Modified shoots of plants
Modified shoots, in comparison with the traditional aboveground plant organs, are capable of performing additional functions. What features of the structure is this possible?
Features of the structure of the shoot
The shoot is the terrestrial part of the plant. It is based on the stem. This is the axial part of the shoot, on which the leaves and buds are located. Depending on the location in space, there are erect, creeping, curly, creeping, clinging shoots.
The places of attachment of the leaves to the stem are called nodes, and the distance between them is called internode. On the shoot, there are also rudimentary organs called buds. If leaves develop from them, they are vegetative, and if flowers are generative.
Escape functions
The aboveground organ of plants performs the function of vegetative reproduction. In the course of this process, a multicellular part is split off from the whole organism, due to which its integrity is restored.
The shoot plays an important role in the implementation of growth and regeneration. Due to the presence of chloroplasts in the cells of green plastids, the leaf provides the plant with organic substances that are synthesized during photosynthesis. The resulting carbohydrates are used for various life processes.
Modified underground shoots
But to perform additional functions, typical features of the structure are not enough. Therefore, modified shoots are often found in nature. Due to the formation of various thickenings and changes in shape, they can store water and nutrients, ensure the viability of plants in an unfavorable period, and occupy an advantageous position in space.
Modifications or metamorphoses of the shoot can develop in the soil or be aboveground. The first group includes tubers, bulbs and rhizomes. Aboveground modifications of the shoot are whiskers, antennae, thorns. Let's consider their structure in more detail.
Bulb
The well-known onions and garlic are also an underground modification of the shoot. At its base there is a flat stem, which is called the bottom. Vegetative buds develop on it, from which leaves are formed. They are of three types:
- filmy;
- juicy;
- young.
The first type of leaves will perform the main function of the bulb. They store water with solutions of mineral substances. Dry scarious leaves provide protection from mechanical damage and adverse conditions. From the vegetative buds of the bottom, young leaves grow, which are often called green onions.
Bulbous plants under the ground tolerate drought and frost. For example, tulips, crocuses, lilies grow and fade during the humid and warm season, after which young bulbs form underground. They are usually dug up after flowering, stored in a cool place, and planted at the end of summer.
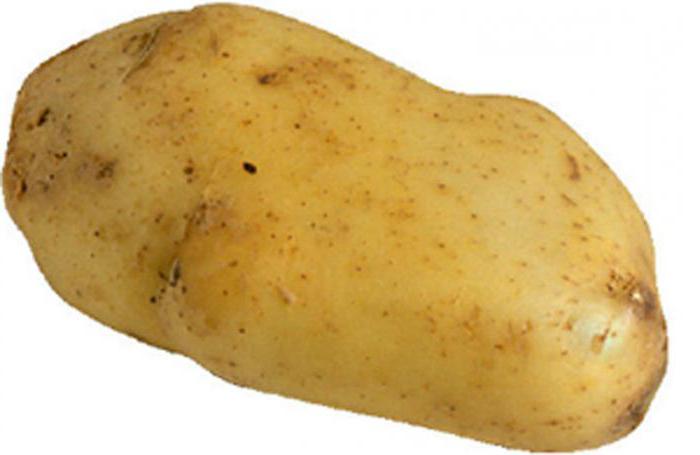
Why is a tuber a modified shoot?
Many modified shoots grow underground. For example, tubers of potatoes or Jerusalem artichoke. Therefore, they are often confused with another vegetative organ of plants - the root. It is very easy to prove that the tuber is a modified shoot. Its thickened part is the stem. It accumulates starch, a reserve carbohydrate of plants. The covering tissue of this shoot is the bark. We cut it off when we "peel potatoes". Another proof is the presence of kidneys. They are called eyes. In spring, young shoots develop from them.

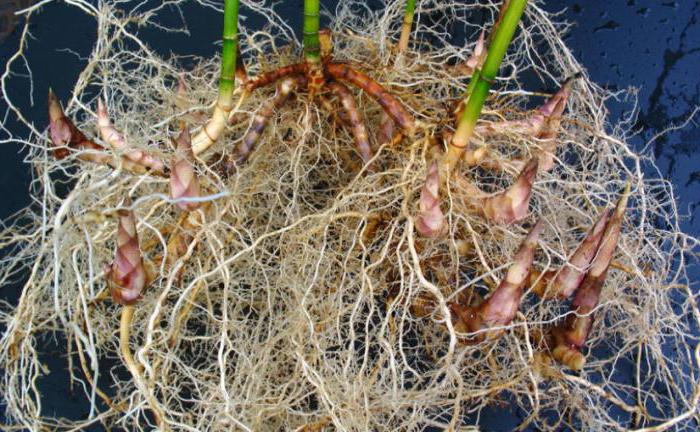
Rhizome
Rhizome is a modified shoot that is also located underground. Despite the name, it has nothing to do with the underground organ of plants. The rhizome consists of elongated internodes on which vegetative buds develop. In the spring, leaves develop from them. Soil nutrition is provided by the fibrous root system, which grows in bunches.
If you have ever tried to get rid of the evil wheatgrass weed, you know that it is quite difficult to do it. Often pulling out leaves from the soil, we leave the shoot itself with viable vegetative buds, so after a certain time they appear again. The presence of rhizomes is typical for lily of the valley, kupena, mint, irises, asparagus.

Mustache and antennae
And these above-ground modified shoots are often confused with each other because of similar names. In fact, they have different origins, and therefore functions. Mustaches, or stolons, are found in strawberries, strawberries, chlorophytum, saxifrage. Most often, these are creeping shoots with elongated internodes and a system of adventitious roots. Simple leaves develop on them. These structures are able to take root and give rise to a new organism. This is how they reproduce.
Antennae are formed in grapes, ranks, peas, and beans. They can develop from a stem or leaves. They help the climbing plants to hold onto the support. As it grows, the antennae, like a spiral, twist around various objects. As a rule, if such structures are not in contact with the support, they dry out and die off.

Cladodius
Almost every lover of indoor flowers grows a zygocactus ("Decembrist") in the house. His escape is called a cladodium. This modification is a flattened stem that acts as a leaf. This is manifested in the fact that cladodium carries out photosynthesis. The stem origin proves the formation of flowers on it, which never form on the leaves. The same modified shoots are found in prickly pear, asparagus, smilax.
The meaning of escape modifications
Metamorphoses of vegetative organs significantly increase the adaptive capacity of plants. Modified shoots perform additional functions in the plant organism in the form of preserving a reserve of substances and providing an additional method of vegetative reproduction.
Thanks to them, a person receives a large amount of planting material. We eat potato tubers, leeks and garlic, which are rich in carbohydrates, biologically active substances and vitamins. Medicinal infusions are prepared from the rhizomes of valerian and lily of the valley.
The most common mutated shoots in nature are bulbs, tubers, whiskers, tendrils and rhizomes.