management and financial system was extremely ineffective, which laid the foundation for future problems and crisis. Corruption was widespread, the ruling elite did not want reforms. After a series of lesions in opium wars, China was forced to conclude non-equivance contracts with European powers, opening their markets and transferring the main ports for foreign control.
The Manchurian dynasty was overthrown as a result Xinhai revolution (1911). The Empire Qing collapsed and was proclaimed the creation of the Republic of China. In 1912, with the support of the United States and Japan, the Romintan's revolutionary party was created. And in 1921, with the support of Russian organizations, the Communist Communist Party of China was created. Since 1927, armed clashes, which took place in civil war begins between the Hominthane and PDA. In the 1930s, the Japanese intervention begins, for some time interrupted the conflict. After the defeat of Japan in 1945, the war between the Homintandan and the CCP resumed. By 1949, the CCP army established control over most of the country.
October 1, 1949it was proclaimed the formation of the People's Republic of China. Chairman of China's Communist Party Mao Zedongsolemnly announced this from the stands on Tiananmen Square. The next day, the Soviet Union was the first to admit the PRC and concluded an agreement on friendship, union and mutual assistance with it.
The emergence of Chinese civilization
Culture Yangshao
This focus of agricultural neolithic arose in the Juanhe basin at about the VI-V millenniums BC. e. For the Ancient Chinese Neolithic, the Middle Eastern types of cereals (wheat, barley) and domestic livestock breeds (cow, sheep, goat), a potted circle and other innovations are already well known to the west of China by that time. Painted ceramics and skills of growing grain crops, familiarity with domestication of cattle (pig), allow you to tie the culture of Jancheo with similar cultures of painted ceramics, in particular the Middle Eastern. In this case, it is not about the effect in the form of mass migration. The prevailing racial type on the ancient Chinese plain ancient times were Mongoloids (inclusions of the European and Australoid racial types are single), and this particularly distinguishes the ancient Chinese focus of civilization.
Bronze Age in China
The beginning of the Bronze Age was recorded by archaeologists from the middle of the II millennium BC. e. At the end of the era of Neolithic in the Lunshan-Lunchanoid Neolithic Environment of the Egrovers of the Juanhe basin, a fairly developed bronze culture appears Shan-Yin. It can be assumed that the civilization of the Bronze Age in China again, many must many of the cultural influences from the outside. This is told about the high rates of the appearance and heyday of the bronze age: the development of the bronze, the appearance of writing, the construction of lush palaces and the construction of tombs, the art of carving on stone, finishing utensils, decorations, weapons. On the relationship of civilizations most convincingly evidenced by the Inan battle chariots identical to Indo-European. Dawnian China did not know any horses or chariots. Thus, Indo-European tribes could play a certain role in the process of the genesis of Chinese civilization. At the same time, Injans were also Mongoloids, so again it is difficult to talk about migrations in significant sizes.
Ancient China. Doomper period.
The Ancient Chinese historiographic tradition begins the history of China with the description of the period of the reign of five legendary emperors. The time of their dominion is perceived as the golden age of wisdom, justice and virtue. Sage Yao transferred his throne capable and virtuous Shuya, and that is great Yuu.Starting from the board of which the power began to be inherited. Yu is considered the founder of the first dynasty Sia. Chinese historiographic tradition believes that the Dynasty of China's Rules at the end of III and the beginning of the II millennium BC. e. Her last unfinished representative of the Jesi was confused his authority and was deprived of the moral right to manage the subnet. He was defeated virtuous Cheng Tanfounded a new dynasty Yin.
There is reason to believe that no Sia existed at all. When the first innovative legends were recorded, the term was designated the aggregate of the Chinese lands and the population. It is possible that the invasion of hents to the Juanhe basin over time and were comprehended as a replacement of one (Sia) Other (Intex).
Yinskaya community ass in Anyana. Here quickly quickly developed a large protogation led by the All-Russia Ruler. Governor Wan was also the high priest. The position became hereditary in the last four rulers. The administration was divided into three main categories of senior administrators, lower managers, officials responsible for military training and hunting. Van and his approximal fell out of harness about the crop, preparation and clearing of fields. Book of songs Shizhinmention of large fields treated with the teams of peasants under the control of supervisors. All craft products were also used centrally. A similar model was in the royal and temple farms of ancient Egypt or two-frequencies.
The most important source of the Shang-Yin era is dentative inscriptions on specially processed laminy blades and shells of turtles. In total, more than 150 thousand such inscriptions were discovered. Apparently, the Injans lived with a compact team of unintermakers, cohesive joint ritual-religious practices, sacrifices in honor of their common ancestors, deities and spirits. It is known that the Injans practiced human sacrifices from among the prisoners of neighbors. The rite of communication with dead vans and ancestors was important. The existence of the team depended on their will and support, according to the ideas of hents. Informing the ancestors about the situation and current problems, referring to them with requests, the Injans recorded the essence of the affairs on the bones and carried out the rite of divination.
Injans led active foreign Policy, including wars and expanding their territories at the expense of neighbors. The greatest power of the Injans reached at Dina. Armed with combat chariots, consisting of professional archers and spearkers, the Inin Army was a formidable force that kept in the obedience of neighbors.
Among such neighbors treated jusisywho lived to the west of Shan-Yin. Their capital was Zongzhou. The Zhou rulers recognized the tinsente of the Yinsky Vana. Over time, they managed to strengthen and then create a tribal coalition, which ultimately defeated the Shang-Yin in a decisive battle of Muu in 1027 BC. e. The new Lord of the Ancient China became U-Van..
China during the period of Western Zhou (1027-771 BC.)
A few Zhou tribe, defeating the hents, turned out to be at the head of a major military-political association, the limits of which came far beyond the former territory of Shan-Yin and practically covered almost the entire pool of Juanhe. Skiful Inician Masters was built for Joussians new capital Chengrzhou. She became the place of stay of a significant part of the Zhowa administration, as well as the main military center where 8 armies were located. The rest of the administration, 6 armies and Wang himself, continued to live in Tzungzhou, in the area of \u200b\u200bthe former generic settlements Joussians. Hence, the name of the described period (Western Zhou) went.
During this period, the doctrine of Mandate Neba (Tian-min), according to which the sky presents the mandate on the management of a subwayless virtuous ruler, thus depriving the authorities of the unfinished. Protecting a legitimate idea, Jusimen managed to establish an effective centralized administration, based on the 14th armies of the center in the two capitals. The aristocrats and merits of the aristocrats were usually appointed to administrative positions, primarily from the number of Zhowa and Yin kindergarten. There is information that capable administrators promoted up the service staircase. An important innovation was the creation of a system of exercises provided to the hereditary possession and management of relatives and an approximate ruler. The owner of the lot was relying a squad of the Zhusztsev soldiers. At first, the owners of the lotion were closely connected with the center, depended on its help and military support. Over the years, however, the situation changed. The rulers of the lots already in the 4-6th generations already felt themselves with full owners in their lands.
Power decline Vana and strengthening
The number of initial valits has been reduced over time. One of them from the very beginning was larger in the neighboring, which helped them faster and easier to overcome rivals. Others were favorably located, which allowed them to rich or grow lands at the expense of weaker neighbors. Third, outskirts, boldly increased their limits at the expense of wars with the tribes of the external belt. Fourth, on the contrary, turned out to be clamped stronger neighbors and in an unequal struggle gradually lost the legacy of fathers. All this led to the strengthening of several large lots.
One of the rulers of Western Zhou, Xuan-Wan I tried to conduct a number of reforms aimed at strengthening the central government, for example in the field of taxation. However, reforms came up to the resistance of others and, most importantly, turned out to be too late. Son Xuan-Vana, Yu-Van., I put my favorite concubine above the legitimate wife, the daughter of the ruler of Shen's daughter. That in union with neighboring barbaric tribes I invaded Tzugzhou and Summors Yu-Vana. After that, the son of Yu-Vana, PIN-WAN, was forced to 771 BC. e. transfer your residence to the Eastern Capital, in LooThat has become the beginning of the Eastern Zhou period. Land in the area of \u200b\u200bthe old capital Zuzungzhou Pin Van gave one of the allies, which on the basis of these lands created a new lot Qin- The one that 500 years later united the kingdoms of Zhowsky China as part of a single empire.
The period of Zhango ("Fighting Kingdoms", V-III centuries. BC)
This is the time of large-scale shifts in all spheres of China's life, from the productive forces to ideology, from mastering the outflows to wars. During this period, China joined iron Century. In addition to the role in production, iron tools literally revolutionized the army. A numerous and well-armed infantry came to change the chariots, and then the cavalry. There were battles with the participation of many dozens and hundreds of thousands of warriors, a military strategy and tactics developed, which was reflected in treatises about military art (Sun Tzu).
The period of Zhango was the time of coexistence and internecine struggle of the seven of the largest kingdoms (Wei, Zhao, Han, Qin, Qi, Yan and Chu). The kingdom competing with each other was the fierce wars. Gradually shed a country map, on front edge There are the most powerful states. Most of them were carried out by the reforms of a legist type. The most fully and radically such reforms were carried out in the middle of the IV century. BC. in Qin. The beginning of them put a legist Shanan.
First, community land use was strictly regulated. Large families were to be divided into small. A circular guilty system was created: the yards were combined into heels and dozens, in which all the residents of Qin were obliged to follow each other and respond to each other.
