Difficult oil of the Tyumen suite. Characteristics of the Yemegovskoye field on the map
Development of oil fields. Krosnoleninskoye deposit.
Basic design solutions for the development of the Krasnoleninskoye field.
At the first stage of the development of the Em-Egovskaya field, the commercial oil and gas potential was associated with the weathering crust of the basement, deposits of the Tyumen and Vikulov suites. The main object of exploitation was the deposits of the Tyumen suite (YuK2 - 9), the Vikulov suite (VK), and the weathering crust (KV), due to poor knowledge, were not considered in the first design documents.
In 1978, the Siberian Research Institute (SibNIINP) prepared a new project document for the development of the field "Principal scheme of the pilot industrial operation of the Krasnoleninsky oil and gas region." Where, at that time, with poor knowledge of the deposits, the submitted work of the Central Commission for the Development of Deposits (CCD) was not accepted. On its basis, from the standpoint of additional study of geological and production statistics of productive strata in the Yem-Egovskaya area of the field, a pilot work was determined with the opening of 270 wells using the areal inverted 9th development system, area 450 * 450 m (TsKR protocol No. 750 dated November 28, 1978).
During the development of exploratory wells in the area, flow rates from 8 to 155 tons per day were obtained.
Subsequently, 4 project documents for the development of the field were approved (1982, 1989, 1990-1991 and 1996);
1. Technological scheme of the ODP Em - Egovskoye and Palyanovskoye deposits (TsKR protocol No. 9712 dated April 21, 1982);
2. Technological scheme of the pilot project Em - Egovskoy and Kamennaya areas of the Krasnoleninskoye field (compiled in 1989) (Minutes of the Central Committee for the Development of the Russian Federation No. 9321 dated 07.11.1990);
3. Draft OPR Em - Yegovskaya and Kamennaya squares (drawn up in 1990) (Minutes of the Central Committee of the Kyrgyz Republic No. 4421 dated 31.03.1991). Technological indicators of experimental - industrial development of Yem - Yegovskaya and Kamennaya areas (compiled in 1991).
4. Supplement to the TECHNICAL SCHEME Em - Egovskaya and Palyanovskaya areas (TsKRMPR protocol No. 22121 dated 11/21/1997). SibNIINP for the development of the Abalak Formation, only one project document was drawn up in 1997. Currently, the development of the Abalak Formation is carried out on the basis of the "Addendum to the TECHNICAL SCHEME of the development of 1996". I will give a brief description of this document.
Supplement to the TECHSCHEME of the Yem-Egovskaya and Palyanovskaya areas (Abalak suite, 1996).
The last design document for the formation YUK1-2 of the Em-Egovskaya area is "Addition to the TECHNICAL SCHEME for the development of the Em-Egovskaya and Palyanovskaya area (Abalak suite)", approved by the Central Committee of the Republic of Kazakhstan (TsKRMPR) (protocol No. 2212 dated 21.04.1996).
The need to draw up a project document is caused by the actual commissioning of a new object into commercial development - the Abalak suite, which is characterized by high productivity and relatively insignificant reserves (the average oil-saturated thickness of the object is 1.6 m). The deposit was put into development in 1992, by joining drilled wells. object YuK1. Resources for Jurassic deposits were not submitted to the GKZ for evaluation.
In "Supplement to TECHSCHEME field development
Yem – Egovskoy and Palyanovskaya areas” calculations of technological indicators of the development of the Abalak suite were made for three development options, which differ in the number of wells and the volume of production drilling in the undrilled part of the area.
Taking into account the peculiarities of the geological structure of the deposit, the high zonal heterogeneity of the object, the placement of wells was carried out individually and in stages, starting from supposedly more productive zones. Wells are primarily located on seismic profiles and in fairly confidently traced zones of small-sized uplifts and high-gradient slopes, so well placement is uneven. Of the three options, the second development option was adopted, which provides for the following main solutions:
- allocation of one development object;
– development of deposits in natural mode;
– individual placement of wells on the basis of a complex of geophysical surveys (seismic and gravity exploration);
– drilling since 1997 of 30 appraisal wells. with core sampling and a full range of well logging, a total stock of 119 wells;
– experimental waterflooding, organization of transfer of 10 wells. from prey;
– Hydraulic fracturing in low-permeability intervals.
