What low pressure is life-threatening numbers
High blood pressure is a symptom of various diseases. It does not always give painful sensations, and a person may not be aware of the presence of hypertension. At the same time, prolonged pressure often forms serious complications. No wonder he is called "the silent killer." Maintaining high blood pressure inside the vessels forms deadly pathologies, causing strokes and heart attacks.
In this article we will look at how high blood pressure is formed and why is it dangerous? Which of the complications have the most dire consequences? And why is it necessary to pay attention to pressure and measure its value periodically?
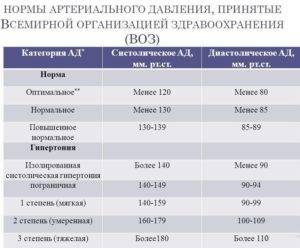
High pressure indicators
Normal pressure is considered to be 120/80 mm Hg. Art. This is an average rate valid for most average healthy people. Indicators are also considered normal if the figures exceed the average or do not reach them by 10-20 units. Therefore, the norm is blood pressure from 100/70 mm (for a person of small stature or thin build) and up to 140/90 mm (for a tall, large person).
Pressure is called high if its values exceed 140/90 mm Hg. Art. It is with these numbers that the countdown of pathology and the formation of complications begins.
High blood pressure can be slightly or very high. According to its indicators, three degrees of hypertension are distinguished - the so-called mild, moderate and severe. They differ not only in the value of blood pressure, but also in the consequences of the disease (complications) and the speed of their formation.
Hypertension is conventionally divided into the following stages:
- The first 140-160 / 90-100 mm - mild hypertension;
- The second is 160-180 / 100-110 mm - medium or moderate hypertension;
- The third is more than 180/110 mm - severe hypertension, the most dangerous increase in pressure.
Now let's turn to what changes occur in the body with an increase in pressure. Why is high blood pressure dangerous, and why are the highest numbers the most undesirable for a person?
What high blood pressure is considered dangerous?
A slight increase in pressure (up to 160 mm) forms a pathology for a very long time. Therefore, first-degree hypertension is not considered dangerous. It is not accompanied by pathological changes in the heart, blood vessels, brain, kidneys, and therefore doctors say that first-degree hypertension has no risks and is not accompanied by pathological changes in organs.
A moderate increase in pressure (up to 180 mm) forms internal pathologies for several years. So, due to stable blood pressure above 160 mm, hypertrophy of the left ventricle of the heart and narrowing of the retinal arteries (which causes visual impairment) are formed. Complications of moderately high blood pressure - on the face.
The third severe degree of hypertension, blood pressure above 180 mm Hg. Art. accompanied by a strong narrowing of the arteries and blood vessels, loss of their elasticity and rupture. Therefore, the main danger of the third stage is hemorrhage. Pressure above 180 is most dangerous. It often leads to rupture of blood vessels. What forms a heart attack in the heart muscle, and a stroke in the brain cells.
Doctors insist on the need to reduce blood pressure, the indicators of which even exceed 140/90. It must be understood that short-term jumps above 140 (for systolic) and 90 (for diastolic) do not bring tangible harm, except for unpleasant sensations.
Such jumps are possible with physical exertion, slight stress, changes in atmospheric pressure. But a long stay of the body in a state of hypertension is harmful. It forms a number of pathological processes and destructive changes in organs and tissues.
How blood pressure rises
Blood pressure forms the movement of blood through the vessels. It is created by the contractions of the heart muscle and the tone of the vascular walls. Thanks to pressure, all human organs are supplied with blood, oxygen, and nutrients.
An increase in pressure above normal occurs when the available blood flow weakens. Its speed and amount of blood become insufficient to fully supply the body with oxygen. And then the regulatory mechanisms increase blood pressure.
A pathological increase in pressure occurs if:
Thus, an increase in pressure occurs due to disturbances in the work of the circulatory or vascular systems. It is a prerequisite for survival. Increased pressure is necessary for the body to push through viscous blood, or to normalize the speed of blood flow through the vessels.
Due to the increase in pressure, the cells of the body continue to receive the necessary nutrition and oxygen. But those organs that work "for wear and tear", over time, they themselves lose their tone, elasticity, the ability to adequately respond to changes in the environment. This creates conditions for the development of further pathologies - the so-called complications.
What suffers primarily from a chronic increase in blood pressure in a person?
Target Organs
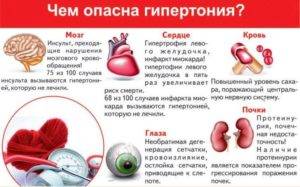 Those human organs that, with an increase in pressure, perform strenuous work and carry an additional load, suffer from hypertension in the first place. These include the human heart and blood vessels. They are called “target organs”, since it is they that form in them various pathologies.
Those human organs that, with an increase in pressure, perform strenuous work and carry an additional load, suffer from hypertension in the first place. These include the human heart and blood vessels. They are called “target organs”, since it is they that form in them various pathologies.
Also, the target organs include those organs, the state of which depends more on blood supply than others. These are the human brain and excretory organs - the kidneys. What happens in the cells of the heart, brain and kidneys with frequent high blood pressure?
Why is high blood pressure dangerous for the heart?
The heart is the main motor of the human body and the circulatory system. With increased pressure, it works more often and forms more powerful blood ejections. With prolonged overstrain of the heart muscles, the following cardiac pathologies are formed:
- Left ventricular hypertrophy (from forced contractions to push blood and create pressure). Expressed in thickening of the heart wall. This thickening requires an increased blood supply to the heart, which becomes impossible with the development of hypertension. This initiates cardiac arrhythmias, cardiac tissue necrosis, and myocardial infarction.
- Depletion of the tissue of the left ventricle of the heart - occurs due to constant stress and, as a result, lack of nutrition.
- Heart failure - is formed due to the fact that overstrain of the heart leads to insufficient rest, relaxation. Fatigue forms, which prevents the heart muscles from contracting fully (which is called chronic heart failure).
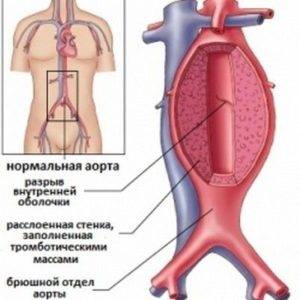 The blood vessels form the main bloodstream. With chronic high blood pressure, the vessels are tense, often spasmodic and covered with cholesterol plaques. Constant overstrain of the vascular walls does not allow them to relax. This leads to malnutrition and partial replacement of the muscle wall with connective tissue.
The blood vessels form the main bloodstream. With chronic high blood pressure, the vessels are tense, often spasmodic and covered with cholesterol plaques. Constant overstrain of the vascular walls does not allow them to relax. This leads to malnutrition and partial replacement of the muscle wall with connective tissue.
If the replacement of muscle walls with connective tissue occurs in the organs of vision, then vision gradually deteriorates until it is completely lost. If the processes occur in the limbs, then atherosclerosis of the vessels of the arms and legs is formed, the limbs become cold.
If pathological changes occur in the vessels of the brain, then there is a violation of cerebral circulation, constant headaches are formed, flashing of flies before the eyes, dizziness, sudden falls. But this is not a complete list of complications that form in the blood vessels of a person at high pressure.
The most dangerous complications of hypertension are stroke and heart attack. They accompany ruptures of thinned degraded vessels in the brain or heart. These complications cause necrosis (death) of brain and heart tissue.
They are dangerous with lethal outcome (death). This is why you shouldn't give a damn about constant high blood pressure. Even moderate moderate hypertension creates conditions for the degradation of the vascular walls. What makes it possible to develop a stroke or heart attack with a possible surge in pressure.
Why high blood pressure in humans is dangerous for the kidneys
Gradual vascular sclerosis causes a number of pathological changes in the kidneys. The most dangerous of them is a violation of the excretory function, in which toxins accumulate in the blood. This is due to the so-called microalbuminuria or protein seepage through the kidney filter. This pathology is formed with increased pressure. As a result, protein is detected in urine tests.
A small increase in pressure: why is it dangerous?
A sudden and sharp increase in pressure - by 20 or more units, brings a number of unpleasant sensations. The head hurts and dizzies, flies flicker in the eyes, the face turns red, there is a feeling of fullness in the head and eyes.
A sharp jump in blood pressure increases blood flow and makes the heart work faster. The pulse becomes more frequent and tachycardia appears. Why is sudden high blood pressure dangerous?
For a healthy person, a short-term increase in pressure even to high values is not dangerous. Its vessels will adequately respond to any increase, the elastic walls stretch and compensate for the accelerated blood flow.
Increased pressure is dangerous for those people whose vessels are spasmodic and sclerosed. In this case, they are not able to adequately respond - to stretch out and let the increased blood flow through. Which often leads to their breakup.
Small fluctuations in blood pressure do not have any consequences if they are short-lived. In this case, they do not have time to form pathological changes and are poorly felt by a person.
Small increases in pressure become painful when present. If a person's pressure stably exceeds the norm (more than 140/90 mm), then this creates conditions for the development of vascular pathology.
This also indicates a malfunction in the body, the accumulation of toxins, or constant stress. Which also requires attention and treatment.
Increased systolic and diastolic pressure: which is more dangerous?
 The first digit in the measurement of pressure indicates its value at the time of contraction of the heart muscle (when pushing blood through the vessels). It is called upper or systolic. The first figure shows the maximum pressure, its value is the most critical for a person.
The first digit in the measurement of pressure indicates its value at the time of contraction of the heart muscle (when pushing blood through the vessels). It is called upper or systolic. The first figure shows the maximum pressure, its value is the most critical for a person.
The second figure shows the so-called dystolytic or lower pressure, which is maintained by the walls of the vessels between the contractions of the heart. It is always 40-50 units lower than systolic.
In most cases of high blood pressure, both numbers are above normal. For example, 140/90 or 180/100 are indicators of high blood pressure of varying degrees.
However, there are situations in which the pressure does not rise correlatively, but mainly only the upper or only the lower figure. What is the danger of increasing individual BP figures?
High first digit: why is it dangerous?
The upper systolic pressure is determined by the state of the heart muscle, the frequency and strength of its contraction at the time of blood ejection. Doctors say that the upper pressure reflects the state of the myocardium, and they call it cardiac. High upper pressure with a normal low pressure indicates heart disease.
In addition, with a high upper pressure against the background of a normal low pressure, a large difference between the indicators is formed. In medicine, it is called pulse pressure.