Secondly, a new system of social ranks was introduced, which were assigned to any person for his merit, primarily the military. From a certain level, the ranks gave benefits and privileges, up to the right to official ownership and income from it. For excessively rejected owners who received benefits from secondary classes, crafts and trade were used to be applied, a peculiar expropriation mechanism was applied. It was possible to avoid trouble with the acquisition for considerable social rank.
In 350 BC. All the kingdom was divided into government-managed counties. A system of measures and scales was unified, they were fixed behind the peasants. The distribution of surplus was under the stringent control of the authorities.
Concerned the rapid growth of the power of Qin, the remaining six tried to create a coalition against him. The whole second half of Zhango passed under the sign of intrigue, skillful diplomacy. However, intrigues and complex unions did not help. The latter Palo Kingdom Chu and in 221 BC. e. Qin in Zheng.The future emperor Qin Shi-Huangdi completed the association of China under his power.
Empire Qin
In Zheng accepted the new title "Qin Shihuandi" ("The First Military-Emperor of the Qin Dynasty"), the country was turned into a bureaucratic centralized empire. The state subjugated to strict administrative control of all parties to the lives of people, the population selected all the weapons and shouted it to the bell. In the whole empire, there was a single legislation. Its foundation was the system of guarantees. The death penalty was used for all sorts of provinces, including small. Often executed or turned the whole family of the criminal in state slaves.
The territory was divided into 36 administrative districts, in each district, civilians focused in the hands of one official, and the military - the other. The supervision of them was carried out by a special service of inspectors - entriters of the emperor. The emperor appointed two advisers who were responsible for ensuring that the decrees were performed immediately. In his submission, the advisers had numerous central departments. One of the important was the authority of the Yushi Dafa. The duties of his officials included storing the state archive and checking the work of the districts.
In the country they walked mass work on the construction of roads and canals. This contributed to the development of trade and increased management efficiency. In order for the road with less frequently demanded repairs, uniform axes were introduced. Throughout the empire, 700 palaces were built for Qin Shi-Huangdi. One of the most beautiful cities The empire became the capital of Sanyan. During the reign of Qin Shihuandi was erected by the Great Chinese wallsand the giant tomb for the emperor. It placed 6000 terracotta warriors in the guards in full size. Trucks were made due to the most severe operation, taxes for the peasants reached 2/3 of the harvest.
Money, units of measure and weight, as well as writing, were unified throughout the country. It was ordered to destroy all the works of the Doczyn era, so that people had nowhere to learn about old times and orders. For the commitment of antiquity and resistance, the reforms were executed hundreds of Confucian scientists.
Qin dynasty caused universal hatred, and after the death of Qin Shihuandi in 210 BC. e. Immediately began uprising across the country. In 207 BC e. The detachments of the rebels took the capital and overthrew the Son Qin Shihuandi. However, China has existed as a single state from that moment. The teams of the Chinese Empires, who came to the change of Qin, in political and economic plan a lot borrowed from their predecessors. The Qin Empire existed only 14 years, but by the number of events and the importance of the changes that occurred is the whole epoch for China.
Drop Qin
Qin Shihuangi sought to find the secret of immortality, but in 210 BC. e. Suddenly died at the age of 49. His heir was the younger Son, who joined the throne under the name of Ersh Huangdi (210-207 BC. E.).
In 209 BC e. The country began in the country, the imperial troops began to move on the side of the rebels. One of the armies was headed by a small official Liu Ban. In 202 BC e. He unites China under his power and takes the imperial title name Gao-Tzu (202-195 BC. E.).
Han Dynasty
Gao-Cu is becoming the founder of the new Han dynasty (206/202 BC. E. - 220 g. E.).
The state management system has been changed. At least half of the territory of the country Gao-CzU gave to the hereditary drips to the closest associates: the seven most important of them got the titles of Vanov. In their possessions they enjoyed broad authority. Vanya could independently assign and disperse officials, collect taxes and establish duty. In the rest of the country, an administrative apparatus was revived, which existed with the Qin dynasty. A number of measures were taken, sharply improved the position of the people and encouraged the development of production. Gao-CUU significantly reduced the tax tax (up to 1/15 crop). Many categories of the population were exempt from all duties.
The highest flourishing of the Han Empire reached the Board of the Emperor U-D. (140-87 BC. E.). U-di conducted reforms aimed at the further centralization of the state. The official ideology becomes the teaching of Confucius was introduced by the system of training officials. The governors of the districts were to find out and recommend the government of the capable young men. Candidates went to study at the Specially Created Academy in the capital, whose graduates were appointed after passing the exams in the state apparatus. The right to enter the Academy had all the free people, regardless of the rank of knowledge.
At the end of II century BC e. Chan troops make hiking against Syunnu in the north, in Korea, west to East Turkestan and to the borders of modern Vietnam and Myanmar. The territory of the Han Empire has increased by almost one third however, as a result, he plunged into the economic and social crisis. The government was usurped by one of the relatives of the emperor, began folk unrest, the largest of which were the uprising of the "redobrov" and "green forest". The peasant armies overthrew the usurper, then grabbed each other.
The winner of this crossbob was released by Liu, who proclaimed himself with Emperor Guan U-di and founding the Eastern Dynasty, or Late, Han (25-220). The capital was moved to the east, to the city of Luoyang. At this time, the Han Empire establishes permanent trade and diplomatic relations with Parfia and the Roman Empire. In the second half of the I-II centuries. The empire leads almost continuous wars with neighbors.
The end of the Eastern Han dynasty also laid the folk uprisings, the most powerful of which was the uprising of the "yellow dressings", which began in 184. e. In 220 N. er, after the death of U-di, China decays into three independent kingdoms: Wei, Shu and U. This event is conditionally considered the end of the history of ancient China.
History of Ancient China, Summary
The first empire of the ancient China - Qin existed only a half dozen years, but she laid the solid socio-economic foundation of the Han Empire. The new empire has become one of the strongest powers of the ancient world. Its more than four-hour existence was an important stage in the development of all East Asia, coinciding with the epochs of the rise and crash of the slave-owned production method. For the National History of China, it was an important stage of consolidation of the ancient Chinese nationality. The Zhango-Qin-Han era for the historical development of China and all East Asia has the same meaning as the Greek World for Europe. Ancient Chinese civilization laid the foundation of a cultural tradition, which is traced further throughout the centuries-old history of China until the new and the latest time.
Features of the study and periodization of the history of the ancient China
No other people showed a greater diligence in historical events, which began to lead their chronicles at the beginning of the first millennium BC. And subsequently, they punctually updated their dynasty for the dynasty.
In Chinese historiography, the use of dynasty periods. Each dynasty has its own name other than the surname of the rulers. Ethnonyms were first used as such names (the name of the nationality founded by this state) and toponyms (the names of the specific possessions of the future founders of the dynasties). From the XII century. The dynasties are indicated by philosophical categorical terms, for example, the yuan literally "initial" that is, the lack of principle of true rule, min - "enlightened".
Between the dynasty periods, the periods of the "troubled time" - the administrative-territorial fragmentation of the country, which indicate the terminological definitions: "The Epoch of Fighting Kingdoms", "The Epoch of Six Dynasties", "Trozenia" and so on.
The traditional Chinese state with deep antiquity was hardly a classic embodiment of the principle of power-property and centralized redistribution. While the peasants had put on the ground, treated the earth and paid the tax rente in the treasury, the structure of the Chinese Empire was a fastener. The stability of this kind existed, as a rule, in the framework of the dynasty cycle, not too long, most often no more than for a century. But since the land in significant quantities passed to rich landowners, the situation began to change. The treasury lost the arrival rate, it was often compensated by the increased arbitrariness of the power in the field. This in turn led to the deepening of crisis phenomena.
History of ancient China at school - 5th grade
The history of ancient China in Russian schools is studied in the 5th grade. Task lesson:To form an idea of \u200b\u200bancient China, to acquaint students with the history of ancient China, his geographical position, to form an idea of \u200b\u200bthe contribution of Chinese culture into world history. The topic of the lesson is new for students, but it plays an important role in the study of the section "Ancient East". Expected results: Knowledge of the geographical situation, the natural conditions of the ancient China, the history of the formation of the Qin Power. The ability to show the territory of the Qin Power, the Great Wall of China and the Great Silk Road. To express judgments about the contribution of the culture of ancient China to the world culture. Characterizes the living conditions and occupations of the population, the social system of the ancient China, the position of representatives of different layers. Major terms, concepts:"Great Wall", "Great Silk Road", Confucius.
Treasy Age (220-280) and Jin Empire
After the fall of the second Dynasty of Han and several years of civil engineering, the three most successful commander came to the fore. Cao Cao dominated in the north, in the Juanhe basin, where in 220 his son Cao Lei proclaimed himself as a state ruler Way. Liu Bay declared himself a ruler of the southwestern country Shu. Sun Quan, became the ruler of the southeastern part of China, the kingdom W.. A short period of triequiments, led to the formation of two independent states on the weakly mastered by the south of China.
Already by the middle of the III century. Power in the kingdom of Wei moved to the mighty clan of the commander of the Sum. In 265, he founded the new Dynasty of Jin, which soon, in 280, managed to subjugate Shu and U, uniting under his authority again all China, however, only for several decades. From the beginning of the IV century. Nomadic northern tribes one after another began to invade North China, Jin's empire ceased to exist, the Nan-Bay Chao, southern and northern dynasties began.
