What is partial pressure of oxygen
Even people who are far from mountaineering and diving know that it becomes difficult for a person to breathe in certain conditions. This phenomenon is associated with a change in the partial pressure of oxygen in the environment, as a result, in the blood of the person himself.
mountain sickness
When a resident of the flat area comes on vacation to the mountains, it seems that the air there is especially clean and it is simply impossible to breathe it.
In fact, such reflex urges for frequent and deep breathing are caused by hypoxia. In order for a person to equalize the partial pressure of oxygen in the alveolar air, he needs to ventilate his own lungs as best as possible at first. Of course, staying in the mountains for several days or weeks, the body begins to get used to the new conditions by adjusting the work of internal organs. So the situation is saved by the kidneys, which begin to secrete bicarbonate to enhance ventilation of the lungs and increase the number of red blood cells in the blood that can carry more oxygen.
Thus, in mountainous areas, the level of hemoglobin is always higher than in the plains.
acute form
Depending on the characteristics of the organism, the norm of partial pressure of oxygen may differ for each person at a certain age, state of health, or simply from the ability to acclimatize. That is why not everyone is destined to conquer the peaks, because even with a great desire, a person is not able to completely subjugate his body and make it work differently.
Very often, unprepared climbers with high-speed ascent may develop various symptoms of hypoxia. At an altitude of less than 4.5 km, they are manifested by headaches, nausea, fatigue and a sharp change in mood, since the lack of oxygen in the blood strongly affects the functioning of the nervous system. If such symptoms are ignored, then swelling of the brain or lungs is formed, each of which can lead to death.

Thus, it is strictly forbidden to ignore the change in the partial pressure of oxygen in the environment, because it always affects the performance of the entire human body.
Immersion under water
When a diver dives into conditions where the atmospheric pressure is below the usual level, his body also faces a kind of acclimatization. The partial pressure of oxygen at sea level is an average value and also changes with immersion, but nitrogen is a particular danger to humans in this case. On the surface of the earth in flat terrain, it does not affect people, but after every 10 meters of immersion, it gradually contracts and provokes various degrees of anesthesia in the diver's body. The first signs of such a violation may appear after 37 meters under water, especially if a person spends a long time at depth.