Jurassic deposits reserves
Yem-Egovskaya area, listed on the balance sheet of the Russian Federation
Retinue | Balance reserves, million tons | Recoverable reserves, million tons | ||
A, B, C 1 | From 2 | A, B, C 1 | From 2 |
|
Bazhenovskaya (UK 0) | 54.9 | 1 | 10.9 |
|
Abalakskaya (UK 1) | 13.6 | 14 | 3.4 | |
Tyumenskaya (SK 2 - 9) | 327.6 | 283.6 | 122.1 | 57.9 |
| Total: | 343.7 | 352.5 | 126.5 | 69.8 |
- the design level of oil production - 405.5 thousand tons (1996);
– cumulative oil production over 10 years – 2178.8 thousand tons; for 20 years - 2491 thousand tons.
Main technological development indicators
One of the more highly productive is the YuK reservoir (first) of the YuK development facility, the initial geological oil reserves of which were not approved by the State Reserves Committee of the Russian Federation. As of 01.01.2002, the State balance lists 27.4 (million tons of oil) classified under C1 category, which is about 8.5 percent of the oil reserves of all deposits of the Jurassic horizon. Category C2 reserves in the reservoir amounted to 66.4 million tons or 19.4 percent. The distribution of initial recoverable oil reserves by categories of reserves in the YuK1 reservoir was: Category C1 = 6.9 million tons of oil or 5.9%, category C2 = 5.4 or 8.9%.
Table
Oil reserves as of January 1, 2002 (million tons)
On the balance sheet of the RHF Balance sheet АВС1
Since the beginning of development on 01.01.2003, 5017.6 thousand tons of oil or 93.1% of the production from the YuK object has been produced from the YuK1 reservoir. Recovery from initial recoverable category C1 reserves amounted to 72.7%. The current CIN is 0.813. Oil production in 2002 amounted to 99.7 thousand tons or 86.5% of the production from the YuK facility. Liquid production - 107.2 thousand tons. Oil flow rate - 31.1 t/day, liquid - 33.4 t/day. Water cut - 7.0%. Production well stock - 37, active wells - 10. Injection well stock - 3, active wells - 3. The reservoir is developed in natural mode.
Test injection of water was carried out in 1995 in the amount of 5.9 thousand m3, in 2001 in the amount of 61.9 thousand m3 and in 2002 - 186.6 thousand m3.
Comparison of projected and actual levels of oil production in the Abalak suite
Well stock status
The balance well stock of the YuK1 formation is 94 units, of which 87 are in the production fund, incl. - 10 - active, 27 - inactive, 46 - in conservation, 4 - in the piezometer; in the injection fund - 5, incl. 3 - active, 2 - in conservation; 2 - others.
As of 01.01.2003, 77 production wells were inactive, mothballed and piezometers, of which 49 were in production (Fig. 3.2.1, Fig. 3.2.2).
Cumulative oil production per well in this category is 66 thousand tons. The cumulative recovery of the non-performing fund is 3234.4 thousand tons or 64.5% of the cumulative oil production from the reservoir.
Most of the non-operating well stock is characterized by low water cut (93.9% of the shut-off well stock worked with water cut from 0 to 20%), 4.1% of the idle well stock worked with water cut from 20 to 50%, 2% of the shut-off well fund worked with water cut from 50 to 90%.
The operating well stock of the facility is characterized as high-yielding oil and low water cut.
The average oil flow rate of the wells of the operating fund is 31.1 tons/day, the water cut is 7%.
Characteristics of non-performing production well stock
The average fluid flow rate for the wells of the operating stock is 33.4 t/day.
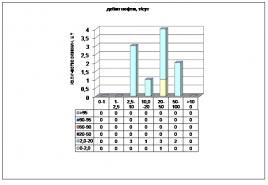
The distribution of wells by fluid flow rate is as follows (Figure 3.2.4):
— from 5 to 10 t/day – 30% of the stock (3 wells);
- from 10 to 20 tons / day - no;
— from 20 to 50 tons/day – 50% of the stock (5 wells);
— from 50 to 100 tons/day – 10% of the fund (1 well);
— from 100 to 150 tons/day – 10% of the fund (1 well).
