"Quantity of heat. Specific heat
The change in internal energy by doing work is characterized by the amount of work, i.e. work is a measure of the change in internal energy in a given process. The change in the internal energy of a body during heat transfer is characterized by a quantity called the amount of heat v.
- this is a change in the internal energy of the body in the process of heat transfer without doing work. The amount of heat is indicated by the letter Q .
Work, internal energy and amount of heat are measured in the same units - joules ( J), like any kind of energy.
In thermal measurements, a special unit of energy, calorie ( feces) equal to the amount of heat required to heat 1 gram of water by 1 degree Celsius (more precisely, from 19.5 to 20.5 ° C). This unit, in particular, is currently used in calculating the consumption of heat (thermal energy) in apartment buildings. The mechanical equivalent of heat is empirically established - the ratio between calorie and joule: 1 cal = 4.2 J.
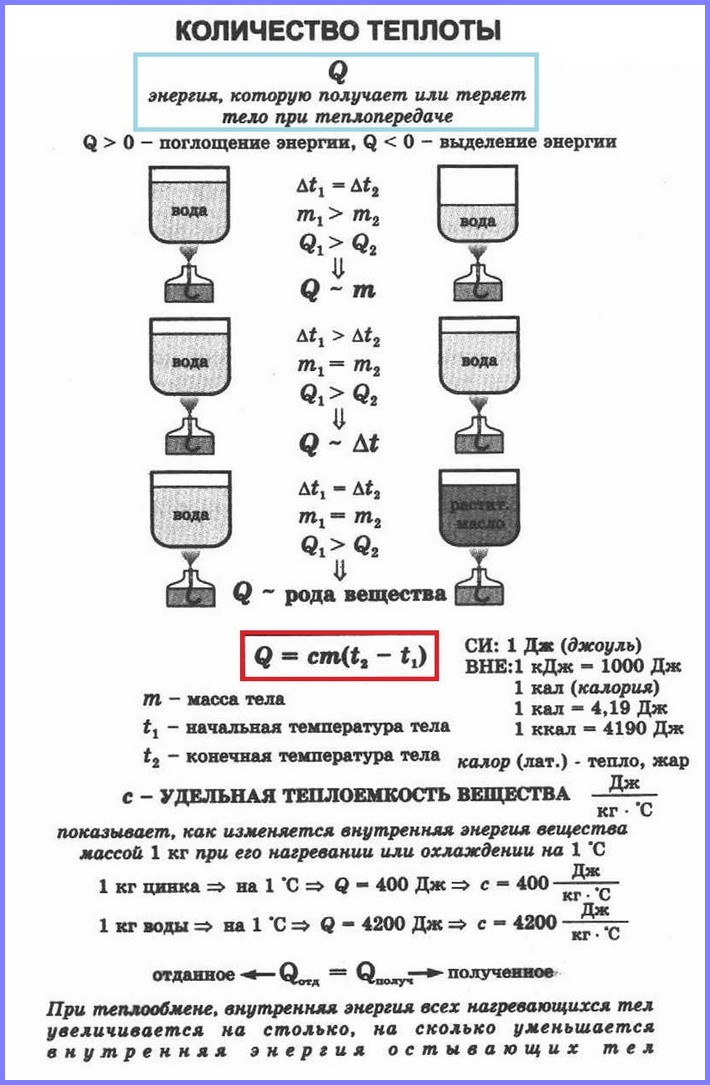
When transferring a certain amount of heat to a body without performing work, its internal energy increases, if the body gives off a certain amount of heat, then its internal energy decreases.
If you pour 100 g of water into two identical vessels, and 400 g of water in the other at the same temperature and put them on the same burners, then the water in the first vessel will boil earlier. Thus, the more body weight, the more heat it needs to heat up. It's the same with cooling.

The amount of heat required to heat a body also depends on the kind of substance from which this body is made. This dependence of the amount of heat required to heat the body on the kind of substance is characterized by a physical quantity called specific heat substances.
Is a physical quantity equal to the amount of heat that must be reported to 1 kg of a substance to heat it by 1 ° C (or by 1 K). The same amount of heat is given off by 1 kg of the substance when cooled by 1 ° C.
Specific heat is indicated by the letter with... The unit of specific heat is 1 J / kg ° С or 1 J / kg ° K.
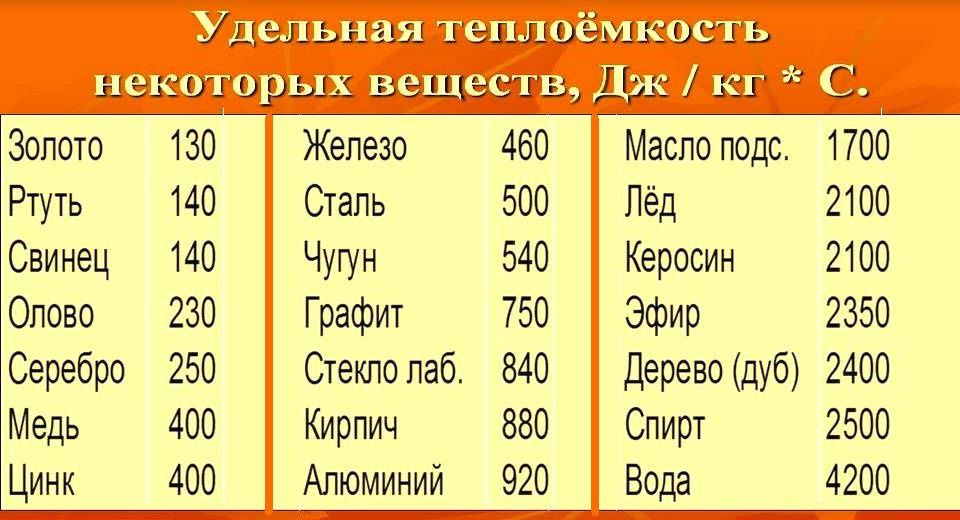
The values of the specific heat capacity of substances are determined experimentally. Liquids have a higher specific heat capacity than metals; water has the highest specific heat, gold has a very low specific heat.
Since the amount of heat is equal to the change in the internal energy of the body, we can say that the specific heat capacity shows how much the internal energy changes 1 kg substance when its temperature changes by 1 ° C... In particular, the internal energy of 1 kg of lead when it is heated by 1 ° C increases by 140 J, and when cooled, it decreases by 140 J.
Q required for heating a body with a mass m from temperature t 1 ° С to temperature t 2 ° С, is equal to the product of the specific heat capacity of the substance, body mass and the difference between the final and initial temperatures, i.e.Q = c ∙ m (t 2 - t 1)
The same formula is used to calculate the amount of heat that the body gives off during cooling. Only in this case, the final temperature should be subtracted from the initial temperature, i.e. subtract the lower from the higher temperature value.
This is a synopsis on the topic "Quantity of heat. Specific heat"... Choose further actions:
- Go to the next synopsis: