Hydrogen production by electrolysis of water - technology and equipment
Water electrolysis is a physicochemical process in which water is decomposed into oxygen and hydrogen under the influence of a constant electric current. The DC voltage for the cell is obtained, as a rule, by rectifying a three-phase AC current. In an electrolytic cell, distilled water is subjected to electrolysis, while the chemical reaction proceeds according to the following well-known scheme: 2H2O + energy -> 2H2 + O2.
As a result of the separation of water molecules into parts, hydrogen is obtained by volume twice as much as oxygen. The gases in the plant are dehydrated and cooled before use. The outlet pipes of the unit are always protected by return valves to prevent fires.
The structure itself is made of steel pipes and thick steel sheets, which gives the entire structure high rigidity and mechanical strength. Gas tanks are necessarily pressure tested.
The electronic unit of the device controls all stages of the production process, and allows the operator to monitor the parameters on the panel and on the pressure gauges, which ensures safety. The efficiency of electrolysis is such that about a cubic meter of both gases is obtained from 500 ml of water at a cost of about 4 kW / h of electrical energy.
Compared to other methods of hydrogen production, water electrolysis has a number of advantages. First, available raw materials are used - demineralized water and electricity. Secondly, there are no polluting emissions during production. Thirdly, the process is fully automated. Finally, the output is a fairly pure (99.99%) product.
Therefore, electrolysis plants and the hydrogen obtained on them are today used in many industries: in chemical synthesis, in the heat treatment of metals, in the production of vegetable oils, in the glass industry, in electronics, in cooling systems in the power industry, etc.
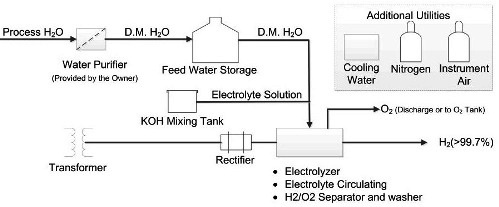
Installation for electrolysis is arranged as follows. Outside is the control panel for the hydrogen generator. Further, a rectifier, a transformer, a switchgear, a demineralized water system and a block for its replenishment are installed.
In the electrolytic cell, hydrogen is produced on the cathode plate side, and oxygen is produced on the anode side. Here the gases leave the cell. They are separated and fed to a separator, then cooled with demineralized water, after which they are separated by gravity from the liquid phase. The hydrogen is sent to a scrubber, where liquor droplets are removed from the gas and cooled in a coil.
Finally, the hydrogen is filtered (filter at the top of the separator), where water droplets are completely eliminated, and enters the drying chamber. Oxygen is usually directed to the atmosphere. Demineralized water is pumped into the washer.
Lye is used here to increase the electrical conductivity of the water. If the operation of the electrolyzer goes on as usual, then the liquor is replenished once a year in a small amount. Solid potassium hydroxide is placed in a liquor tank, two-thirds full of demineralized water, after which the pump mixes it into a solution.
The electrolyzer water cooling system serves two purposes: it cools the liquor to 80-90 ° C and cools the resulting gases to 40 ° C.
The gas analysis system takes hydrogen samples. The drops of liquor in the separator are separated, the gas is fed to the analyzer, the pressure is reduced, and the oxygen content in hydrogen is checked. Before the hydrogen is directed to the reservoir, the dew point is measured in the moisture meter. A signal will be sent to the operator or to the PC to decide whether the produced hydrogen is suitable for delivery to the storage tank, whether the gas meets the receiving conditions.
The operating pressure of the unit is regulated by an automatic control system. The sensor receives information about the pressure inside the electrolyzer, then the data is sent to a PC, where it is compared with the set parameters. The result is then converted into a signal of the order of 10 mA, and the operating pressure is kept at a predetermined level.

The operating temperature of the unit is regulated by a pneumatic diaphragm valve. The computer will likewise compare the temperature with the set one, and the difference will be converted into an appropriate signal for.
The safety of the electrolyzer is ensured by the blocking and alarm system. In the event of a hydrogen leak, detection occurs automatically by detectors. In this case, the program immediately turns off the generation and starts the fan to ventilate the room. A portable leak detector must be kept by the operator. All these measures make it possible to achieve a high degree of safety in the operation of electrolyzers.