Distribution of wells by water cut:
— less than 2% - 10% of the fund (1 well);
- from 2% to 20% - 90% of the fund (9 wells).
The utilization factor for the production fund is 0.27, for the injection fund – 1.0.
Application of EOR methods
Geological and technological activities in the YuK1 reservoir, performed in 2002, ensured an increase in oil production in the amount of 17.1 thousand tons (17.1% of annual production) due to:
— optimization of downhole equipment operation (5 wells – operations) – 14.8 thousand tons;
— other well interventions (1 well – operation) –2.3 thousand tons.
decline oil production
in 2003 is explained by the absence of geological and technical measures. As a result, the average oil flow rate of producing wells will be 30.2 tons/day, instead of 31.1 tons/day in 2002; the planned liquid flow rate is 35.5 t/day (in 2002 - 33.4 t/day).
The production well stock will be 37 units, the operating well stock at the end of the year will be 10. The well stock will not change as compared to 2002. The average annual water cut will be 10% (in 2002 - 7.0%).
Energy state deposits
For the YuK1 reservoir, the reservoir pressure in the production zone is 12.6 MPa. Compared to the initial (26.7 MPa), the pressure decreased by 13.8 MPa. The YuK1 reservoir is being developed in natural mode, in accordance with the decision of the project document approved by the CCR. The wells operating the YuK1 facility, in which there is a significant decrease in reservoir pressure, are put into conservation. On the object it is necessary to carry out experimental - industrial work to find a technology for restoring and maintaining reservoir pressure.
Since the beginning of development, 61.876 thousand tons of water have been injected into the reservoirs, fluid withdrawal is compensated by 2.85%, the current compensation is 103.7%. Development of oil fields.
Administratively, the Yem-Yogovskaya area is located on the territory of the Oktyabrsky district of the Khanty-Mansiysk Autonomous Okrug of the Tyumen region.
The deposit is located on the left bank of the Ob River, which, bending around its area in a knee-shaped channel, flows in the northern, north-western directions. It should be immediately noted that this left-bank area is gentle, there is a vast floodplain area, the width of which is 15-20 km (in the area of the deposit). The floodplain adjoins the field in the area of the Palyanovskaya area. In connection with the noted factor, the area of the deposit can be divided into two sections in geomorphological terms. Palyanovskaya area (eastern section) has absolute relief marks from + 25 to 40 m., Em-Yogovskaya area (western section) is more elevated, there is a greater fluctuation in absolute terrain marks from + 40 to 170 m.
In general, the territory of the deposit is a hilly-ridged plain with deep valley-ravine erosive systems. There is a general uplift of relief forms of the terrain in the western direction.
The hydrographic network of the deposit area is represented by a significant number of rivers and small streams. In the southern part (practically along its southern border) of the deposit, the Tal River flows in a wide direction with numerous channels, the largest of them, the left-bank tributary Talovy, is one of the sources of the river and originates from the deposit area, flowing in a southerly direction. In the area of well 15, the Tal River flows into the Em-Egan River.
The Em-Egan River flows directly through the territory of the deposit (Em-Egovskaya area), flows in a latitudinal, south-eastern direction, and with its tributaries covers almost the entire area of the Em-Egovskaya area. The largest of the tributaries, the Small Yem-Egan River is the main source of the river.
In the northern part of the Yem-Egovskaya area, the Potymets River flows and originates. It also flows in a latitudinal direction, but in the area of wells 14 and 162, it abruptly changes its course to the north, and there it flows into the Hugot River.
As already noted, the Ob River flows in the eastern part of the area with numerous tributaries and channels, of which the largest channel, Endyrskaya, flows almost along the eastern boundary of the deposit in a northerly direction.
Lakes are developed throughout the area, they are confined mainly to floodplain and swampy areas of the area. Of the largest, one can note such as Kholodnoye (2 * 1 km.), Located in the central part of the field. Lake Big Em-Ekhovskoe (4 * 4 km.) and Small Em-Ekhovskoe (2.5 * 3 km.), Located in the southern part of the area under consideration. A little to the east of them is Lake Bolshoi Sor.
