Biology teacher - sheet
The shoot is the aerial part of the plant. A vegetative shoot is laid in the process of development of the embryo, in which it is represented by a kidney. A bud is a stalk and leaf primordia, can be considered the first bud of a plant.
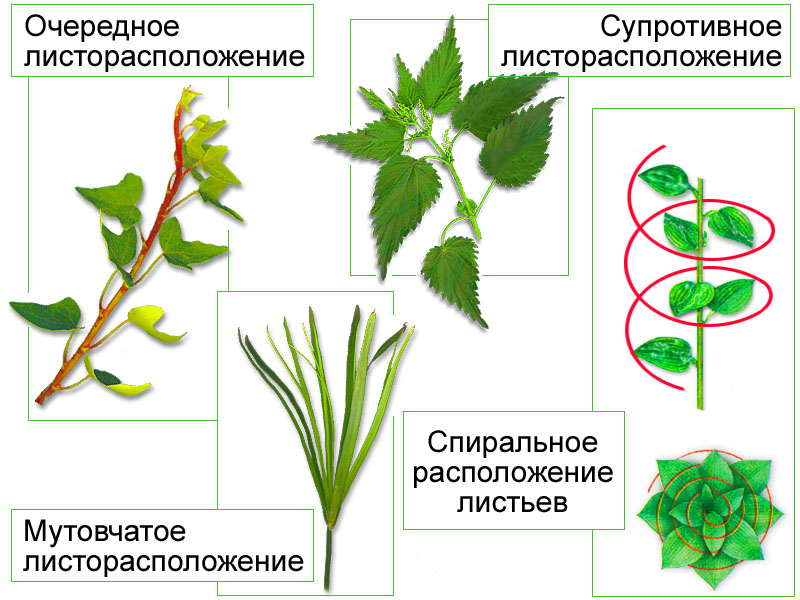
A bud is a rudimentary shoot; new shoots grow from it in the spring. There are apical, axillary, (located in the axils of the leaves) and adnexal buds. Adnexal buds are formed due to the activity of the cambium and other educational tissues in different places - on roots, stems, leaves. The section of the stem from which the leaf and bud originate is called the node. The section of the stem between adjacent nodes is an internode.
The axial part of the kidney is a short rudimentary stem, on it are rudimentary leaves. In the axils of rudimentary leaves, small rudimentary buds can be found. A vegetative shoot develops from a vegetative bud, and a generative shoot with the beginnings of a flower or inflorescence develops from a generative bud. Kidneys are distinguished naked and protected by leathery scales.
Sheet
The leaf is a flat lateral organ of the shoot.
External leaf structure
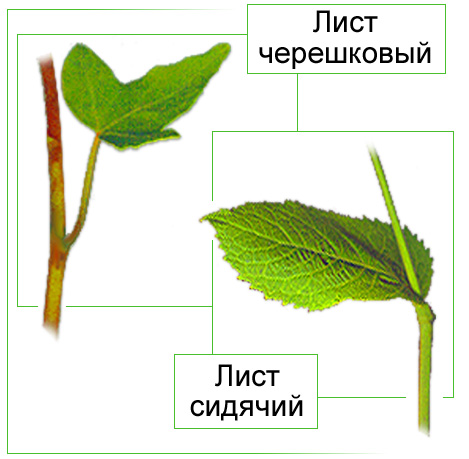
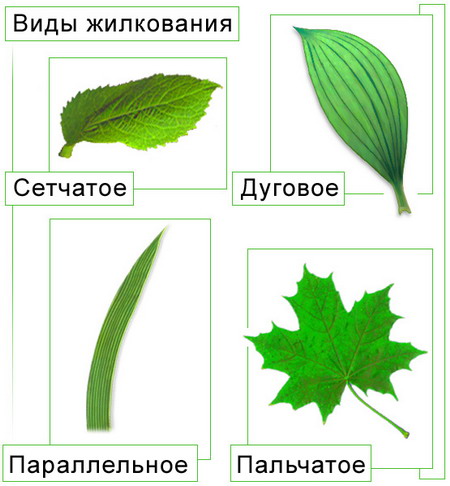
. In dicotyledonous plants, the leaf consists of a flat expanded plate and a stem-like petiole with stipules. The leaves of monocotyledonous plants are characterized by the absence of petioles, the base of the leaf is expanded, into the sheath, covering the stem. In grasses, the entire internode is covered with a sheath: The leaves of dicotyledonous plants are simple and complex. Simple leaves have one leaf blade, sometimes strongly dissected into lobes. Compound leaves have several leaf blades with pronounced cuttings. Pinnately compound leaves have an axial petiole, on both sides of which there are leaflets. Palmately compound leaves have leaflets extending like a fan from the top of the main petiole. 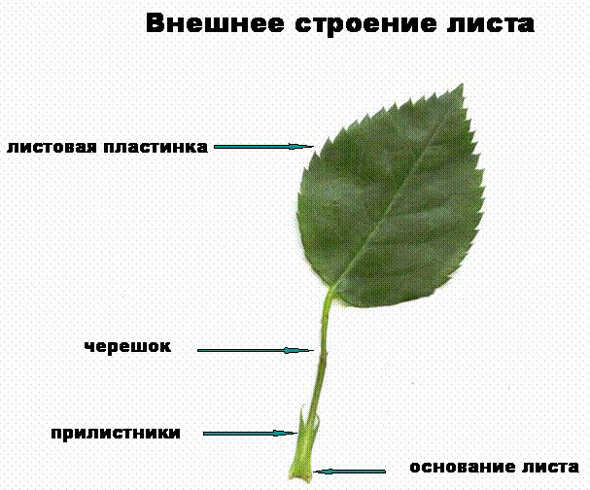

The internal structure of the leaf.