Nan-Bay Chao (IV-VI centuries)
The conquerors of North China were relatively retarded compared to the Chinese peoples. Under the influence of Chinese culture, nomads to the V-VI centuries. They fell so much as the end of the VI century. Their descendants became ordinary Chinese. Proverb "You can conquer the empire, sitting on horseback, but it is impossible to manage it, sitting on horseback"- Meaning that the impact of Chinese culture sooner or later led to assimilation and the chitaization of any ethnic groups won. Moreover, the ingenians were in northern China only 20%; All the rest of the population, despite the mass migrations of the Chinese to the south, was Chinese.
The southern dynasties also quickly replaced each other (Sun, 420-479; Qi, 479-502; Liang, 502-557; Chen, 557-589; the late Liang coexistently, 555-587). The Center for Chinese Culture focused on the south: there were outstanding scientists, poets, thinkers, energetically developed in China in China in the II century. Buddhism. Already with V c. On the fertile fields of the rice belt began to assemble two harvests per year, which is practiced and so on. In the south, new cities began to be created in a rapid pace, developing old and new types of crafts, flourishing trade and consumer money relations.
The flourishing of the Chinese Empire (VI-XIII century)
Dynasty Sui (581-618)
In 581, the commander of the kingdom of Northern Zhou Yang Jiang united all the northern and then the South China under his authority, proclaiming a new dynasty. The new emperor conducted a series of reforms, seeking to strengthen the state, knock the soil from under the feet of "strong houses". Each Pacquer should have had his own field and pay tax. His son Yan-di reared 10 thousand rich families from different parts of the country to the capital of Loyang rebuilt. Luxury palaces were built in the Luoyang area, as well as huge granaries, and for the transportation of tax grain from the south, which was already the main resident of the country, the Great Channel was died, tied by Yangtze with Huanghe. The maintenance of this structure with all its gateways and other devices was occupied, according to some data, up to 80 thousand people. Jan-di led several colossal buildings at the same time, tried to lead an active foreign policy and constantly fought and eventually the country could not stand the burden. Rebells broke out, Jan di was killed.
Tang Dynasty (618-907)
The ruler of the Tang Dynasty proclaim himself proclaimed himself one of the warlords and relatives of Yang-di on the women's line Lee Yuan. He and his son Lee Shi-Ming (Tha-Zong, 626-649) laid the foundation of the prosperity of the Chinese Empire. Land reform And the implementation of the tax system within the framework of the appreciation of land use was provided by a regular influx of income, and the state - the necessary workforce (labor service). It also contributed to strengthening the infrastructure of the empire - roads, canals, dams, palaces, temples, whole large cities were built. The craft and trade, including the treason craft, where the best masters of high qualifications were usually focused, who worked in the order of labor service or excess of this. Craft and trade was under the strict control of the state, special officials, which through the head of the tuan and khanov (shops and shop-guilds) strictly regulated every step of urban residents.
In the tongue, the empire was divided into 10 provinces (Dao), which in turn were divided into areas (Zhou) and the counties (Xian). All officials were appointed from the center and they were also controlled. This feature attached to the administrative bureaucratic system of China strength and sustainability. The work of the executive bodies and the entire state system, primarily the apparatus of the authorities, officials, strictly controlled the censors-prosecutors of the Special Chamber of Yushtai, who had great powers, including the right to submit reports to the highest name. The executive power was represented by two chancellors (Tszaisani or Zhichens) - the left (he was usually considered senior) and the right one, each of which conducted three of the six departments of the Chamber of Shashushen, a kind of Council of Ministers. The first group of departments treated the management of the ranks (selection of personnel and appointment throughout the empire), rites (control over compliance with the norms of behavior, the protection of public order) and taxes. To the second - managing military affairs, sentences and public works (the implementation of labor duties, construction, including irrigation).
The power of the county chief was very big and therefore was usually controlled most strictly. It was limited as a period (no more than 3 years in one place, followed by moving to another), and the place of service (in no case there is not where the official comes from). The empire paid special attention to the important problem of the training and principles of staff recruitment. In Tansk China, it was done on special exams on the degree in county, provincial and metropolitan centers, under the strict supervision of special commissions sent by the part, and in a closed room and in writing under the motto. For the successful examination of the exam, there was a good to know the compositions of the ancients, primarily the classic Confucian canons, and also be able to creatively interpret the stories from history, to distrast on the topics of philosophical treatises and possess a literary taste, to be able to compose poems. All this, of course, in a strictly Confucian spirit, with respect to the relevant mandatory form. Better than others copied with the task (3-5% of the candidates-applicants) were honored with the desired degree and, most importantly, they received the right to pass an exam on the second degree, and the owners of two on the third.
Song Dynasty (960-1279)
This period is also considered the time of the heyday of the Chinese Empire in the field of economy, culture, administration. The number, population and well-being of cities grew. New crafts appeared: the production of porcelain, silk, products from varnish, wood, ivory, etc. It was at this time that the powder and the compass were invented, it became widely spread. Agriculture and Agrotechnology reached great success, crop grain varieties were derived, the cultivation of Indian cotton began.
However, all this was combined with the onslaught of northern nomadic tribes (chuck, Tanguts) and the small attempts of the Soon Empire to reflect this Natisk. China was forced to pay a humiliating tribute, but it did not help and he lost the territory behind the territory, the city outside the city.
In 1127, Zhugzheni captures the capital of the Song Empire - Kaifyn and captured the imperial family. One of the sons of the Emperor runs to the south, in Hangzhou, which later becomes the capital of the new - South South Empire (1127-1280). The promotion of the Zhurzheney army to the south restrains only the Yangtze River. The border between Jin and the South Sun Empire is installed on the Mezzani of Juanhe and Yangtze.
Against the backdrop of Tan-Sun, the subsequent centuries were already a period if not always decline, then in any case stagnation.
Mongols and Dynasty Yuan (1280-1368)
Conquer the peoples of Southern Siberia, neighboring the Mongolian Stepha, the Army of Genghis-Khan in 1210 began a war with Chuzhseni and in 1215 he was already taken by Beijing. Mongols have left for the conquest of South Susoon China. In 1280, China was entirely under the rule of Mongols, and the Great Khan Khubilai became the Chinese emperor of the Mongolian dynasty Yuan (1280-1368).
China's economy after half a century Warred in decline, agriculture and trade were upset. Confucian officials were forced to give out their place to Mongols and people from other areas of Asia. The Chinese were considered the people of the third and fourth grade (after the Mongols themselves and Sam-Zhen, i.e. immigrants from other countries). However, after a few decades, confusion officials began to come to the administration (confusion officials began to function (from 1317, the examination system began to function); The descendants of the first Mongolian rulers who frequently anti-wives in the wives, more and more turned into ordinary Chinese. However, the usual assimilation scenario of the invaders did not take place.
After a series of cataclysms, the most catastrophic of which was a breakthrough of dam on Juanhe in 1334, which took hundreds of thousands of lives. In the country, displeasure to Mongols sharply increased. The uprisings began to flash, whose participants were called "Krasnopovaznosniki". The leader of the rebels Zhu Yuan-Zhang (1328-1398) in the end and took the imperial throne, founding the Ming Dynasty.
China during the Ming Dynasty (1368-1644)
Like the previous Emperors of Zhu Yuan-Zhang, the Emperors of Zhu Yuan-Zhang did a lot to strengthen the central authority, starting with agrarian reforms. A fixed taxation was introduced with relatively low taxes, and some categories of yards sometimes were released from taxes, as it happened before. The system of duties was universal, but was implemented alternately.
Successfully driven Mongols from the territory of China, the Minsk Army held several successful military campaigns and in the south, in the Vietnam area. The Chinese fleet, headed by Zheng He, from 1405 to 1433 committed several maritime expeditions to countries South-East Asia, India and even towards the eastern coast of Africa.
By the same period include the establishment of trade relations with neighboring countries. Trade was extremely profitable for ingenians. They represented their products as the "gifts" from the authorities of their country, the Chinese, perceiving them as a manifestation of Dunnic trade with "barbarians", "died", and the volume and value of the imperial awards and complains were to exceed the "tribute" How much the prestige of the Chinese emperor was valued by the Chinese themselves above the prestige of "Danikov rulers".
The MIN dynasty existed for almost three centuries, the last half of this period is in the conditions of a protracted crisis. Over a year and a half of the tightened political struggle in the tops for the necessary country of reform, the process of rupture of peasants has achieved extremely degree. At the head of the next uprising was Tzu-Cheng (1606-1645). In 1644, the troops were taken by Beijing, and he himself, having ended with Min, declared himself an emperor. However, he did not work on the throne.
Periodization of the history and culture of the ancient China
Ancient period - V - III thousand BC.
The Shan yin period is gray. II thousand BC. (XVI - XI centuries. BC), I Chinese state
Periods of Zhou and Zhango XI - III centuries. BC.
Qin dynasty - 221 BC - 206 BC.
Han Empire - from 206 BC - Han Dynasty
Since the end of the end of the III century n. e. to gray XIX century Middle Ages continued in China. The period of the ancient Chinese civilization ended in IIіvek \u200b\u200bAT.