Wetlands of the area are developed mainly in the upper reaches of the rivers and in the floodplain part of the left bank of the Ob River. The swamps are impassable and impassable. As a rule, they abound in a significant number of small and insignificant lakes.
The distance from the eastern borders of the area to the Ob River is 15-20 km.
The Em-Egovskoye deposit is located in a forest zone, within which the vegetation is represented mainly by pine and cedar-spruce forests.
The wetlands are dominated by mixed forest. Coniferous tree species are developed within the swamp massifs and floodplain sections of the Ob River, on elevated areas of the terrain, hills, which are called "Tracts".
The climate of the region is sharply continental with long cold winters and short, fairly warm summers. The average annual temperature is minus 1.8 0C. The average temperature of the coldest month, January, is minus 25 0С (with a minimum decrease to -35 0С - 40 0С), and the average temperature in July is + 15 0С (with a maximum of up to + 30 0С).
The average annual rainfall ranges from 450 to 500 mm. Of which most of them are in the spring-autumn periods. The thickness of the snow cover averages 0.8-1.0 m, reaching 1.5 m in low areas.
Freezing on the rivers begins in October, and their opening occurs at the end of April, at the beginning of May.
The area under consideration is practically uninhabited. There are no settlements directly on the deposit area. The nearest settlement, located in the southeastern part, is the village of Palyanovo, lying at the mouth of the Endyr River, on the southern shore of Lake Bolshoi Sor.
In the northern part of the field (10-15 km., to the north of its boundaries) are located the settlements of Sosnovy and Leafy. Larger settlements are located on the Ob River - Krasnoleninsky, Urmanny, Keushki, Sosnovo and others.
Soils in the area of work are podzolic-alluvial-gley, peat soils are developed in swampy areas of the area. Various types of alluvium and sand-gravel mixture are developed in river valleys and floodplain terraces.
The studied Em-Yogovsky license area (LU), which is part of the Krasnoleninskoye oil and gas condensate field, is administratively located in the Oktyabrsky district of the Khanty-Mansiysk Autonomous Okrug (KhMAO) of the Tyumen region. The nearest large settlement is the city of Nyagan (Figure 1).
Brief information about the geographic and economic conditions of the study area is given in Table 1.
The exploratory drilling project for the Yem-Yogovskaya area was drawn up in 1970, and exploratory drilling began in 1971. Within the area, industrial oil was obtained in exploratory well 2d in 1971 from Jurassic deposits.
History of field development
field formation well development
In 1953, the West Siberian Aeromagnetic Expedition carried out magnetic prospecting on a scale of 1:1,000,000. Based on its results, zones of predominance of positive and negative magnetic fields were identified.
In 1955, the Khanty-Mansiysk party 37/35 carried out a magnetic survey at a scale of 1:200,000, and local positive and negative magnetic anomalies were identified against the background of regional fields.
Table 1 - Geographical and economic conditions
|
Name |
Geographical and economic conditions |
|
|
Information about the relief, swampiness, degree of dissection, seismicity of the study area |
The Krasnoleninsky oil and gas region is located in the western part of the West Siberian Lowland on the left bank of the Ob River. Swampiness 30-35%. The dissection of the relief is strong with a.o. from 24 to 208 m. There is no seismicity. |
|
|
Characteristics of the hydraulic network and sources of drinking and technical water, indicating the distance from them to the object of study |
The hydrographic network is represented by the rivers Endyr, Seoul and the Endyr channel and their numerous tributaries. During the flood period, navigation is possible only along the river. Endyr at 4050 km from the mouth. At the mouth of the river Endyr is a large lake Bolshoi Sor, also navigable in high water. Swampiness is widely developed in the southeastern and southern parts. |
|
|
Average annual and extreme air temperatures and precipitation |
The average annual temperature is -1.8 0С, the average temperature in January is -25 0С, and in July +15 0С. Extreme temperatures from +30 0С to -52 0С. The average annual rainfall is 450-500 mm, of which 70% falls in April-October |