 The lower diastolic pressure is determined by the state of the vessels. In the intervals between heartbeats (discharge of blood from the heart into the bloodstream), the tone of the vascular walls is maintained by the general pressure in the circulatory system. Basically, the lower pressure is formed by the peripheral arteries farthest from the heart muscle. These are the thinnest vessels and capillaries through which blood enters the tissues.
The lower diastolic pressure is determined by the state of the vessels. In the intervals between heartbeats (discharge of blood from the heart into the bloodstream), the tone of the vascular walls is maintained by the general pressure in the circulatory system. Basically, the lower pressure is formed by the peripheral arteries farthest from the heart muscle. These are the thinnest vessels and capillaries through which blood enters the tissues.
A high indicator of lower pressure can signal a poor state of blood vessels, their low elasticity, the presence of cholesterol deposits. It also forms after drinking alcohol, hypothermia, and stress.
Note: with hypothermia, prolonged exposure to the cold, blood circulation in the peripheral vessels is reduced - the limbs are freezing. This causes an increase in the lower pressure figure - the body is trying to restore blood circulation in the fingers and toes by increasing the vascular tone.
In addition, the lower pressure increases with an increase in blood volume, with the so-called saline hypertension (when a person's blood pressure rises due to the use of too many foods with salt preservatives).
Note: beer drinkers suffer from persistent increases in diastolic blood pressure. This drink causes fluid retention in the body and an increase in lower blood pressure. Therefore, men are more likely to suffer from increased lower pressure than women.
Why is high lower blood pressure dangerous? High diastolic pressure accompanies atherosclerosis and low vascular elasticity. Therefore, high rates of the second figure indicate a possible rupture of the vascular walls and internal hemorrhages.
In addition, an increase in the second digit of the measured pressure occurs with kidney disease. In renal pathology, this occurs due to the excretion of the renin substance by the kidneys, which increases the muscle tone of the vessels.
The lower pressure is called vascular and renal. The main danger of its increase is the absence of any painful symptoms in the initial stages of development.
progipertoniyu.ru
What determines the level of blood pressure?
Blood moving through the vessels puts pressure on their walls. The presence or absence of a generally accepted normal blood pressure indicator (120/80) is predetermined by several factors:
- the degree of vascular resistance;
- cardiac functionality;
- total blood volume.
Despite the fact that deviations from the standard values to the lower side are not considered by many at all a pathology, since all systems and organs are working as expected, the doctors have known for a long time what the dangerously low pressure in humans is.
What does blood pressure say?
In addition to the external manifestations of this condition in the form of general weakness of the body, shortness of breath, dizziness and loss of coordination, hypotension can cause more serious consequences. The first alarming signals received by the patient must necessarily serve as a reason for seeking advice from specialists. In addition, if the danger of low blood pressure has receded, which quite often lulls the vigilance of patients, this does not mean at all that a repetition is not expected. 
By itself, blood pressure is an indicator that can declare disturbances in the work of such vital organs as the lungs, heart, and circulatory system. This predetermines the need for regular pressure measurements, especially since its value is not static and constant. You can find out what the danger of low blood pressure in humans is by familiarizing yourself with the features of blood circulation.
Human systolic and diastolic blood pressure
As you know, when measuring the pressure of a patient, doctors draw conclusions about his condition by two values:
- Systolic pressure is the upper indicator showing the level of pressure during the ejection of blood into the aorta.
- Diastolic pressure - the lower indicator, fixes the moment of blood flow into the vena cava.
If the first criterion is able to determine the blood pressure during its transportation through the vessels from the heart to the rest of the vital organs, then the second indicates its value in the intervals between heart contractions. At the moment of short-term relaxation of the myocardium, blood pressure is measured.
What pressure is considered normal?
Probably everyone knows that 120/80 is the most common indicator that is considered the unconditional norm. Although recently, experts have begun to assert with greater confidence that the most comfortable blood pressure for a person is 115/75.  It is difficult to determine what critical low pressure is dangerous for a person, as well as to find out the norm for the same person. The fact is that blood pressure, at which the patient's well-being is satisfactory, is a purely individual value. It is almost impossible to establish with certainty that this particular indicator is optimal for a particular person.
It is difficult to determine what critical low pressure is dangerous for a person, as well as to find out the norm for the same person. The fact is that blood pressure, at which the patient's well-being is satisfactory, is a purely individual value. It is almost impossible to establish with certainty that this particular indicator is optimal for a particular person.
What is the characteristic of low pressure?
Meanwhile, BP 90/60 is considered by doctors around the world to be unambiguously low. Whether low blood pressure is dangerous for a person with such indicators depends largely on what he feels at this moment, what the symptoms are.
The most common manifestations of hypotension, in which the thought of pathology immediately arises, is considered:
- Regular sleepiness, lethargy, rapid fatigue. Any activity (physical, mental) leads to instant fatigue, after rest and a night's sleep, relief, as a rule, does not occur.
- Headaches (cephalalgia with low pressure often occupies the occipital and temporal lobes; the nature and intensity of the pain syndrome is similar to migraine: monotonous, pulsating or dull).
- Nausea, vomiting.
- Frequent dizziness, short-term loss of consciousness, impaired coordination of movements.
- Irritability, inattention, absent-mindedness.
Is low blood pressure dangerous in humans? This can be determined based on the above symptoms. Such signs of hypotension can cause great discomfort and suffering to the patient. How can you avoid this? It is possible to prevent the development of pathology, especially if you are not at risk. But even if this is not the case, it is still possible to help yourself. The reasons why the systolic or diastolic blood count may fall are presented below.