China \u003d Middle Kingdom \u003d Eastern and Central Asia appears about 6 thousand years ago as ancient civilization on Earth.
Chinese writing has become the basis of the writing of Koreans, Vietnamese, Japanese.
Chinese great inventions: silk, powder, compass, porcelain, paper, brushes, mascara, typography.
Religion and spiritual schools of the ancient China
The main religions of the ancient China were confucianism and Taoism.
Confucianism - the founder of Confucius ≈ (551 - 479 Gg BC) goes back to the teachings. He wanted to give the authority to the ancient traditions. He did not leave any written works, his ideas reached us in the late book "Lun Yu". His theory is the basis for practical life and completely conservative.
The main virtues who need to imitate, from the point of view of Confucianism, were such: humanity, honesty, decency, wisdom, loyalty.
They are implemented in the fundamental relations between people, and the ruler should show a moral example, and to bring order in series in all spheres of life: in his state - his family - its own character - his heart - his thoughts, and initially he must come to insight.
Confucius has developed a program to streamline concepts, Ideal in it is a noble husband - a sage. Meng-Tzu (374 - 289 BC) believed that the person is kind on nature, therefore, the basis of all virtues is concluded in the man itself. The highest goal goer should be the well-being and morality of the people.
From the XI century in ancient China, neoconfucianism becomes the dominant religion. He had a dualistic character: there are two main starts of the world - lie (world mind) and q. (the principle of material activity).
At the same time a doctrine appears Yin Yang, based on understanding "Book of Changes" ("and Jing"). Yang is the beginning of a male, bright, durable, strong, yin is the beginning of a female, passive, dark, pliable. These are two cosmic origin. And their interaction will explain the emergence and transformation of all things and phenomena on Earth. Five main elements were created from their interaction: fire, water, metal, wood, earth.
Universal order and rules:
Family - Eternal Sky established by the order of relations in the family
Society
Etiquette - system of rules and norms of human behavior - ritual
Spiritual life - Rules for all spiritual manifestations of life
Art - Laws in Music, Literature and Painting
Taoism.
Its classic text is the book "Dao de Dzin" (about the V - III centuries. BC). The author is the legendary philosopher Lao Tzu, but its existence is not proven.
"The book about the path (Tao) and the properties of nature, a person" is attributed to Lao Tzu.
Tao is unnamed and inexplicable, as it is outside the system of language concepts, this is the supreme principle on the other side of all the differences.
Several abstracts of daisy wisdom.
According to Taoism, the true wisdom is to allow Tao to lead themselves, and abandon egoistic activities. The sage acts through navigation: this is not an inaction, it is a sensitivity to what is happening and the absence needs intervention. "Tao forever in the eyelids there is a misunderstanding, and yet - nothing remains unresolved!"
In all, it is necessary to comply with the minimum need.
The sage lives in simplicity and acts through imaginary weakness. It is compared with water: "It is useful to everyone alive, but, despite all the softness of water, nothing rigid will not harm her!" NB! Creative task: how do you understand this ancient Chinese wisdom?
Zhuang Tzu (IVEK BC) - the second ideologist of Taouaism, despised the Confucianism for the loss of the initially virtuous simplicity.
Dao is amenable to description only in paradoxical, abolishing themselves with the wording, for example: Dao is nothing, Dao is all!
The spirit should abandon the resistance, and then the wind will incur be it, like a sheet ... you need to find my daoist stream and get into it, and then everything will be done in life by itself, automatically. But the main work is to post the right goal.
NB! Creative task: write down the lyrics of V. Vysotsky "Kraul" and find the ratio between its idea and Taoism.
Mo Tzu (V - IV BC BC) - the third ideologist of Taoism, who created his new form - Moism. The reason for evil is in the absence of love for near.
Several paradoxical definitions of Dao:
Dao is all, Dao is nothing
Path of the Universe
The eternal variability of the world, subordinate to the laws of nature
Equilibrium is possible thanks to the female and male principle - Yan + Yin
Natural laws of the universe, it is impossible to break them, otherwise the harmony of life is disturbed
Way of nature
Path of individual life
Merilo man - Earth, Merylo Earth - Sky, Merylo Sky - Tao, Merilo Dao - It is
Inspiration from the innermost abdomen of the universe
Non-existence, emptiness, silence,
Nothing - the abode of the Great Dao
The source of all things \u003d
Manifestation of things in the Seem of the World, breaking them out of emptiness
Rhythm of the Universe
Energy flows
Everything in the universe moves in space and time, obeying the rhythm of the Great Tao
Nature
Absolute Spirit
Universal mind
Mysterious pattern capturing the laws of the Universe
Ancient period - V. – III thousand BC
The tribes settled the valleys of the China River approximately V - III milk. BC.
Settlements consisted of global huts
Farming, animal husbandry, handicraft - developed gradually
Artworks: Yangshao vessels - the first ceramics in Drvnoy China, the extraordinary correctness of the forms
Complex geometric drawings on the vessels of an undelivered symbolism
The Shan-Yin - XVI - XI centuries period. BC.
Shan's period - Yin (The name of the period is given by the name of the tribe) was marked by the creation of the first Chinese state in the Valley of the Juanhe River.
The first ideas about the universe were formed by the ancient Chinese cosmology and the philosophy of being, here is its main postulates:
Nature phenomena is only the will of the spirits and gods
Demining of all the phenomena of nature: clouds, rain, wind, thunder and appeared in different animal images
The defenders of the living were their dead ancestors, from here there was such a developed cult of ancestors, during which the living served the souls of the dead, cared for graves, put all the handicraft products in it
Sky is the Supreme Deity of the Universe
Performances of the Earth and the Sky: Earth - Square, China - in its center, and the sky is a circle. Semicircular sphere above the square of the earth; Hence the ancient name of China "The Middle Kingdom" and "Podneby Empire"
The sacrifices of the sky took place on round altars outside the settlements, square altars were created right on Earth as small images of the whole land
The ruler of the state China was called "Van", he was at the same time and \u003d at the same time the Supreme Priest in the state.
Development of science, technology, architecture and art:
During this period, it appeared: silkworm, bronze casting, hieroglyphic letter, basics of urban planning
Bronze cast
Image of animals, birds
Thread on jade, bone, wood
Decoring nature and ancestors
Decorative art objects (bronze, jade)
Lacquer utensils (only in China)
Magic vessels for sacrifices, heavy, bronze, with rich terrain
The relief included images of birds, dragons, cicades, bulls, rams, their task - to protect a person and sowing
Capital - Shang, in the city - Palace of ruler on a rectangular platform
Underground burials knew: two underground cruciform chambers, their area - 400 m²
Zhou and Zhango periods
In the XI century BC. The state of Shan-Yin was conquered by the tribe Zhou, but by the end of the VII century. BC. Began the protracted internecine wars.
Period V - III centuries. BC. In Chinese history named Zhango - It means "fighting kingdoms". During this period, the extensive areas of neighboring territories were attached to China.
Iron deposits were opened, iron implements began to appear. Trade developed. For the first time, round coins appeared. Strengthening the role of the state. Growing cities.
A significant event happened to science: the first educational institution was opened, which was called the Academy.
During this period, two main religious teachings, spiritual schools, two Oldequoy Philosophy - Confucianism and Taoism are born and develop.
Development of architecture and other types of art:
Sculptures from marble
Imperial mausoleums
Wall painting and stone reliefs of buried temples:
Image of scenes of life, legends, musicians
Labor of people on salt cops (relief from Ganda)
Image of man (carving, casting)
Pictures on silk "Girl, Phoenix and Dragon"
Silk fabrics and "Great Silk Road"
III centuries. BC. - The Great Wall Wall began to build
Cities-Fortress
The main feature of the ancient Chinese architecture - Pagoda: roof with bent corners
Brief chronological table of history and culture of ancient China
4 thousand BC. - Culture Yangshao (4000 - 2400 BC): Red ceramics, geometric spiral pattern
≈ 2500 Gg BC - appearing acupuncture (\u003d acupuncture)
≈ 2400 GG BC. - Culture "Longshan" near the River Juanhe (Yellow River)
≈ 2160 BC. - The first evidence of the observation of the sun
≈ 2000 GG BC. - Semi-Lady Dynasty Sia
XIX - XVIII BC BC. - Hetta base their state
End of the XVIII century. BC. - the era of the Shan Yin dynasty, to 1025 BC.
Bronze technique
Writing
Ancient Chinese Bronze Ritual Items
XIV. BC. - Construction plan of Anyan, new capital of the Shan-Yin era
≈ 1025 GG BC. - Zhou dynasty (replaced Shang-Yin)
distribution of writing
722 GG BC - The period "Spring and Autumn", East Zhou (722 - 481)
growing cities - Palaces - the capital
≈ 600 Gg BC - Ancient Chinese Poetry "Schizhin" (Assembly)
481 BC BC. - The period of "warring kingdoms"
End of IV century. BC. - Chinese philosopher Zhuang Tzu - the author of the work with his name, beginning of Taoism
III century BC. - Confucianism (or Meng Tzu is the name of the work), Taoism ("Dajetjin" \u003d "Book of the Path (Dao) and the properties of nature, man", is attributed to Lao Tzu
"Zhuang Tzu" - also the Taoice direction in religion
Han Fei (233 BC) - Treatise "Han Face-Shl" - the concept of "law"
Created quasibumaga - from silk fiber
221 GG BC - the beginning of the rule of the I emperor Qin Shihuandi, the unification of China
The beginning of the construction of the Great Wall
213 BC BC. - The emperor ordered: burn all old books as a symbol of old orders
210 GG BC - Warriors of painted clay in the natural value of burial
≈ 206 d, Do AT. - Completion of the Qin Dynasty, the beginning of the Han Dynasty (206 BC - 220 AD)
200 Gg BC - The capital is transferred to Chan-An
165 BC BC. - for the first time there are official exams when setting government officials
134 BC BC. - Chinese emperor U-di, the beginning of the Board of Mandarins
125 GG BC - Open the possibility of trade with India and Iran
119 GG BC - Han Empire - breaks nomads and takes control of the "Great Silk Road"
80 GG BC - Smy Tsyan writes "Historical notes" - the first prototype of the history of China
23 GG N.E. - The beginning of the Eastern Dynasty (younger) Han, the capital - Cancer has been renamed Luoyang
40 g. - uprising in Vietnam against Chinese invaders
48 g. - South Hongna - Syunna recognize the power of the Han Empire, its territory extends to 2 sides of the Chinese wall
58 G. - Min Di - Liu Zhuang became the emperor of China - the territory of the state expands
68 - I Buddhist settlements in China (Luoyang \u003d Henan)
105 g. - The invention of paper fiber paper Chinese scientist Tsai Lun
123 G. - Northern Hunnu are defeated by the Chinese
184 - the uprising of "yellow dressings" (leaders were supporters of Taoism)
190. - The beginning of the board of the Xian Di dynasty (Liu SE) is the last Chinese emperor of the Eastern Dynasty I Han
220 g. - The beginning of the period of internal fragmentation - until 581.
220 - 280 GG - Treasy Age: Empire disintegrates 3 independent states: North - Wei (Capital Loyang), Cao Pay Center - Shu (Capital Chendru, Han Liu Baem); South part - Capital Washang, then - Nanjing
260 g. - China Liu Hui opens the solution of the system of equations and calculates the number π ≈ 3,14159
265 - Sum Yan captures power in Wei, Shu and bases a new dynasty: Western Jin
317 - came the era of South and Northern Dynasties (317 - 589), in Egypt - Coptic art appears, the art of monophysites appears, distinctive from Hellenistically-Roman
420 - The Western Jin dynasty in the south of China is replaced by the Sun dynasty, which ruled in Nanjing
325 G. - Shapa II and National Synod enshrines the final text of the "Avesta" - the sacred book of Mazdis
479 - Sun dynasty is replaced by the Qi dynasty.
General conclusion in the culture of ancient China.
The global importance of the Ancient Chinese culture is its unique harmonic compound of strength and weakness, hardness and softness, social and individual, material and spiritual, active and contemporary, etc.
The symbols of Yin and Yang have become at all times for all the peoples of the land of the Saving Monad's understanding of the unity and the struggle of the opposites, which formed the basis of European dialectical philosophy.
The Tea Ceremony of Ancient China for all subsequent stormy and tragic periods of human struggle for their existence began forever invented and the best way to relax the tired people.
Humanity is obliged to the Chinese many technical achievements (compass, seismic, paper, powder and much more).
Chinese culture refer to the number of traditional. Many this gave reason to believe that it is no matter how capable of scientific and technical progress. However, firstly, scientific and technical progress is important, but far from the only indicator of the level of cultural development of society. Secondly, referring to the ability of society to satisfy their everyday requests, the ancient Chinese culture between I B. BC. and xy in. AD It was more efficient than the culture of the West. In the ancient Chinese culture, the contemplative attitude of a person to nature was encouraged, and this gave their fruits: among all the ancient peoples, the Chinese were the greatest naturalists.
And the lifestyle of the ancient Chinese society is very instructive for modern humanity.
The theory of daoioism and the image of the Great Tao is uniquely able to connect a person with his personal space, the universe, the universe, give us to feel our neoplace in the limitless expanses of time and space, stretch our hand to the tenderness of the Great - to the Small ...
NB! Creative task: What spiritual personal discoveries allowed you to make acquaintance with the ancient Chinese culture and what does it mean for you personally?
The history of the ancient China is divided into four periods associated with the Board of a certain dynasty:
- 1) Yin (Shang) - XVI-XI centuries. BC.;
- 2) Zhou - XI-III centuries. BC.;
- 3) Qin - 221-207. BC.;
- 4) Han - 206 BC - 220 AD.
During the fourth period, the process of developing a slave-ownership state begins to feudal.
The formation of the Ancient Chinese state according to the Chinese tradition was associated with the conquest of the Shan Shang Neighboring tribes. The need to hold in the obedience of the conquered population has intensified the process of formation of the state.
The state system of the ancient Chinese state over time was transformed into a classic oriental despoty. The king was a focus of the highest state power, the commander of the army, the highest court, the Supreme Priest, leading its origin from God. Higher positions in the state appointed relatives of the king, and smaller - judges, scribes, tax collectors and others - professional officials.
At the highest level in the social hierarchy there was a king (van). Then the Shan slave-owned aristocracy and priestly came. The next step was occupied by the slave-owned aristocracy of the conquered tribes. Depending on the proximity to the king of the aristocracy possessed titles that were given the right to certain privileges.
The bulk of the population was free communities. In the period of the state, Yin (Shang) community has played a big role. Community land use was organized on the system "well fields". All lands were divided into two categories: "Public" field and "private" fields. The "public" field was processed together with the entire community, the entire harvest was made by the elder of the community and then the king. "Private" fields were individually used by the family, which was also the entire harvest. The whole land was considered as state ownership and was at the disposal of the king. In private property there were slaves, houses, tools of labor.
Slaves could own both individuals and the state. Sources of slavery were: Military capture, selling for debts, appeal to slavery for some crimes, receiving slaves as a date. Slaves were in the position of livestock; They could not have any family nor property.
In the XII century The Yin State (Shang) experienced a deep crisis. At the same time, one of the tribes was strengthened by one of the tribes - Zhou, who was under the control of the state of Shan. In 1027 BC. The Zhou tribes caused the defeat of the troops. On the change of the empire, the state came a state based on Zhou tribes.
The Board of the Zhou dynasty is divided into three periods (the period of Western Zhou, Eastern Zhou and Zhangho ("Fighting Kingdoms")), which consistently replaced each other.
The first rulers of Zhou distributed their relatives and leaders of the friendly tribes of the Ducks into hereditary possession. Total registered about 200 such complaints. The owners of the devals formed a price of hereditary nobility - Zhu Hou. The most noble titles - Gong and Hou - wore the nearest relatives of the ruler. Guna and Hou, in turn, complained to their close relatives of Daifu titles. The lower layer of Zhowa aristocracy was serviced people - Shi - descendants of noble people on the side line.
The supreme power in the state was in the hands of the king (Vana), who was called the son of the sky (Tian Zi). The entire territory of the country was divided into areas led by the rulers appointed by the king. However, essentially these were individual kingdoms. Centralized state apparatus during the entire period Zhou did not exist.
During the kingdom of Zhou, the king was still the Supreme Owner of the Earth, but the ownership of a slave-owned nobility was gradually turned into a private property, which could be alienated, to lease, mortgage. For farmers, a community and community land use continued to maintain their importance. However, during the period of "warring kingdoms", the system of "well fields" occurs and further strengthening individual land tenure.
Over time, the areas of traditional stay of Zhou began to be exposed to more frequent raids of Western tribes, and in 771 BC. The ruler of China Pin Wan was forced to transfer the capital to the East. The period of Eastern Zhou began or, as it is also called, "separated kingdoms" (Chunzu). Once in the land of the specific rulers, Chinese Vanya preserved only the nominal power. Increased fragmentation and rivalry between the lots, which turn into actually independent states. In the central regions, there were relatively small kingdoms based on the closest relatives of the Zhowsky kings. These include the kingdoms Lou, Wei, Zheng, Han, Jin, and others. It was their rulers who were the first to call their own possessions of the middle states. On the re-ferey there were larger and powerful states: in the east, the kingdom of qi, in the west Kingdom of Qin, in the lower reaches and the average course of the Yangtze River Kingdom, Yue and Chu.
From VII century BC. These states entered the fight for the championship, which was originally conducted under the slogan of the restoration of the Government of the Zhouse rulers. The concept of "hegemon" (BA) occurred, the power of which was based on a bare force, unlike the king (Vana), which was affected by the subjects of "strength of virtue." For the first time, the title took in 651. The ruler of the kingdom of Qi Huai-Gui. Later, it was repeatedly transitioned to the rulers of other kingdoms. In 544 BC. The rulers of the lots have concluded a world agreement, which, however, was respected long.
In V c. BC. The country broke up into a variety of independent states, which were led by a fierce struggle.
The formal date separating the era of "separated kingdoms" from the "Fighting Kingdoms" era is considered to be 481 BC. - The year of the end of the oldest Chinese chronicles "Chun Qui". However, for the opposition of two periods there were objective reasons associated with deep changes in China's social and economic life. In many kingdoms, political reforms were carried out, aimed at limiting the privileges of the generic aristocracy and the strengthening of the sole power of the ruler. The main goal of these transformations was the mobilization of all the forces of the state in the struggle for survival.