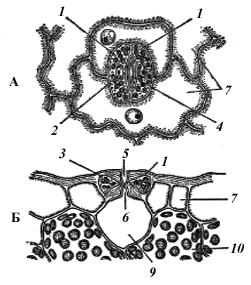
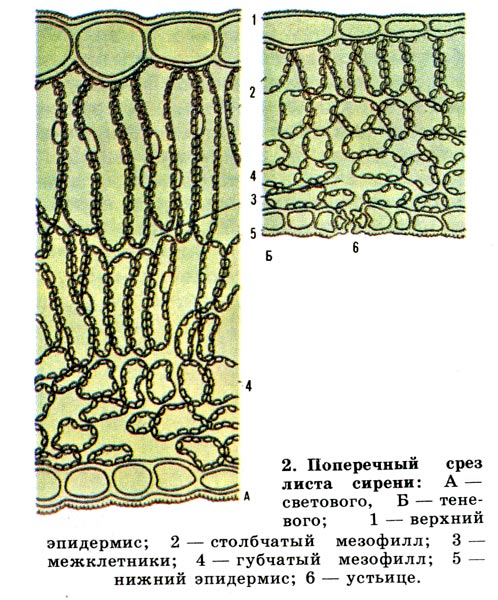
Outside the leaf is a skin of colorless cells, covered with a waxy substance - the cuticle. Under the skin are cells of the columnar parenchyma (palisade tissue) containing chlorophyll. Deeper are the cells of the spongy parenchyma with intercellular spaces filled with air. In the parenchyma there are vessels of the conducting bundle. On the lower surface of the leaves, the skin has stomatal cells involved in the evaporation of water. Evaporation of water occurs to prevent overheating of the leaf through the stomata of the epidermis (skin). This process is called transpiration and provides a constant flow of water from the roots to the leaves. The rate of transpiration depends on air humidity, temperature, light, etc. Under the influence of these factors, the turgor of the guard cells of the stomata changes, they close or close, delaying or enhancing the evaporation of water and gas exchange. In the process of gas exchange, oxygen enters the cells for respiration or is released into the atmosphere during photosynthesis. 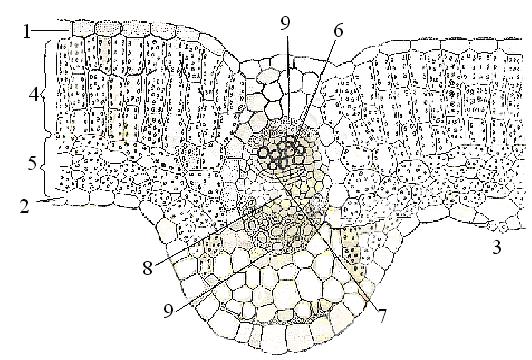
Cellular structure of the leaf
Part of a leaf | cells | fabrics | functions |
leaf skin (epidermis) | Cells are transparent, closely adjacent to each other The stomatal apparatus consists of: A) paired bean-shaped guard cells B) stomatal gap between them | coverslip | Physical protection Bacteria and drying protection Lets the sunlight through Evaporation Gas exchange |
leaf pulp | 1) columnar (palisade) tissue consists of green cells tightly adjacent to each other 2_ spongy tissue consists of loosely arranged cells, between which there are intercellular spaces | basic, photosynthetic | Photosynthesis Photosynthesis Gas exchange transpiration |
Leaf veins are vascular bundles | 1) Vessels are dead cells 2) Sieve tubes are living cells with sieve-like holes. 3) Fibers are dead elongated cells with sharp ends, with lignified shells. | Conductive Conductive mechanical | Conduct water and minerals from bottom to top Carry organic matter from top to bottom Give the sheet flexibility and strength, elasticity |
Leaf modifications:
antennae - serve to secure the stem in a vertical position; needles (in a cactus) play a protective role;
scales - small leaves that have lost their photosynthetic function;
trapping apparatus - the leaves are equipped with columnar glands that secrete mucus, which is used to capture small insects that have fallen on the leaf.
spines