Causes of low diastolic blood pressure
With low diastolic pressure, general signs of hypotension appear in the form of impotence, dizziness and nausea. The ideal indicator is considered to be one that is less than systolic by 30-40 mm Hg. Art. Hence the establishment of the widespread norm of 120/80 with a difference of 40 mm Hg. Art. The diastolic value is considered low if there is a difference of more than 50 units between it and the systolic value. 
Many patients do not immediately detect low blood pressure, regularly suffering from symptoms of weakness. Even fewer people, having discovered a disease in themselves, go to the doctor with this problem, since not everyone knows about the danger of a person's low lower pressure, especially if such a deviation does not cause significant troubles and inconveniences. The well-being of a person with low lower pressure depends on the causal factors that provoked changes in blood circulation. The most common are:
- heart failure;
- renal failure or chronic adrenal disease;
- allergic reactions;
- pain shock;
- disorders of the thyroid gland.
How to prevent hypotension?
Particularly noteworthy is the low lower pressure, the reasons for which are indicated above. Every person should know how to increase the diastolic rate. In the end, such knowledge may one day be useful to someone else.
Compliance with the rules of a healthy lifestyle, as well as sufficient time in the fresh air and moderate physical activity are the main secret to normalizing diastolic blood pressure. A regular and full night's sleep for 7-8 hours is undoubtedly also an important guarantee of excellent well-being. But taking medications with low diastolic pressure is a serious step that is best done in conjunction with your doctor.
What is the risk of low diastolic blood pressure?
What is the danger of a low diastolic pressure in a person, if its indicator is capable of dropping even to the level of 40 mm Hg? Art., interesting to all patients with hypotension. Feeling unwell is not all. The fact is that low blood pressure does not allow the required volume of blood to be delivered to the heart and brain, and with it oxygen. Hypoxia in these vital organs is the main threat posed by low blood pressure. A complication such as impaired peripheral circulation and cardiogenic shock is a direct consequence of oxygen starvation. 
Fainting and stroke are also highly likely to develop when lower (diastolic) pressure is critical. In addition, a radical restructuring of the arteries due to a prolonged course of hypotension ultimately leads to the transition of the disease into a more dangerous form of cardiovascular disease - hypertension. In this form, the disease is much more severe.
Causes of low systolic blood pressure
Diastolic indicators below the norm indicate the possible development of serious pathological processes, primarily from the side of the cardiovascular system. Meanwhile, low upper blood pressure is often associated with other causes, including:
- tachycardia, arrhythmia, bradycardia (heart rhythm disturbances);
- pathological features of the functioning of the heart valve;
- diabetes;
- first trimester of pregnancy;
- excessive physical activity.
The systolic indicator gives detailed information about the intensity with which the heart "pump" pushes blood. Within the normal range, its value is about 110-120 mm Hg. Art. To understand how low blood pressure is dangerous for a person and how great the threat is, you can use the critical indicators of both diastolic and systolic indicators. With extremely low blood pressure, the patient often faints. With systolic 60 mm Hg. Art. gradually loses touch with reality, becomes cloudy in the eyes, legs become "wadded". It is important to have time to call someone for help while possible.  To help the patient, it is necessary to lay him in such a horizontal position so that the legs are above the level of the head.
To help the patient, it is necessary to lay him in such a horizontal position so that the legs are above the level of the head.
Threat of low systolic pressure
The lowest pressure in a person is considered critical when its upper values are in the range of 40-60 mm. rt. Art. The patient is already unconscious, and if such pressure remains for 7-8 minutes or more, then the person can leave this world. The heart rate also drops to a minimum and can be 45-60 beats per minute. An emergency call for an ambulance and the arrival of a team of doctors will give the patient a chance to recover. However, the consequences of the state he endured can leave an indelible mark on his life until the end of his days.
Danger to a pregnant woman
The danger of low blood pressure in systolic values is also present during pregnancy. This is due to hormonal changes in the body. An acceptable decrease in the upper values is considered to be a decrease to 10 mm Hg. Art., and the lower - up to 15 units. Blood pressure in pregnant women generally reaches its minimum at 22-24 weeks. 
Such a decrease is not considered dangerous either for the fetus or for the expectant mother. Meanwhile, fainting is a common symptom of hypotension in pregnant women. Loss of consciousness often leads to falls, which is a potential threat to the baby. Dehydration, which is diagnosed quite often in pregnant women, can also provoke a decrease in blood pressure.
Hypotension classification
Low blood pressure is classified into several types:
- Orthostatic lowering of blood pressure. Most often it occurs with a sharp change in body position (with a sharp rise), when blood flow to the extremities increases, and the heartbeat does not increase. It is characterized by concomitant attacks of dizziness, loss of coordination, in rare cases, even consciousness. This type of hypotension is often found in pregnant women, despite the fact that elderly people are considered the main risk group for the onset of the disease.
- Postprandial hypotension manifests itself in patients of the older age group after eating.
- Vegetovascular dystonia is the most common type of hypotonic disease. Such a decrease in pressure is observed in patients with hot weather conditions, with overwork, stress, etc. The disease is often found in young people.