In the III century. BC. The winner in this struggle was the king of Qin, which turned into a strong centralized state. Shang Yana's reforms were of particular importance for strengthening the Qin Empire - the sander of the Qin State (died in 338 BC). In order to centralize the state, administrative division was carried out on a territorial basis, the free sale and purchase of land was legalized, taxation was established in accordance with the number of land treated, it was re-equipped and reorganized by the army. In each of the 36 educated areas were scheduled for two ruler, military and civilian, the former aristocracy was put under the strictest control. Wealth and government merits were the criterion of knowledge, old titles were destroyed. Severe laws were introduced for the slightest misdeed. The reforms Shang Yana contributed to the sharp strengthening of the Qin Army and the state as a whole. In 249 BC. The Qin Army defeated the domain of the Zhousky king, putting the end of the Zhowa dynasty. In the following years, the rulers of Qin managed to defeat the rest of the state. By 221 BC The country's union was completed.
The ruler of Qin took the title of Huangi (emperor) and entered the story under the name Qin Shihuandi, i.e. First Emperor Qin.
Having completed the association of China, Qin Shihuandy immediately made a number of symbolic gestures confirming his position of the only lord. He traveled the whole country, setting memorable steles at different strokes, ascended to the sacred mountain of Tishan and made the sacrifice of the sky on her top, began the construction of grandiose palaces in the capital, etc. However, royal innovations, aimed at the unification of the political and public life of the Empire, had much greater importance for the follow-up history of China. Qin Shihuandi abolished previous specific possessions and introduced a unified country management system, dividing China on 36 regions, which, in turn, were divided into the counties. Unified state service rules and criteria for evaluating officials of officials were introduced, and local officials were charged with the duty almost every day to submit to their heads about the state of affairs in the suspension; Even the absence of an official in the sick service should have identified documented. Money has been unified, uniform lengths of length and weight, a single writing, even a single axis width for the cart has been introduced. Qin Shihuandi introduced a single name for its subjects - "black-headed". The subject of the empire was forbidden to own weapons, and from the 6 giant statues, which were set in the Cinema capital from the cinestic authorities of Iron Swords, and other weapons. Qin Shihuandi took care of the safety of the external borders of its empire. He conceived the construction of a grand wall along the northern frontiers of China, togeting several million people for work. This wall was supposed to protect China from nomadic Syunnu raids. At the same time, Qin Shihuandi sent troops to the south - to the region of modern provinces Guangdong and Fujian. There were built fortresses and new areas were established, the first Chinese population of which was referred to as references.
Qin Shihuandi took decisive measures to ensure ideological uniformity. He forbade his subjects to reading any books with the exception of those that could bring practical benefits (the latter were attributed to the management on agriculture, crafts, medicine, fortunate). In 213 BC The famous "burning books" took place, followed by the execution of more than 400 scientists, suspected in disloyal regime.
However, the rapid grandiose construction work turned out to be an exorbitant heavy burden for the treasury, and the adopted administrative control measures are far from such effective as Qin Shihuandi counted. As soon as he died and was buried in his grand tomb, as unrest began throughout the empire, quickly grew into armed rebellion. The authority of the successor Qin Shihuandi - Erishawandi ("The second emperor") was clearly insufficient to ensure that the Cine Army could hold back the wave of popular perturbation. Acute social contradictions and folk uprisings led to the elimination of the Qin monarchy. In 209 BC On the lands of the former kingdom of Chu flared up a powerful uprising. Three years later, one of the rebel armies, headed by a rural old-fashioned Liu Bana, caused a decisive defeat by the Qin Troops. Erishawandi was killed by His courtiers, and Liu Ban, taking the capital of the empire, became the founder of the Hairy dynasty. Soon he managed to spread his power to all China.
Liu Ban did not restore the Qin management system. He complained to the seven of his closest companions of the title of Van, and later distributed hereditary diets to another 130 comrades. However, all hereditary possessions were in the eastern and southern regions of the empire, whereas in the western part of the areas and counties established by Qin Shihuandi are preserved. The order headed by Liu Bana was preserved for about half a century after his death, when the throne occupied his son and grandson. Embeding to the throne in 140 BC Liu Bana Emperor U-di has taken decisive measures to strengthen the central government. Now the goet was supposed to share between all the heirs of his owner. At the same time, the U-di restored the authority of inspectors that controlled the local administration existed in Qin. The rulers of the areas from now on charged to the duty to recommend for the service of capable young people, and a special academy was created in the capital to prepare future officials. The main government department was the Secretariat of the Emperor.
The kings of the new dynasty were undertaken repeated attempts to weaken the severity of social contradictions. At the end of the i century. BC. Emperor U-Di introduced restrictions on the size of land possessions and the number of slaves owned. No one could have more than 138 hectares of land and 200 slaves.
After the death of U-di on the Han Prestrol, the minor rulers were. At the court, Favoritism flourished, the authorities often fell into the hands of temporarys from among the relatives of the Empress or servants of the Imperial Harem. At the same time, the wide masses of the peasantry - the constant support of the throne - ruined and replenished the ranks of the vagrants or bathers in the farms of major landowners.
The weakening of the Han House led to the change of power. The relative of the Empress Van Manman in 8 g., Becoming "Yes Si Ma" - Han's Higher Sannis, captured power as a result of a coup. In 9, AD He proclaimed himself with the emperor of a new blue dynasty. Having come to power in the conditions of the growing struggle of the masses against major landowners, Van Mans conducted a number of reforms.
Wangman found his public ideal in the descriptions of the Rannezhou. He forbade buying and selling the land, which was declared royal, restored the community land tenure system. Each family was allocated arable one. The sale of slaves was banned, but at the same time the number of state slaves increased. The state regulation of market prices and interest on loans was introduced, monetary reform was carried out and new taxes were introduced. There was a state monopoly on a coin chasing, mountain and river crafts. Van Man sought to focus in the hands of the state all sources of income and create a strong bureaucratic empire. The office of government officials was increased, the appointment of a position was practiced on an examination basis.
However, to prevent the crisis of the slave-ownership state, all these reforms, of course, could not. In 12, under pressure from rich landowners, a ban on the sale and sale of land and slaves was canceled. At the same time, drought and floods, which happened to a rare constancy for several years in a row, caused hunger in the central regions, followed by armed meters. The most fame received the rebel detachments from Shendong, whose members were called "redobrov", as they smeared the face with red paint, to resemble the demons to their appearance. Their leader issued himself for the sibling of the Han dynasty. In 23, "Krasnobrov" managed to take the imperial capital. Van Mai died in his palace.
However, the victory went to the descendant of the notable branch of the Han House of Liu, who in 25 g. Proclaimed the restoration of the Han dynasty. Since Liua chose Loyang his capital, his dynasty was named East, or late Han.
The history of the Nostdhankian dynasty largely resembles the history of its predecessor. At first, the central authorities restored control over the entire territory of the country, although calm in the empire was purchased by the cost of compromise between the administration and the local elite. Over time, the growth of large land ownership and the ruin of the peasantry pushed the state. The politically decline of the dynasty, as in the Epoch of Early Han, was expressed in the elevation of the imperial favorites from among the relatives of the Empress and Palace Enunov, which led to the exacerbation of the struggle between these temporars and regular officials. The social base of power was steadily narrowed, and at the same time tax revenues were reduced in treasury.
In 184, an uprising broke out, known as the uprising of yellow bandages, immediately swept the majority of the central regions of the Empire. The performance of yellow bandages was suppressed by government troops and squadrons of provincial magnates, but the Han Yard finally lost control over the country. In 189, the Palace Guard learned the beating of Enuns of the Imperial Harem, and then the troops came from the border of General Dong Zho completely plundered the capital. Hanskaya Power actually ceased to exist. True, formally, the power of the Han Emperor was held for another 30 years, while applicants for the throne found out the relationship between themselves. Almost all this time, the Han Emperor was in the rate of commander Cao Cao, who deftly took advantage of the authority of the Han House in order to strengthen in the central regions of the former empire. In 220, Cao Pi, the eldest son Cao Cao, forced the Han Emperor to renounce his title and proclaimed the welling of the Wei dynasty.
Cao Pi, who overthrew the last Han sovereign, failed to become the ruler of all of China. The commander Liu Bay, who settled in Sichuan, declared himself the emperor of the Han dynasty (in history, his kingdom is called Shu or Shu-Han). In November 222, EXAMPUT Liu Bei Last Sun Quan, proclaimed the creation of the kingdom of y in the areas of the lower and middle course of the Yangtze.
The kingdom of Wei was the strongest among new states. The basis of his power was the system of military settlements, which consisted of about 80% of the consolidated population. At the same time, a new system of selection and qualifications of officials was introduced. From now on, all civil servants in accordance with their "merits, virtues, talents and behavior" were divided into nine ranks. In the areas established special positions of Zhongzhenov ("impartial and direct") who made the selection of candidates for the service. The latter was assigned the "rustic" category that determined their personal abilities. The "Rustic" category institute has secured the dominance of the local elite, very quickly ensuring the right to possess the highest second category.