|
|
Prevailing wind direction and strength |
Average wind speed - 4.4 m/s, prevailing direction - southwest, west |
|
|
Snow cover thickness and distribution |
The snow cover is 0.7 m, reaches 1.5 m in lower areas and lies for 180 days |
|
|
Brief description of the flora and fauna |
The Yem-Yogovskaya area is located in the forest zone, where the vegetation is represented mainly by spruce-cedar and pine forests. The wetlands are dominated by mixed forest. The animal world is rich and varied. There are ermines, elks, foxes, deer, wolves, bears, squirrels, hares, sable. Muskrats and otters are found in reservoirs. In summer, there are many waterfowl on rivers and lakes. From game birds: partridges, ducks, capercaillie. There are a lot of fish in the rivers, mostly non-water species. |
|
|
Geocryological conditions |
The area belongs to the territories where permafrost rocks are localized at depths of more than 100-150 m. |
|
|
Information about settlements, distances to them; on the composition of the population; about the leading sectors of the national economy |
There are no settlements in the LU region. The city of Nyagan is located 110 km from the square. The population density is low, the indigenous population is Khanty, Mansi is engaged in fishing and hunting. Oil and gas production occupies a leading place in the region's economy. |
|
|
Operating and under construction oil and gas pipelines |
Interfield oil pipeline DNS-CTP Em-Yogovskoye - CPS Yuzhny 25 km, main oil pipeline Krasnoleninsky-Shaim |
Figure 1 - Overview map of the Krasnoleninskoye oil and gas condensate field
In 1956-1957, the gravimetric parties of the Khanty-Mansiysk oil exploration expedition, based on the results of gravity exploration, compiled a scheme of tectonic zoning of the basement, and the Krasnoleninsky dome was identified for the first time.
In 1957-1961, the joint ventures 14/57-58, 7/58, 3/59, 3/60, 15/60-61 of the TTSU expedition carried out seismic sounding (SOM) on a scale of 1: 500,000. A vast territory of the river basin was studied. Ob, including the clarified tectonic structure of the Krasnoleninsk zone, a structural map was built along the bottoms of the platform Mesozoic.
The Em-Yogovskoye local uplift was identified based on the results of seismic work sp 09/60-61 in 1961 (MOV), on a scale of 1:100,000. carried out by joint venture 19 / 69-70 in 1970.
In 1961-1962 sp 20/61-62, a seismic survey (SEM) was carried out at a scale of 1:100,000, as a result, the Em-Yogovskoye uplift was detailed and prepared for drilling.
Areal seismic surveys (MOV, MOGT-20) at a scale of 1:50,000, 1:100,000 within the Yem-Yogovskaya area were carried out in the period from 1970 to 1983. Based on the results of these works, structural maps were compiled for reflecting horizons A, B, M, M1 (K) and G, local uplifts were prepared for deep drilling.
During the entire time, regional seismic surveys were also carried out, the purpose of which was to study the relief of the basement. As a result of the work, numerous faults, areas of local inflections, and zones promising for the search for structural-stratigraphic traps have been identified.
Since 1989, detailed seismic surveys of CDP-20 at a scale of 1:25,000 sp 13/89-90 PGO "Tyumenneftegeofizika" have been carried out on the Yem-Yogovskaya area, including using the CDP-30 method.
JSC "Sibneftegeofizika" in 1999 carried out detailed seismic surveys of MOGT-20 with a density of 2-2.5 km/km2, in the northern part of the central dome of the Yem-Yogovskaya area. In 2001, a reinterpretation of the work performed by MOGT-30 in 1989-91 was carried out. sp 13 on Malo Em-Yogovskaya Square. As a result, the geological structure of the pre-Jurassic formations, the Jurassic and Lower Cretaceous parts of the section was refined along reflecting horizons
A, T2, T1, T, P, B, M, M1, M11, D. The block structure of the work area was established. The zones of development of the weathering crust and the Triassic complex were identified, the structure of deposits of the Tyumen formations was detailed, the proposed zones of the development of fractured reservoirs in the deposits of the Bazhenov and Abalak formations were mapped, and the contours of the oil-bearing capacity of the Vikulovskaya deposit were refined.
In 2007-2008 CDP-30 works were carried out in the southwestern part of the license area (Figure 2).

Figure 2 - Scheme of study by seismic surveys of the Yem-Yogovsky license area
To study the velocity characteristics of the section, to clarify the stratification of the reflecting horizons identified in it, seismic logging and work using the VSP method were carried out. In the area, such studies were carried out in wells: 30034g, 30042g, 2014, 30025g, 1g, 586g.
In the Khanty-Mansiysk Autonomous Okrug, in the vicinity of the city of Nyagan, speaking the language of oilmen, there is the most promising area of the Tyumen suite - Em-Egovskaya area. Almost half of all reserves of the Tyumen suite are concentrated here - this is 170 million tons of hydrocarbons. The deposit has been developed since the 80s of the 20th century, but negligible amount of black gold was raised from these deposits - only 5.5 million tons.
Hard-to-recover reserves of the Tyumen suite
The undeveloped reserves of the Tyumen suite are classified as hard-to-recover reserves. Such reserves are concentrated in complex geological conditions, characterized by very low permeability and productivity.
Until now, all activity has been directed to the development of traditional, so-called "light reserves" - this is oil, which was literally "on the surface". Traditional technologies turned out to be ineffective, but new methods and incentives for their development make it possible to approach hard-to-recover reserves.
To extract TRIZ, wells are drilled horizontally. First, the drilling tool goes under the earth's surface to a depth of more than 2,000 kilometers, and then it starts moving parallel to the horizon or with a small angle of inclination.
The Yem-Egovskaya area was chosen for technology testing and preparation for further drilling, as here the most successful structure of reserves and the use of this technology is possible with maximum efficiency.
New technologies, of course, require the use of other techniques, equipment, materials and high costs. The amendment to the tax code on the application of differentiated coefficients to the production tax, that is, benefits, has become a powerful incentive for the development of TRIZs. The intensification of work at TRIZ made it possible to produce an additional 370 thousand tons of oil, and in the future the account will go to millions of tons.
40% TRIZ
In total, hundreds of millions of tons of oil remain in reserve at the Krasnoleninskoye field. Not only in the Yem-Yegovsky area, but also in the Talinsky and Kamenny - these are the sections of the Tyumen Formation, where 40% of the reserves are classified as hard-to-recover.
116 bush (literal name) - many wells from one site. There are 16 of them here and all of them are already working on the TRIZ technology. Average initial debit, i.e. the average amount of oil produced per day from one such well is 60 tons. Before the advent of new technologies, the debit of oil was a multiple lower.
Bush 177-A will go down in history not only for the Nyagan oilmen, but also for the entire oil industry of the country. Here, for the first time, they began to apply the technology of horizontal drilling and for the first time extracted hard-to-recover oil reserves.
Bush 240 is still at the very beginning of development. Geologists have already decided that all of it will be developed by horizontal wells with multi-stage hydraulic fracturing. The first well is currently being drilled, which will take 40 days. This is more than the due date, since the well is the first, the oil companies need to study the section of the reservoir.
One pad can be developed for years: while one well is working, others can only plan.
The length of horizontal wells in the Em-Yegovsky area varies from 400 to 1000 meters. Such a well makes it possible to cover the entire large section of oil-bearing capacity and to include all those dissected and discontinuous reservoirs into the overall effective development.
After a well is drilled, the oil does not start to spurt, as it may seem, it needs help to "come out" from the bowels. To do this, in the horizontal section of wells, the technology of multi-stage hydraulic fracturing or multi-stage hydraulic fracturing is used.
Pipes are lowered into the well, through which up to 100 tons of a special mixture of proppant and gel are pumped in a few minutes at a pressure of about 300 atm. A break occurs in the reservoir, and a network of very thin cracks is formed, only a few millimeters wide, through which oil and gas enter the well.

The fracturing mix consists of proppant, gel, water and chemical binders. The proppant consists of the smallest granules that clog the crack and prevent it from narrowing, but at the same time perfectly pass oil. This mixture is pumped into the well to a depth of 2-3 km. From now on, all wells at Yem-Ega will be developed using multi-stage hydraulic fracturing technology.
Due to the lack of technology, hard-to-recover reserves have long faded into the background. Today it is a second wind for fields such as Em-Ega. Oil will be produced here for several more decades.