Today, everyone should know why a person's low blood pressure is dangerous. With a rapid heartbeat and pulse, it is difficult for the heart to pump blood through the vessels, which means that the supply of oxygen to the limbs and organs becomes insufficient. To normalize pressure, you need to take a contrast shower and thoroughly massage the body with a special massage brush. It is impossible to get carried away with such a famous remedy for low blood pressure as coffee or chocolate: this is an excellent solution for one-time relief, but if the decrease in blood counts has become regular, it is imperative to consult a doctor. 
How to normalize low blood pressure?
The specialist will be able to confirm or exclude the diagnosis, prescribe appropriate medications, if necessary, and monitor the patient's condition. Self-medication can be life-threatening.
fb.ru
What pressure indicators are considered low
The answer to the question: how much is low pressure is ambiguous. The generally accepted safe lower limit of the normal blood pressure for systolic and diastolic values is 100/60 mm Hg. Art. But in practice, one has to deal with situations where they are much lower, but at the same time the person does not feel any discomfort and leads an active lifestyle.

According to classical concepts, hypotension is accompanied by circulatory disorders in the form of:
This impairs the delivery of nutrients and oxygen to all internal organs, which disrupts their normal functioning. The most vulnerable to hypoxia (oxygen starvation) are the brain and heart.
Due to the adaptive reactions of the body, a decrease in blood pressure is not always accompanied by signs of microcirculation disorders and oxygen starvation, but only under certain circumstances.
Physiological or pathological hypotension - all individually
If a person has blood pressure below 100/60 mm Hg. Art. does not cause any symptoms and signs of impaired blood circulation, this can be perceived as a variant of the norm - physiological hypotension. It is an individual feature and is more often observed in young women (from adolescence to 40–45 years) for many years.
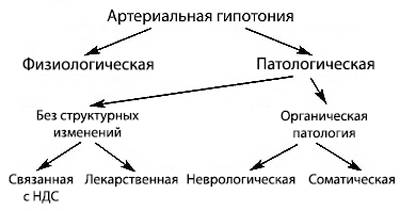 Types of arterial hypotension
Types of arterial hypotension Therefore, some experts recommend taking 90/60 mm Hg for the lower limit of the pressure norm. Art. It is difficult to judge whether this is correct or not. After all, it has been established that, despite the absence of pathological manifestations, people with persistent hypotension are more susceptible to various diseases throughout their lives: anemia, decreased immunity, neurogenic disorders, arrhythmia. After 45 years, about 85% of them become hypertensive with a strong increase in blood pressure, which is resistant to medication treatment.
It can be extremely difficult and not always safe to eliminate the usual hypotension. This is due to the fact that all body systems that regulate blood pressure (nervous, autonomic, hormonal) have adapted to maintain it at a low level for a long time. They have established such a balance among themselves, in which the body does not experience pronounced rearrangements. If you artificially try to increase the pressure, this balance is destroyed and a hypotensive person develops pronounced disorders even at 100/60 mm Hg. Art., not to mention higher.
Pathological hypotension is considered if it is accompanied by complaints and characteristic disorders. This happens more often in people with normal or high blood pressure, when it drops downward. At the same time, the brain and heart undergo oxygen starvation, which causes the main symptoms of hypotension.
Causes of the problem
Low pressure always caused by a violation of the mechanisms of its regulation. In the table, they are described with an indication of the causes and diseases.
| Pressure reducing mechanisms | Causes and diseases |
|---|---|
| Decrease in the amount and volume of blood | Bleeding: gastrointestinal, uterine, wounds |
| Dehydration: inadequate water and salt intake, diarrhea, vomiting, overheating, excessive sweating | |
| Decreased pumping function of the heart | Heart attack, heart failure, arrhythmia, myocarditis, cardiomyopathy |
| Decreased hormonal activity of the endocrine glands | Thyroid - hypothyroidism |
| Adrenal glands - hypocorticism (Addison's disease) | |
| Pituitary gland and hypothalamus | |
| Violation of the nervous regulation of vascular tone | Condition after nervous shocks and psychosis, a change in body position (if you get up very sharply from a lying or sitting position), being in a stuffy, cramped or poorly ventilated room |
| Vegetative dystonia, hereditary features of the regulation of vascular tone | |
| Stroke and cerebral hemorrhage, traumatic brain injury, tumor | |
| Redistribution of blood in the body - excessive expansion of small vessels | Poisoning and intoxication against the background of infections, abscesses, injuries and burns, alcohol abuse, work with toxic substances |
| Overdose of antihypertensive medications: Nitroglycerin, ACE inhibitors, diuretics, antispasmodics (no-shpa, dibazol), beta-blockers, calcium inhibitors. |
|
| Allergic reactions | Household, food allergens, treatment with any medication |
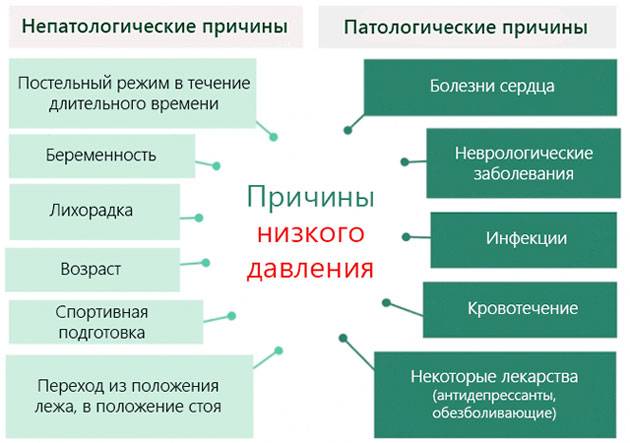 Low pressure reasons
Low pressure reasons The extreme degree of pressure reduction (below 80–90 / 50–60 mm Hg), accompanied by very severe microcirculation disorders, is called shock. He might be:
- hemorrhagic - the result of blood loss;
- cardiogenic - impaired heart function;
- infectious toxic - poisoning, intoxication;
- traumatic - a consequence of severe injury;
- anaphylactic - an allergic reaction.