Cao not long remained the owners in their state. In the 40s The key posts in the army moved to the family of the Sum, and soon the successors of Cao Cao were divided by the fate of the Han Dynasty: in 265. The last Way ruler "lost the throne" Suma Janany, who founded the Jin dynasty. By this time, Yan's Sum was already subordinate to the kingdom of Shu-Han, and in 280 Palo and the South-China Kingdom of W. China was again united under the rule of the Jin dynasty. However, the triumph of the house of the Sum turned out to be short. At the end of 311, internecake broke out inside the reign clan, which led to nomadic tribes, which have long been inhabited by the Northern and Western borders of the Empire. In 308, the leader Syunnu Liu Yuan proclaimed himself by the emperor, and three years later, the cavalry of nomads seized and looted the Jin capital of Loyang. This event can be considered the end of the era of the ancient empires.
Section - I - SHORT DESCRIPTION
Section - II -China in the III century BC - II century of our era
Section - III-Culture of Ancient China
Section - IV -Art of ancient China briefly
Section - V -Religion of ancient China briefly
Ancient China is one of the majestic civilizations of the ancient world. The origin of the ancient China is similar to the origin of Sumer, Ancient India, and Ancient Egypt. The majestic River Juanhe constantly brings from the mountains of fruit soils - lesse.
In the Valley of the Yellow River (Juanhe) an ancient civilization was originated. The first kingdom appeared in the second millennium to our era and was called Yin or Shan.
Modern archaeologists carried out excavations, as a result of which they managed to move the capital of this kingdom Great city Shan and the tombs of some of the Shan kings, and called Vanya. Vana was buried in a fairly deep (up to 10 meters), which was conducted by Lestenka. In the grave, gold jewelry, jewelry made of jade, jasper, and also installed huge bronze vessels. The duties of the bath included the following: to manage the state, the execution of special religious rites as well as the Supreme Court. 
Wang was considered a sacred and inviolable person. In one hundred and twenty-second year BC, a tribe called Zhou, headed by Yu-Vanya defeated the Shangam, thereby establishing their dominance, and most of the residents of the Shang-Yin state were drawn to slavery. In the eighth century BC, the state of Zhou broke up under the blows of nomads; Now, the main role is made by one, then the other kingdoms, of which the largest state was the kingdom called Jin (seventh - the fifth century to our era). After the collapse of State Jin began the difficult period of Zhango (translated as "fighting kingdoms"), when ancient China was divided into two dozen small principalities who were constantly bent among themselves, as well as practically did not obey Zhowsky Van.
6-5 VDO. DE - Time When the first philosophical teachings begin to appear in ancient China. In the sixth century BC in China, a great sage lived in China, his name was Confucius, he was very honored among the Chinese, both at the time and in all subsequent centuries. The teachings of Confucius on respect for the elders, about the "noble man", the importance of education, about modesty, and so on, they were later an important benchmark for relations in China between people - both in the family and in the country itself.
In 221g. e. The ruler Qin In Zheng began to unite the huge territories in the only empire and took the title of Qin Shihuandi, which means "the first emperor of the Qin dynasty." This  The ruler severely destroyed any resistance, using the most terrible species of execution. If a person did not follow the law, then in this case the whole family of this person was punished: his family members simply turned into slaves forcing them to work on heavy construction work.
The ruler severely destroyed any resistance, using the most terrible species of execution. If a person did not follow the law, then in this case the whole family of this person was punished: his family members simply turned into slaves forcing them to work on heavy construction work.
When Qin Shihuandei established his own power in the Empire, he began a war with nomads-Huns, which often attacked the northern side on his borders. He decided to fix his victory forever, while building a powerful border wall, which was named the Great Chinese walls. After the fall of the Qin Dynasty, Liu Bang comes to power. He reduced taxation and canceled some of the most cruel laws that were introduced in ancient China with Emperor Qin Shihuandi. Liua Ban, who was then inherited by the eleven of his descendants, became the founder of the Han dynasty. In the era of the Han dynasty, the main features of the Ancient Chinese state have developed. In ancient China, the foundations of the Chinese civilization and its culture were laid - art, literature, science. In two hundred and twentieth year, the Han dynasty passed into decay, and several states independent of its territory were formed on all of its territory. This event is considered to be the end of the ancient period in Chinese history.
Natural conditions of ancient China briefly
The ancient Chinese inhabited the North-Chinese Plain, located at the East East of Asia, from the West to the East Plain crossed Juanhe (Yellow River), carrying a lot of fertile il. Stayed, Il filled the channel and forced the river to change it. Juanhe flooded the fields, washing the village. The people nicknamed her "Mount China". Persistently labor, cutting out the forest, having a swamp, strengthening the banks of the rivers, the ancient Chinese turned their homeland into the country of developed farming. The Valley of the Yangtze River (Blue River), located south of Juanhe, was conquered by the Chinese later, rivers, especially Yangtze with their numerous tributaries, served in ancient times the most important ways of the message.
Classes.
In the middle of the second millennium BC. E, the area of \u200b\u200bJuanhe and her tributaries inhabited numerous tribes of hunters and fishermen. One of these tribes, the Yin tribe, managed to subjugate their neighbors. Recently, dozens of initsess settlements are excusted with archaeologists. Many thousand inscriptions on the bones of animals and turtle shields were found. This allows you to learn life and classes. ancient population China.
The main occupation of the ancient Chinese, those in the Valley of Juanhe, was agriculture. It was favored by a soft, moderate climate, fertile soil and an abundance of moisture.
Millet, wheat, barley, rice have grown on the fields. During the year, two harvest was retracted: in the first half of the year, the Vintage millet was removed, and in the second wheat. The ground was treated with wooden hiding, wooden hoes, stone sickles.
Cattle breeding, fisheries, hunting acquired auxiliary value, except cattle and horses, the ancient Chinese bred sheep, goats, pigs, the dairy products by the Chinese in antiquity in writing were not used.
Initially, the farmers themselves made the simplest agricultural tools, clay dishes, fabrics. Over time, the craft turns into a special, independent branch of production. Previously, the craft of a loaf, demanding special skills and skills. The bronze holders melted and rolled the metal and did from non-refined and various utensils. Potters began to selection beautiful and durable dishes, using a pottery circle and a stove. From ancient times, the Chinese were able to produce thin  silk fabrics. Mastery was kept secret.
silk fabrics. Mastery was kept secret.
With the development of agriculture and crafts, trade arises and develops. Trade was carried out not only with immediate neighbors, but also with peoples on the shores of the Pacific Ocean. The role of money was initially performed by precious shells. It was difficult to produce them. Therefore, they began to make artificial sinks from gems and bone. Then they began to cast from the bronze ingots in the form of shells and other items. So in China there were metal money.
Ancient slave states.
In the second millennium BC. e. The Chinese have slavery. The main source of it - war with neighbors, especially with northern nomadic tribes. The slaves were also obtained in the form of Dani from the conquered tribes.
The work of slaves began to be applied in the economy. During this period, slaves were still in the collective ownership of the community. Slaves not only forced to work to exhaustion, but also sacrificed the gods. Archaeologists excavated burials with the burials of hundreds of people who killed a violent death. These were sacrificed slaves.
Along with the burials containing rich things, as well as "sacrificing slaves, excavated graves, in which there are no things. This suggests that rich and poor, slaves and slave owners appeared in society.
To keep in the obedience of slaves and poor people, the slave-owned know the state. At the head of the oldest Chinese state, a military leader becomes van. His support was to know numerous officials. They charged the unbearable grades from the population. For the service Wang crushed the approximate land and slaves. It led to the development of major land tenure.
In the XII century BC e. The Zhou tribe, who lived to the west of the state Shan-Yin, subordinates the hents. The state of Zhou was formed. In addition, many other slave-owned states appeared in China.
The farmers in these states lived by communities, but each family received the land on the use of land. Tools of labor, cattle, seeds were also privately owned
noah family. Generic and tribal to know, using their position of the community leaders, began to seize the best lands. Free communities were exhausted from Malozhella, they fell into debt dependence on their rich neighbors - large landowners. 
The displeasure of the peasants was reflected in the songs, blame the greed and cruelty of the rich. In one of these songs, large landowners are compared with Hagoning rats, eating the fruits of human labor:
"Our rats, our rats, do not herole our millet. We live with you for three years, and there is no concerns from you ... Our rats, our rats, do not hero be sowing. We live with you for three years, and the awards are not visible from you. "
In the cities there were skillful artisans. From clay and metals, they made beautiful dishes. From the middle of the first millennium BC. e. The Chinese was known to the lacquer. Laco covered furniture and other wooden products. The juice of the lacquer tree was poisonous, so artisans who made beautiful, elegant things were too dying.
In the first half of the first millennium BC. e. The Chinese trade relations are expanding. Trade development contributed to the emergence of the first coins of metal. Gradually, the city turns into craft and trade centers.
China's northern borders were constantly attacked nomads, which later became known as "Gunns". Chinese states have concluded alliances among themselves, since the forces of one state it was impossible to fight nomads. But these unions were fragile. Often Chinese states fought with each other. Internecial wars ruined the economy of China and led to an even greater strengthening of the operation of workers.
China - country with ancient history. It is believed that the first slave states in the territory of modern China appeared in the 21st century BC. (Xia dynasty).
In 221 BC There was a first major centralized state - the Empire Qin.
