Topic 2.1. History of the study of the cell. Cell theory.
1. Give definitions of concepts.
Cell- an elementary unit of the structure and life of all organisms, having its own metabolism, capable of independent existence, self-reproduction and development.
Organoid- a permanent specialized structure in the cells of living organisms that performs certain functions.
Cytology- a branch of biology that studies living cells, their organelles, their structure, functioning, the processes of cell reproduction, aging and death.
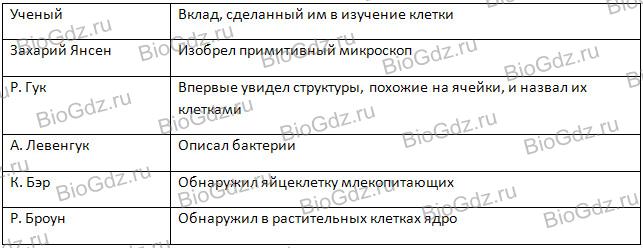
2. Distribute the names of scientists from the above list (the list is redundant) according to the corresponding columns of the table.
R. Brown, K. Baer, R. Virchow, K. Galen, K. Golgi, R. Hooke, C. Darwin, A. Leeuwenhoek, K. Linnaeus, G. Mendel, T. Schwann, M. Schleiden.
Scientists who contributed to the development of knowledge about the cell
3. Fill in the left column of the table.
HISTORY OF THE STUDY OF THE CELL
4. Specify the features common to all cells. Explain what properties of living matter make all cells have common features.
All cells are surrounded by a membrane, their genetic information is stored in genes, proteins are their main structural material and biocatalysts, they are synthesized on ribosomes, and ATP is used as a cell energy source. All cells are open systems. They are characterized by growth and development, reproduction and irritability.
5. What is the significance of the cell theory for biological science?
The cell theory made it possible to draw a conclusion about the similarity of the chemical composition of all cells, the general plan of their structure, which confirms the phylogenetic unity of the entire living world. Modern cytology, having absorbed the achievements of genetics, molecular biology, biochemistry, has turned into cell biology.
7. Fill in the missing terms.
Human erythrocytes have the shape of a biconcave disc.
The composition of the bone tissue includes large osteocytes with numerous processes. Blood leukocytes do not have a permanent shape. The cells of the nervous tissue, which have the ability to excitability and conductivity, are very diverse.
8. Cognitive task.
The first description of a cell was published in 1665. In 1675, unicellular organisms became known. The cell theory was formulated in 1839. Why does the date of the birth of cytology coincide with the time of the formulation of the cell theory, and not with the discovery of the cell?
Cytology is a branch of biology that studies organelles, their structure, functioning, processes of cell reproduction, aging and death in a cell. At the time of discovery of the cell, the cell wall was described. Further, the first cells were discovered, but their structure and functions were not known. Knowledge was not enough, they were analyzed by T. T. Schwann, M. Schleiden, and they created a cellular theory.
9. Choose the correct answer.
Test 1
The cellular structure has:
1) iceberg;
2) tulip petal;
3) hemoglobin protein;
4) a bar of soap.
Test 2
The authors of the cell theory are:
1) R. Hooke and A. Leeuwenhoek;
2) M. Schleiden and T. Schwann;
3) L. Pasteur and I. I. Mechnikov;
4) C. Darwin and A. Wallace.
Test 3
What position of the cell theory belongs to R. Virchow?
1) Cell - the elementary unit of the living;
2) every cell comes from another cell;
3) all cells are similar in their chemical composition;
4) a similar cellular structure of organisms is evidence of the common origin of all living things.
10. Explain the origin and general meaning of the word (term), based on the meaning of the roots that make it up.
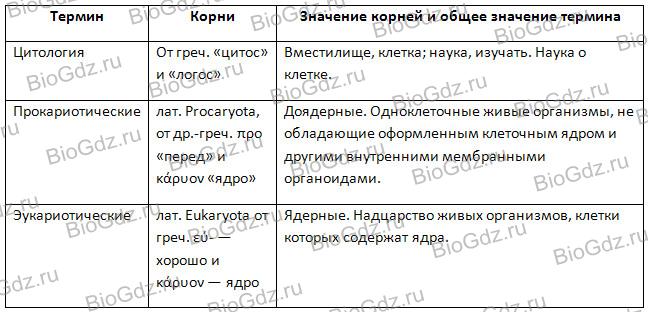
11. Choose a term and explain how its modern meaning corresponds to the original meaning of its roots.
Cytology- originally meant the study of the structure and functions of the cell. Later, cytology turned into an extensive branch of biology, became more practical and applied, but the essence of the term remained the same - the study of the cell and its functions.
12. Formulate and write down the main ideas of § 2.1.
People learned about the existence of cells after the invention of the microscope. The first primitive microscope was invented by Z. Jansen.
R. Hooke discovered cork cells.
A. Van Leeuwenhoek, having improved the microscope, observed living cells and described bacteria.
K. Baer discovered the egg of mammals.
The nucleus was discovered in plant cells by R. Brown.
M. Schleiden and T. Schwann were the first to formulate the cell theory. “All organisms consist of the simplest particles - cells, and each cell is an independent whole. In the body, cells act together, forming a harmonious unity.
R. Virchow substantiated that all cells are formed from other cells by cell division.
By the end of the XIX century. the structural components of cells and the process of their division were discovered and studied. The emergence of cytology.
The main provisions of modern cell theory:
a cell is a structural and functional unit of all living organisms, as well as a unit of development;
cells have a membrane structure;
nucleus - the main part of the eukaryotic cell;
cells reproduce only by division;
The cellular structure of organisms indicates that plants and animals have a common origin.