Let's talk about how to determine the type of hybridization
Let's talk about how to determine the type of hybridization, and also consider the geometric structure of the molecule.
The history of the appearance of the term
At the beginning of the twentieth century, L. Paulingle proposed a theory of the geometry of molecules with a covalent bond. The overlap of electron clouds was taken as a basis for the formation of a bond. The method became known as valence bonds. How to determine the type of hybridization of atoms in compounds? The author of the theory proposed to take into account the mixing of hybrid orbitals.
Definition
In order to understand how to determine the type of hybridization in compounds, let us analyze what this term means.
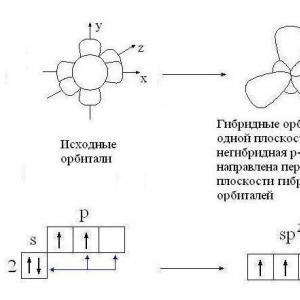
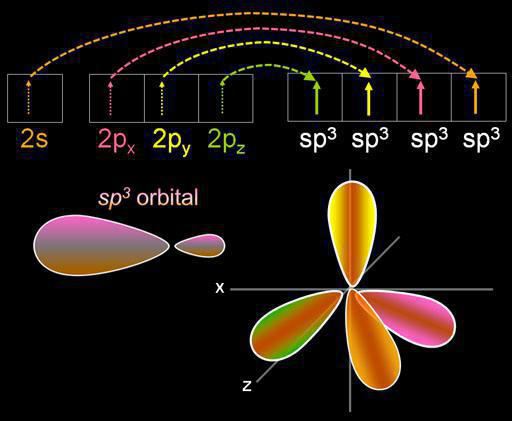
Hybridization is the mixing of electron orbitals. This process is accompanied by the distribution of energy in them, a change in their shape. Depending on the quantity of s- and p-orbitals mixed, the type of hybridization can be different. In organic compounds, a carbon atom can exist in the sp, sp2, sp3 state. There are also more complex forms in which, in addition to the sp, d orbital are involved.
Rules for detecting inorganic substances in molecules
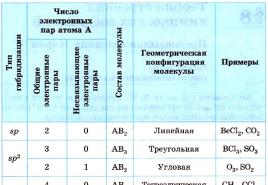
It is possible to identify the hybridization variant for compounds with a covalent chemical bond of the ABp type. A is the main atom, B is the ligand, n is a number from two or more. In such a situation, only the valence orbitals of the main atom will enter into hybridization.
Determination methods
Let's talk in more detail about how to determine the type of hybridization. In the chemical sense, this term implies a change in the energy and shape of the orbitals. A similar process is observed in cases where electrons of different types are used to form a bond.
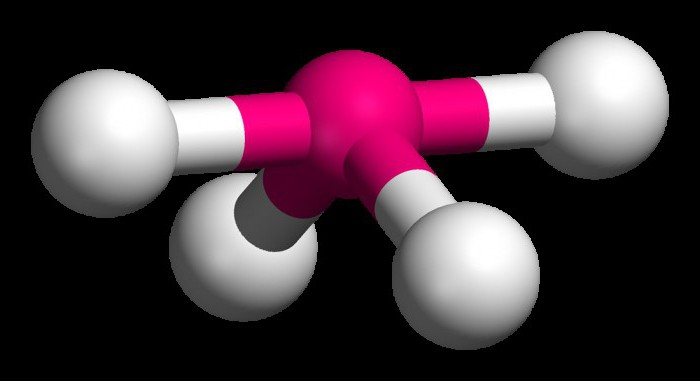
To understand how to determine the type of hybridization, consider a methane molecule. This substance is the first representative of the homologous series of saturated (saturated) hydrocarbons. In space, the CH4 molecule is a tetrahedron. A single carbon atom forms bonds with hydrogens, which are similar in energy and length. In order to form such hybrid clouds, three p- and one es-electron are used.
Four clouds mix, and there are four identical (hybrid) species, having the shape of an irregular figure eight. This type of hybridization is called sp3. All hydrocarbons containing only simple (single) bonds are characterized by this type of hybridization of the carbon atom. The bond angle is 109 degrees 28 minutes.
Let's continue talking about how to determine the type of hybridization. Examples of the ethylene series give an idea of sp2 hybridization. For example, in an ethylene molecule, out of four, only three are used in the formation of a chemical bond. The remaining non-hybrid p-electron is spent on the formation of a double bond.
Acetylene is the simplest representative of the СН2п-2 class. A feature of this class of hydrocarbons is the presence of a triple bond. Of the four valence electrons of a carbon atom, only two change their shape and energy, becoming hybrid. The two remaining electrons take part in the formation of two double bonds, determining the unsaturated nature of this class of organic compounds.
Conclusion
Considering the issue concerning organic and for take into account hybridization, while there is an alignment of their energy and form. An electron located near the nucleus of a bound atom is characterized by a set of orbitals that have the same information about the type of hybridization makes it possible to evaluate the chemical properties of a substance.