Starting with the Han era (206 BC - 220, N.E.) in China, there was a process of formation of feudal relations. The feudal society experienced a period of his heyday during the board of the Tang dynasty (618 - 907). At this time, agriculture, various crafts and trade reached a high level of development. The whole country was covered with a network of terrestrial and waterways of the message, broad economic and cultural ties were established with many countries of the world, including Japan, Korea, Persia, India and others. Science, literature and art flourished.
In the 13th century, China subjected to the invasion of Mongolian conquerors and almost 100 years (1271-1368) was under their power. By this period, China's visit to the first Europeans, including the Venetian merchant Marco Polo.
The Chinese Dynasty Min (1368-1644) came to replace the Chinese Dynasty of the Mongolian Dynasty, during the reign of which the gradual decline of feudalism begins. At the same time, the Chinese economy appears the primitives of new production relations. Trade is developing, first manufactories appear.
At the end of the first half of the 17th century, Manchuri invaded China, which founded the Qing Dynasty (1644), which was ruled by the country until 1912. The Zing rulers led the policies of self-insulation and sought to substant the existing feudal order. As a result, China in its development lagged behind the forefronts of Europe. Economic and military weakness of the Qing China were especially brightly manifested during the first opium war (1840-1842), due to the defeat in which he was forced to give the UK Hong Kong.
The second half of the 19th century - the beginning of the 20th century were the time of an acute socio-economic crisis. China more and more falls under the power of the great powers of the time that divided it into spheres of influence.
Overlooking the Sinhai Revolution under the leadership of Sun Yatsen, under the leadership of Sun Yatsen, put an end to the authorities of the Qing dynasty, the republic was proclaimed in China.
In subsequent years, China took part in the First World War on the side of the Entente countries, and in the early 1930s, aggression from Japan was subjected. The Japanese militarists in 1930 occupied the northeastern provinces, creating a Manyzhou's puppet state there, and in 1937 they began an open war against China. In August 1945, after joining the war with Japan's Soviet Union, the Japanese Quantong Army capitulated, and the Japanese invaders were expelled from China.
From the late twenties and until 1949, the internal political situation in China was characterized by a tense struggle for the power between the ruling party of the Gomindan and the Chinese Communist Party. As a result of the Civil War 1945 - 1949. Homintandan's power was overthrown, and on October 1, 1949, the creation of the People's Republic of China was proclaimed.
Proclaiming its goal for the construction of socialism, the Chinese leadership in the 50s took as a basis the so-called "Soviet economic model" of the planned economy. In China, the nationalization of industry was conducted, cooperatives and folk communes were created in agriculture. During these years, more than 200 industrial facilities were built with the active support and assistance of the Soviet Union, which laid the foundations of the modern industry.
The 60-70 years of the twentieth century were noted by the exacerbation of the political struggle and the shocks of the "cultural revolution" (1966-1976). After death in the fall of 1976, Mao Zedun, the arrest of the so-called "gang of four" and followed by this return to the active political activity of Dan Xiaopin Chinese leadership was taken a course on the modernization of the economy. 1978 held in December 1978. The third plenum of the Central Committee of the CPC 11 convocation proclaimed the beginning of the policy of reforms and the opening of the country to the outside world. "
Over the past years, China managed to achieve tremendous success in the development of the national economy, raising the standard of living of the population, the creation of the foundations of the market economy, was published in the world in the world in terms of foreign direct investment, became a member of the World Trade Organization. The 16th CPC Congress held in November 2002 put forward the task to increase the country's GDP 4 times compared with 2000, which will allow China to enter into parties characteristic of the average developed countries of the world.
Below are the main epochs of Chinese history in the form, in which they allocate traditional historiography. Called dates can be considered accurate from 841 BC.
*** Doomperatorsky China
1. "Three ruler" and "five emperors": the mythical epoch of the Golden Age, on which, however, the Confucians referred to their theoretical reasoning as well as Christians on the Book of Being.
2. XI dynasty (XXI - XVI centuries. BC). From this epoch the mythical information and a number of archaeological monuments; Compliance between those and others is mounted hypothetically.
3. Shang (Yin): XVI - XI centuries. BC. The first written monuments.
4. Western Zhou (OK.1027 - 770 BC). In the presentation of Confucianis - the Golden Age. In fact, a very loose statehood ending with feudal disintegration.
5. Lego - "Separate kingdoms" (770 - 221 BC): The time of feudal fragmentation. As part of this era, East Zhou (770 - 256) are also allocated; Chunzu ("Spring and Autumn", by the name of the chronicle, edited by Confucius: 770 - 475 or 403; Zhango (fighting kingdoms) - 475 or 403 - 221, the period of struggle of seven of the strongest states (Qin, Chuzha, Wei, Han, Qi , Yan) for the association of the country. The era of philosophical classics, the emergence of the breakdown of Confucianism and Taoism.
*** Imperial China
1. Qin (221-207 BC). The Board of Qin Shi-Huana (Qin Kin C 241, the emperor from 221) is the folding of the Bureaucratic Empire apparatus.
2. Western (senior) Han: 206 (actually 202) BC. - 8 G.N.E. The peak of the political, economic and military heyday of ancient China. Folding the social structure of the empire. Communication S. western countries on the great silk path.
3. Blue (the board of the usurper Van Mana): 9 - 23 GG.
4. Eastern (younger) Han: 25 - 220. The crisis of the ancient Chinese statehood, which ended with the grandiose uprising of "yellow dressings" and section of the country between warlords and local landlords.
5. Treaspension: 220 - 280. Internecine struggle of the Kingdoms of Wei, Shu-Han and W.
6. Western Jin: 265 - 316 (combined the country at 280). Power of the military.
7. East Jin: 317 - 420. Obtained only the south, since the north by 317 was captured by nomads; Here the "16 states of five northern tribes" corresponding to the "barbaric kingdoms" in Europe.
8. "Northern and Southern Yards": 420 - 589. In the south, the ancient Chinese, gradually degrading statehood - Dynasty Sun, Qi, Liang and Chen; Together with the former kingdom of East Jin, they are usually united by the name "six dynasties". The era of six dynasties is a turning point in the history of Chinese culture: the crisis of Confucianism, the short-lasting celebration of Buddhism, the formation of the foundations of medieval artistic culture. In the north, the power of one of the Xianbian tribes - Toba-Wei is dominated, within which nomads are quickly chipped; In 534 it splits. In 589, one of the northern kingdoms - Sui conquered the south and re-combined the country.
9. Sui: 581 - 618. The revival of Confucianism, aggressive wars.
10. Tang: 618 - 906. Political flourishing, replacing from the middle of the VIII century. decline. The central control system, the right, education (including the examination system) receive classical forms that remain in subsequent dynamines and borrowed by other countries. Chinese armies control Korea, Vietnam, at times, steppe and Central Asia. Golden age of poetry: Lee Bo, Du Fu, Van Wei, Bo Juyi. Ideal vertices of Chinese Buddhism. The beginning of the reform of Confucianism. At the end of the era - the Peasant War of Juan Chao.
11. Five dynasties: 907 - 960. Northern China is controlled by ephemeral modes alternating and exposed to the invasions of the tribe of the kidny (in Russian sources - "China"), which conquer the Beijing area. The south is fragmented to "ten kingdoms".
12. Northern Song: 960 - 1127. China is one, but in foreign policy and militarily weak. "Golden Age" of Confucian officials. A kind of "constitutional" monarchy, in which the power of the emperor is limited to the top bureaucracy and official inertia. Registration of the neoconfucian philosophical system. Flooring of poetry in the genre of the century, the appearance of urban novels. The rapid flowering of the economy, the government control over which weakened noticeably compared to the tanning time.
13. South Song: 1127 - 1279. Obtained only south; The North was first under the authority of the Zhurzhenskaya (ancient Golden) "Golden Empire" Jin (1115 - 1234), and then Mongol-Tatars, with the Genghis Hana who had won the districts of the north of Juanhe, and by the end of the XIII century. - All country.
14. Yuan: 1271 - 1368. Founded by Hubilam, the grandson of Genghis Khan (this in his kingdom was looking for the path of Columbus!). The power of Mongol-Tatars, overthrown by the national uprising of the "Red Forces" (1351 - 68). The decline of classical literary genres and the beginning of the heyday of more democratic: drama, aria, novel. At the end of the XIII century. Marco Polo "opened" China for Europe.
15. Min: 1368 - 1644. The founder - Zhu Yuanzhan, the son of a beggar peasant, then a participant in the uprising of the "Red Forces". Attempts by a wide foreign economic and military expansion, whose peak falls at the beginning of the XV century. (Swimming of Zheng He is up to Africa, encouraging foreign trade in its specific form) from 1436 replaced by a course for self-insulation of the country. At the same time, the epoch min is the last period of the political, economic and spiritual heyday of the old China. The end of the Board of the Ming dynasty put the peasant war under the leadership of Lee Zychchen, the result of which the country's conquest was manchuri.
16. Qing: 1644 - 1911. Manchurian dynasty. In 1842, the Nanjing world, which was defeated by China in the "first opium war" with England, laid the beginning of the country in the semi-colony and the deep crisis of the entire traditional Chinese society. The Board of this dynasty ended with a Xinhajian bourgeois-democratic revolution, which is considered the end of the whole old China. The proclamation of the Republic of China was held in Nanjing 1.01.1912. Formal renunciation of the last Godman (Manychur Emperor) PU and - 12.02.1912.