Decomposition of potassium permanganate. Properties of salts of manganic acid
Redox processes underlie the most important phenomena of animate and inanimate nature: combustion, decomposition of complex substances, synthesis of organic compounds. Potassium permanganate, the properties of which we will study in our article, refers to those used in laboratory and industrial conditions. Its oxidizing ability depends on the oxidation state of the atom, which changes during the reaction. Let us consider this on specific examples occurring with the participation of KMnO 4 molecules.
Characterization of the substance
The compound we are considering (potassium permanganate) is one of the most commonly used substances in industry - manganese compounds. The salt is represented by crystals in the form of regular prisms of dark purple color. It dissolves well in water and forms a raspberry-colored solution with excellent bactericidal properties. Therefore, the substance has found wide application both in medicine and in everyday life as a bactericidal agent. Like other heptavalent manganese compounds, salt is capable of oxidizing many organic and inorganic compounds. The decomposition of potassium permanganate is used in chemical laboratories to obtain small volumes of pure oxygen. The compound oxidizes sulfite acid to sulfate acid. In industry, KMnO 4 is used to separate gaseous chlorine from hydrochloric acid. It also oxidizes most organic substances, is capable of converting ferrous salts into the form of its trivalent compounds.
Experiments with potassium permanganate
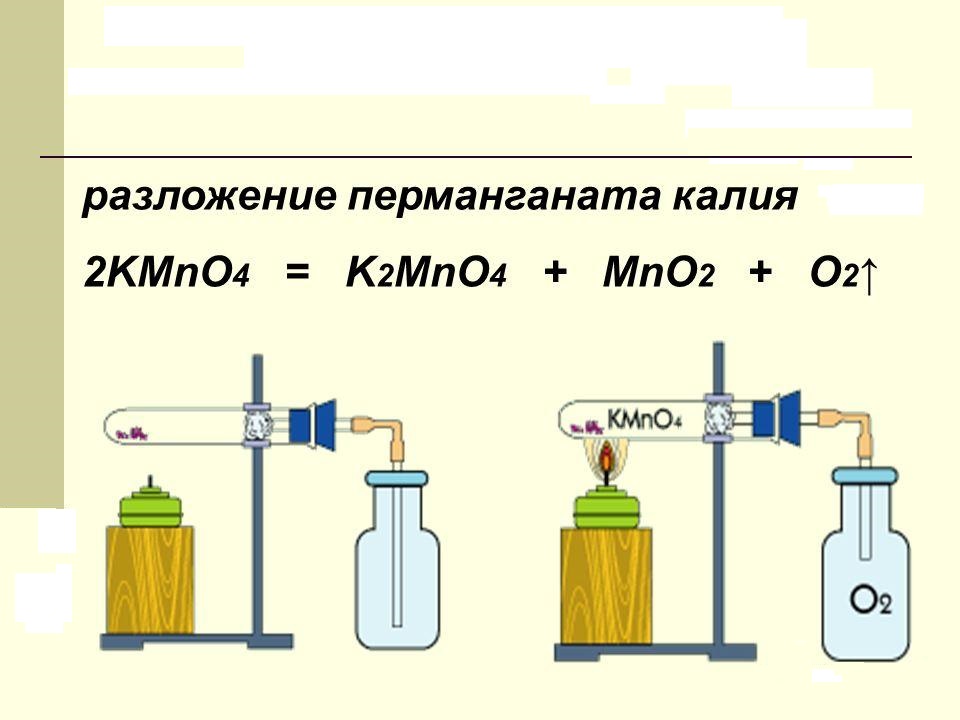
A substance called potassium permanganate in everyday life decomposes when heated. The reaction products contain free oxygen, manganese dioxide and a new salt - K 2 MnO 4. In the laboratory, this process is carried out to obtain pure oxygen. The chemical equation for the decomposition of potassium permanganate can be represented as follows:
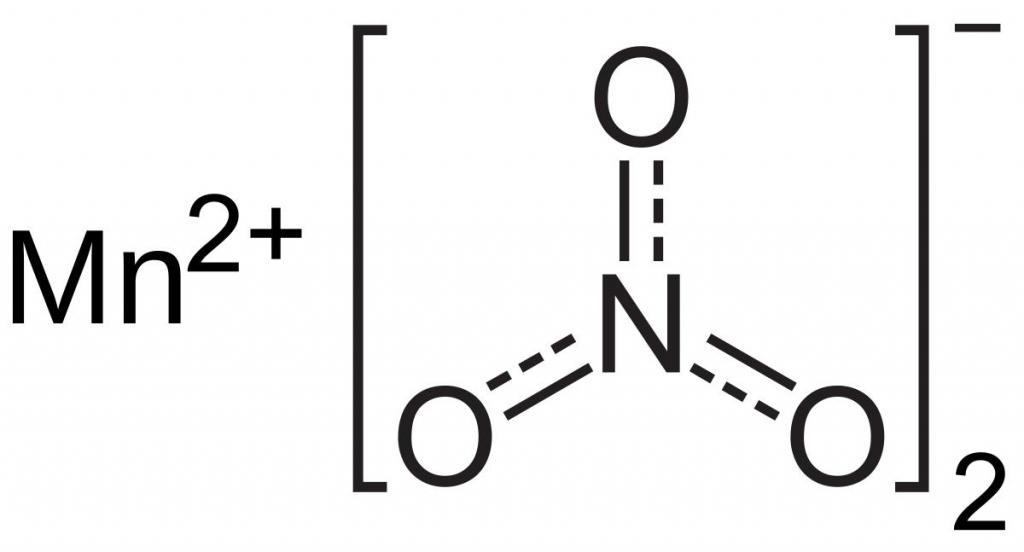
2KMnO 4 = K 2 MnO 4 + MnO 2 + O 2.
The dry substance, which is purple crystals in the form of regular prisms, is heated to a temperature of +200 ° C. The manganese cation in the salt has an oxidation state of +7. It decreases in the reaction products to values +6 and +4, respectively.
Ethylene oxidation
Gaseous hydrocarbons belonging to different classes of organic compounds have both single and multiple bonds between carbon atoms in their molecules. How to determine the presence of pi bonds underlying the unsaturated nature of an organic compound? For this, chemical experiments are carried out by passing the test substance (for example, ethene or acetylene) through violet. Its discoloration is observed, since the unsaturated bond is destroyed. The ethylene molecule is oxidized and is converted from an unsaturated hydrocarbon into a dihydric saturated alcohol - ethylene glycol. This reaction is qualitative for the presence of double or triple bonds.
Features of the chemical manifestations of KMnO4
If the oxidation states of the reactants and reaction products change, then an oxidation-reduction reaction occurs. It is based on the phenomenon of the movement of electrons from one atom to another. As in the case of the decomposition of potassium permanganate, and in other reactions, the substance exhibits pronounced properties of an oxidizing agent. For example, in an acidified solution of sodium sulfate and potassium permanganate, sodium, potassium and manganese sulfates are formed, as well as water:
5Na 2 SO 3 + 2KMnO 4 + 3H 2 SO 4 = 2MnSO 4 + 5Na 2 SO 4 + K 2 SO 4 + 3H 2 0.
In this case, the sulfur ion is a reducing agent, and manganese, which is part of the complex anion MnO 4 -, exhibits the properties of an oxidizing agent. It accepts five electrons, so its oxidation state decreases from +7 to +2.
Influence of the environment on the course of a chemical reaction
Depending on the concentration of hydrogen ions or hydroxyl groups, the acidic, alkaline or neutral nature of the solution in which the redox reaction takes place is distinguished. For example, with an excessive content of hydrogen cations, the manganese ion with an oxidation state of +7 in potassium permanganate lowers it to +2. In an alkaline environment, with a high concentration of hydroxyl groups, sodium sulfite, interacting with potassium permanganate, is oxidized to sulfate. The manganese ion with an oxidation state of +7 passes into a cation with a charge of +6, which is in the composition of K 2 MnO 4, the solution of which has a green color. In a neutral environment, sodium sulfite and potassium permanganate react with each other, and manganese dioxide is precipitated. The oxidation state of the manganese cation decreases from +7 to +4. The reaction products also contain sodium sulfate and alkali - sodium hydroxide.

The use of salts of manganic acid
Potassium permanganate when heated and other redox processes involving salts of manganic acid are often used in industry. For example, the oxidation of many organic compounds, the release of gaseous chlorine from hydrochloric acid, the conversion of ferrous salts to ferric. In agriculture, the KMnO 4 solution is used for pre-sowing treatment of seeds and soil, in medicine, it is used to treat the surface of wounds, disinfect inflamed mucous membranes of the nasal cavity, and use it to disinfect personal hygiene items.
In our article, we not only studied in detail the decomposition of potassium permanganate, but also examined its oxidizing properties and use in everyday life and industry.