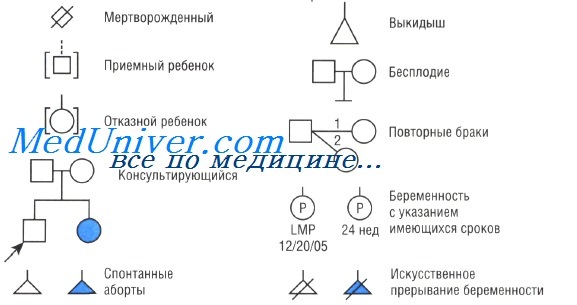
Pedigree in genetics. Symbols used in pedigree diagrams
Monogenic diseases characterized by a certain type of transmission in families. In order to establish the type of transmission, the usual first step is to obtain information about the patient's family history and summarize the details in the form of a pedigree - a graphical representation of a pedigree tree using standard symbols. The extended family depicted in such diagrams is called a genus.
The member through which a family with a genetic disease first comes to the attention of a geneticist (i.e., for identification) is a proband if he or she is sick. A person who draws the doctor's attention to the family by consulting a geneticist is called a consultant; the consultant can be a sick or healthy relative of the proband. A pedigree can have more than one proband if it is counted through more than one source.
Brothers and sisters are called siblings, and the sibling family forms a sibling. Relatives are classified by degrees: first degree (parents, siblings and offspring of the proband), second degree (grandfather, grandmother and grandchildren, uncles and aunts, nephews and nieces and half-siblings), third degree (for example, cousins), and so on, in depending on the number of members of the pedigree between two relatives. The offspring of cousins are second cousins and the child is a cousin of his parents' cousins.
Couples that have one or more in common ancestors are considered consanguineous. If there is only one patient in the family, then he or she is isolated or, if it is determined that there is a new mutation, a sporadic case. When there is clear phenotype similarity among different families with the same defect, the well-established pattern of inheritance in other families with the same disease can be used as the basis for diagnosis and counseling, even if the patient presents an isolated case in the family. Thus, although many patients with genetic diseases do not have similarly sick relatives, it is possible to recognize the disease as genetic.
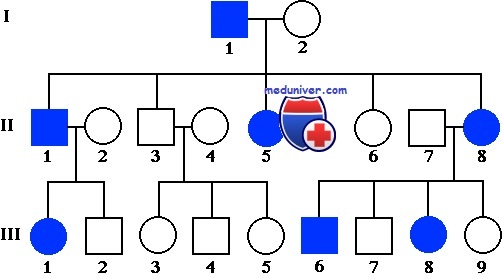
With many diseases family transmission depends on the ability of patients to reproduce. Geneticists use the term "adaptability" as a measure of the effect of a disease on the ability to reproduce. Adaptability is defined as the number of offspring of a patient with the disorder surviving to reproductive age, compared with a suitable control group. Adaptability is not a measure of physical or mental disability.
For example, for some violation of the patient may have normal mental capabilities and health, but the fitness will be equal to 0, since the disease interferes with normal reproduction. In other cases, a serious disabling genetic disorder may have normal adaptability, since the onset of the disease occurs later than the usual age of reproduction.
- Return to the contents of the section "" on our website