It is important to understand that low blood pressure is not only a consequence of various pathological processes and influences. A slight hypotension (less than 90/60 mm Hg), which has arisen for one of the possible reasons, can cause critical circulatory disorders in the heart and brain, from which the indicators will decrease even more.
Possible Symptoms
A person who has decreased blood pressure may note the following symptoms and complaints:
If hypotension is not an independent pathological condition, but just one of the symptoms of various diseases, it is accompanied by other symptoms characteristic of them (they are described in more detail in the table of the section “algorithm for helping patients”).
Patient care algorithm
The primary concern in treating low blood pressure is to determine what the condition is. If it is urgent, there is no time to think - to such a person you need to call an ambulance (phone 103) and start providing first aid before she arrives. In any case, patients should be examined by different specialists: a therapist, cardiologist, surgeon, neuropathologist, endocrinologist.
By differentiated exclusion of the most dangerous causes of lowering blood pressure, taking into account the existing symptoms, you can find the true cause. It may take only a few minutes to eliminate it, a surgical operation, or it may be such that treatment will be required throughout life.
The general algorithm for helping in any case of low pressure looks like this:
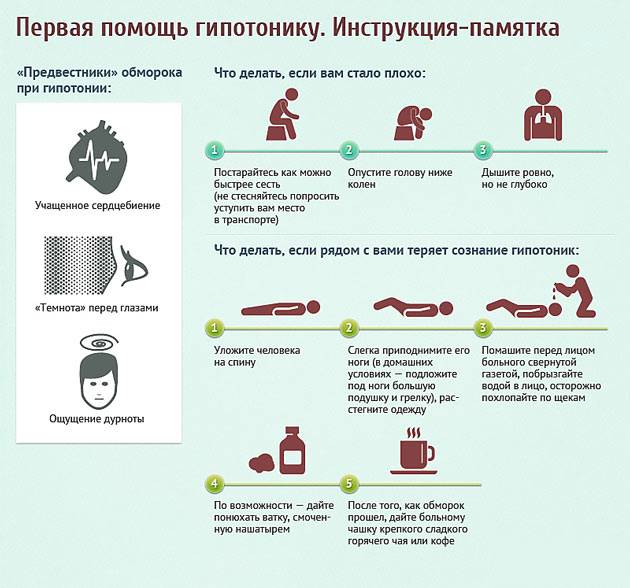 Click on the photo to enlarge
Click on the photo to enlarge | What to look for | Probable Causes of Hypotension | What to do with low pressure |
|---|---|---|
| Cyanosis, puffiness of the face, shortness of breath, chest pain | Pulmonary heart attack or thromboembolism | Give under the tongue Aspirin (Cardiomagnet), nitroglycerin (if the pressure is at least 90/60) |
| Bloody vomit, black feces | Gastric or intestinal bleeding | Cold on the stomach, hemostatic drugs (Etamsilat, Ditsinon, Sangera), Omez |
| Brain signs (weakness of the arms and legs, loss of speech and vision, skewed face) | Stroke, hemorrhage, traumatic brain injury, tumor, brain inflammation | Do not lower the head, lay it on its side, put it in cold, make sure that the person does not choke on vomiting |
| Recurrent or sudden episodes of low blood pressure without any additional manifestations | Vegetovascular dystonia, hormonal imbalance, abrupt change in body position, overheating, stressful situations | Provide rest, give strong coffee or drugs to drink: citramone, caffeine, cordiamine. If there is no effect - injections of Dexamethasone, Prednisolone |
| Constantly low pressure | If there are no complaints - the characteristics of the body | Treatment by a specialist, general tonic preparations for long-term use (months): Eleutherococcus, Tonginal, Pantokrin. |
| The presence of complaints - endocrine or neurovegetative disorders | ||
| Very pronounced (less than 80–90 / 50–60) acute hypotension, disrupting the general condition | Any type of shock, including anaphylactic shock (allergy) | General measures in combination with intravenous drug administration: |
In all cases of a sudden drop in blood pressure, be sure to call an ambulance (phone 103). A dangerous disease can be hidden behind this symptom!
Treatment efficacy prognosis
If a decrease in pressure is a symptom of severe urgent diseases, only specialists in a hospital should increase it. In this case, the prognosis is unpredictable (50% of patients in shock state die). Habitual unreasonable hypotension does not pose any danger to life, but in 60–70% it cannot be eliminated, despite treatment.
Low blood pressure caused by chronic diseases of internal organs and hormonal deficiency is normalized by itself against the background of their treatment. The best treatment and least dangerous are periodic episodes of mild hypotension against the background of vegetative-vascular dystonia, changes in body position, meteosensitivity and other factors.
okardio.com
Signs and causes of low blood pressure
Each person's body is unique. Therefore, it is impossible to talk about strict norms of high or low pressure. There are only average indicators that indicate possible negative changes within the framework of such a function of the body.
What indicators on the tonometer are considered low for different groups of people?
However, there are people for whom the rates are much lower than the generally accepted one (ie, some people initially have a "working" pressure lower than 120 to 80). This is noted within the framework of heredity, and often a person with congenital low blood pressure does not feel painful and does not have any additional complaints. A chronic condition usually does not pose any threat to health and life; some doctors are inclined to believe that such people, on the contrary, are among the long-livers.
Why is the pressure dropping?
Changes in the indicators on the tonometer arise due to the processes occurring inside the body associated with the work of the cardiovascular system and the nervous system.
Within the framework of this, the following grounds stand out:
- a change in the volume of blood in the body, which is characteristic of prolonged bleeding of varying strength, dehydration; due to a decrease in the amount of blood, pressure also decreases;
- slowing down the contractions of the heart and reducing the strength of these contractions; the less often and weaker the heart pushes blood, the lower the pressure also becomes; this can manifest itself, for example, due to a long period of rest;
- poor or improper functioning of nerve endings, which are considered a compensatory mechanism and try to control pressure stability by sending impulses to the brain; when the work of these nerve fibers is disrupted due to internal or external influences, a failure occurs;
- sharp and strong constriction, vasoconstriction; when the blood vessels are significantly compressed, not enough blood enters them, the person's pressure drops.
All these physiological grounds can appear both independently and act in an alliance.
The main reasons for low pressure are highlighted:
- concomitant physiological diseases, in which hypotension is a symptom;
- overwork, lack of sleep, prolonged nervous excitement, chronic fatigue syndrome, insomnia, stress;
- depression;
- starvation, malnutrition, dehydration; low blood sugar can also provoke hypotension;
- lack of oxygen;
- taking certain medications and hobby for various sedatives, soothing teas;
- the predominance in the diet of foods that can lower blood pressure;
- long sleep, minimal physical activity;
- infectious diseases of the blood, serious injuries, bleeding with various bases;
- pregnancy;
- intoxication;
- lack of vitamins, trace elements in the body;
- change of climatic zones and time zones.
However, low pressure should cause concern only when unpleasant symptoms are added to the numbers on the tonometer, which do not allow a person to function normally.
Signs of low blood pressure
- Dizziness, lightheadedness, fainting.
- Headache, especially in the morning. Localization can be different: in the parietal and temporal lobes, in the back of the head, migraine-like pain, a feeling of squeezing in the forehead. Painful sensations can be prolonged, dull or throbbing, similar to severe spasms, pinpoint.
- Darkening in the eyes, "flies" before the eyes, narrowing of the field of view to a small point, defocused vision. This is especially often manifested with a sharp change in body position, then it makes sense to talk about orthostatic hypotension.
- Tinnitus, ringing, perception of sound as through thick film or glass.
- Great weakness, drowsiness, low tone.
- Coldness, sometimes numbness of the limbs.
- Pallor or even cyanosis of the skin, slow pulse (see normal pulse in a healthy person).
- A feeling of lack of oxygen, while often a hypotonic person cannot take a full deep breath ("as if the hoop squeezes the chest").
- Heartburn, belching with air.
- Painful sensations in the region of the heart, behind the breastbone, shortness of breath.
With often low blood pressure, there may also be:
- tremor;
- irritability;
- tearfulness;
- impaired coordination of movements;
- staggering when walking;
- perception of the world "as in a dream";
- inability to concentrate;
- distraction of attention;
- low mental activity;
- constant yawning.
Danger of arterial hypotension
Low blood pressure does not pose a significant threat to health, especially in cases where it does not bring discomfort or is not a symptom of any disease or bleeding.
However, in some cases, significantly pronounced hypotension can affect as follows:
- due to slow blood circulation, "oxygen starvation" can occur;
- with very low blood pressure, there is a risk of developing kidney failure and kidney failure;
- frequent fainting can lead to injury;
- the appearance of nausea and subsequent vomiting can provoke dehydration;
- during pregnancy, low blood pressure poses a certain threat not only to the woman, but also to the fetus, in particular, due to insufficient oxygen supply;
- there is some risk of stroke;
- dangerously low blood pressure and the fact that cardiogenic shock is possible;
- if, against the background of low blood pressure, there is a rapid pulse, tachycardia attacks, then this can become a significant threat to life and requires medical intervention.
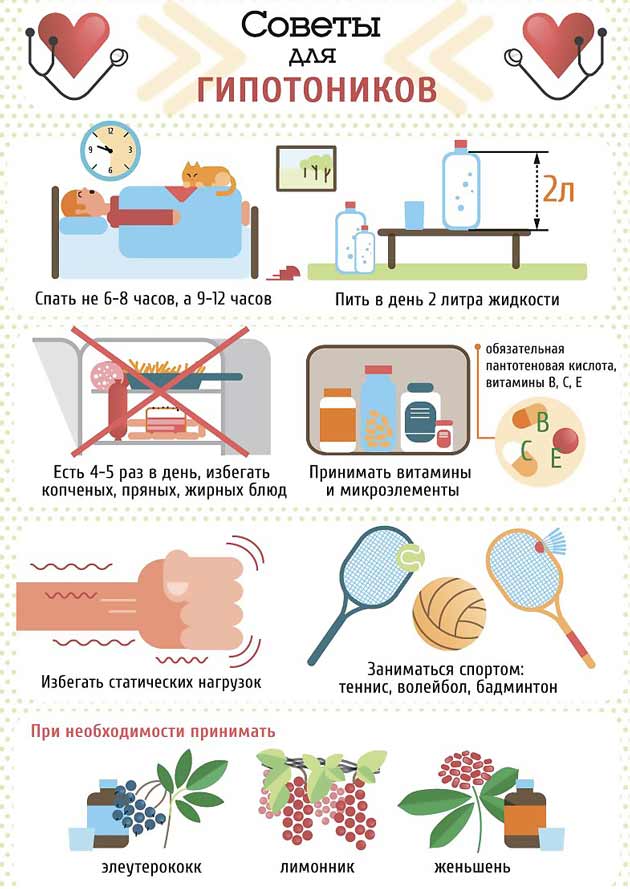
How to raise low blood pressure yourself?
To bring the pressure back to normal when it falls below the permissible limits, any "chemical" preparations are rarely used. Normalization is carried out with the help of herbal medicine, homeopathy, thanks to changes in the usual rhythm of life and in the diet. But there are also a number of emergency remedies that can quickly raise low blood pressure.
- carry out a general body massage or lymphatic drainage;
- get enough sleep, taking more than 8 hours to sleep;
- after waking up, you should not suddenly get out of bed; it is better to lie down for a few minutes, making smooth movements with your arms and legs, doing a kind of exercise; only then slowly sit up in bed, stretch and then get up;
- take regular walks in the fresh air, add more movement and activity to life; it is vigorous exercise that helps to raise low blood pressure without any problems; sports walking, light jogging, swimming pool or fitness center activities and other activities are recommended;
- a contrast shower helps to get rid of malaise with hypotension;
- avoid stuffy and hot rooms as much as possible; as well as sudden temperature changes;
- give up addictions and irregular daily routine, reduce mental stress as much as possible and do not forget to fully rest;
- do not skip breakfast, as well as eat fully throughout the day, supplying the body with a sufficient amount of fluid.
To quickly build up the pressure, you can do one of the following:
- do acupressure for a couple of minutes; massage the point above the upper lip and earlobes with soft, circular movements;
- drink a cup of freshly brewed strong black coffee with a slice of lemon or lemon juice added to the drink; you should drink coffee in small sips, the drink should not be cold;
instead of coffee, in order to quickly increase blood pressure and further normalize it, you can use strong green tea without additives; the drink is drunk only hot; - if the pressure drops very low and abruptly, physical activity will be impossible; then you should take a horizontal position, raising your legs and placing your head as low as possible so that there is an outflow of blood from the lower extremities; at this moment, you can inhale vapors of peppermint essential oil;
- it will also urgently increase blood pressure at home, citramone, which contains caffeine, or a caffeine pill (for more information on how Citramon increases blood pressure, read here).
Medicines that increase blood pressure
Despite the fact that drugs for arterial hypotension are rarely resorted to, there are some drugs available in pharmacies that have a positive effect on the condition.
What pills increase blood pressure besides citramone and caffeine?
- Papazol.
- Guthron.
- Spazmalgon, Nosh-pa and other drugs that relieve spasms.
- Nise, nurofen and other pain pills.
- Camphor.
- Mezaton.
- Dobutamine.
Doctors also recommend some tinctures, often alcohol ones, to raise low blood pressure.
These include:
- tincture of ginseng;
- eleutherococcus;
- leuzea;
- Chinese lemongrass;
- pink radio.
Taking tinctures should be carried out for people prone to low blood pressure, a couple of times a day, 30 minutes before meals. The number of drops is calculated individually. A course of homeopathic tonics is especially required at moments of weather changes, since with low blood pressure meteosensitivity is noted, in the autumn and spring seasons.
Products needed for hypotension
The most common choices that are effective in raising blood pressure at home are drinks and foods that contain caffeine. In addition to green tea or coffee, it is useful to use cocoa, red tea "Hibiscus", black bitter chocolate. In a hopeless situation, Pepsi or Coca-Cola will help raise low blood pressure, but you should not get carried away with carbonated sugary drinks, like caffeine in general.
Do not forget about drinking plenty of fluids. A sufficient amount of fluid consumed per day thins the blood and increases its volume.
- carrot;
- sea buckthorn, dried apricots;
- cottage cheese;
- buckwheat and rice groats;
- caviar and fish;
- eggs;
- lemons and black currants;
- Cherry;
- sorrel;
- butter;
- potatoes, beans;
- liver, red meat;
- pomegranate and pomegranate juice;
- horseradish, onions, garlic, salted nuts.
Folk remedies that increase blood pressure
The list of popular recommendations includes decoctions, tinctures and infusions, extracts of herbs, roots, plants that have a beneficial effect on well-being under reduced pressure. It is also permissible to use herbal preparations that combine individual components.
10 essential herbs to fight arterial hypotension
- St. John's wort.
- Echinacea
- Immortelle.
- Swamp calamus.
- Thistle.
- Yarrow.
- Fireweed.
- Blooming Sally.
- Ginger.
- Azalea roots.
In order not to be bothered by sudden changes in pressure, you need to be attentive and sensitive to your health. In situations of malaise, try to get rid of the root cause; if the correction of the condition does not bring results on its own, it is necessary to seek the advice of a doctor.