When atmospheric pressure exceeds 8 atmospheres, and this figure is reached after 70 meters under water, divers begin to feel nitrogen narcosis. This phenomenon is manifested by a feeling of intoxication, which disrupts the coordination and attentiveness of the submariner.
To avoid the consequences
In the case when the partial pressure of oxygen and other gases in the blood is abnormal and the diver begins to feel signs of intoxication, it is very important to lift it as slowly as possible. This is due to the fact that with a sharp change in pressure, nitrogen diffusion provokes the appearance of bubbles with this substance in the blood. In simple terms, the blood seems to boil, and the person begins to feel severe pain in the joints. In the future, he may develop impaired vision, hearing and the functioning of the nervous system, which is called decompression sickness. To avoid this phenomenon, the diver should be lifted very slowly or replaced with helium in his breathing mixture. This gas is less soluble, has a lower mass and density, so the costs are reduced.
If such a situation has occurred, then the person must be urgently placed back in a high-pressure environment and wait for a gradual decompression, which can last up to several days.
In order to change the gas composition of the blood, it is not necessary to conquer peaks or descend to the seabed. Various pathologies of the cardiovascular, urinary and respiratory systems can also affect the change in gas pressure in the main fluid of the human body.
To accurately determine the diagnosis, appropriate tests are taken from patients. Most often, doctors are interested in the partial pressure of oxygen and carbon dioxide, since they provide full breathing of all human organs.
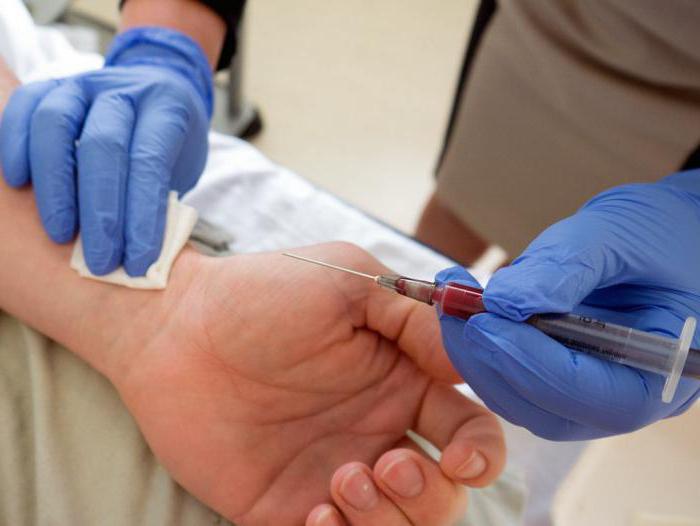
Pressure in this case is a process of dissolving gases, which shows how efficiently oxygen works in the body and whether its performance is in line with the norms.
The slightest deviations indicate that the patient has deviations that affect the ability to use the gases entering the body to the maximum.
Pressure standards
The norm of the partial pressure of oxygen in the blood is a relative concept, since it can vary depending on many factors. In order to correctly determine your diagnosis and receive treatment, it is necessary to contact a specialist with the results of the tests, who can take into account all the individual characteristics of the patient. Of course, there are reference norms that are considered ideal for a healthy adult. So, in the patient's blood without deviations there is:
- carbon dioxide in the amount of 44.5-52.5%;
- its pressure is 35-45 mm Hg. Art.;
- saturation of the liquid with oxygen 95-100%;
- About 2 in the amount of 10.5-14.5%;
- partial pressure of oxygen in the blood 80-110 mm Hg. Art.
In order for the results to be true during the analysis, it is necessary to take into account a number of factors that can affect their correctness.
Causes of deviation from the norm, depending on the patient
The partial pressure of oxygen in arterial blood can change very quickly depending on various circumstances, therefore, in order for the analysis result to be as accurate as possible, the following features should be considered:
- the rate of pressure always decreases with increasing age of the patient;
- when supercooling, the pressure of oxygen and the pressure of carbon dioxide decrease, and the pH level increases;
- when overheating, the situation is reversed;
- the actual indicator of the partial pressure of gases will be visible only when blood is taken from a patient with a body temperature within the normal range (36.6-37 degrees).

Causes of deviation from the norm, depending on health workers
In addition to taking into account such features of the patient's body, specialists must also comply with certain norms for the correctness of the results. First of all, the presence of air bubbles in the syringe affects the partial pressure of oxygen. In general, any contact of the assay with ambient air can change the results. It is also important to gently mix the blood in the container after taking the blood so that the erythrocytes do not settle at the bottom of the tube, which can also affect the results of the analysis, demonstrating the level of hemoglobin.
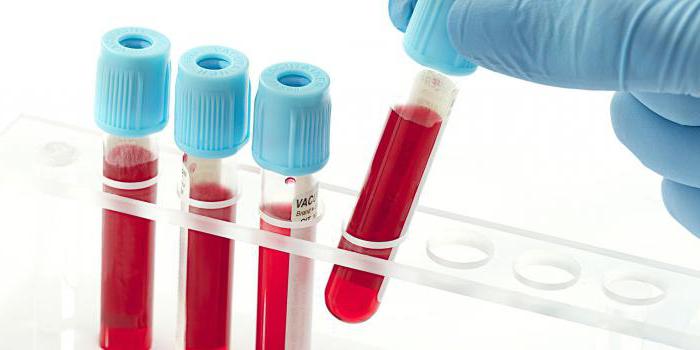
It is very important to adhere to the norms of the time allotted for the analysis. According to the rules, all actions must be carried out within a quarter of an hour after sampling, and if this time is not enough, then the blood container should be placed in ice water. This is the only way to stop the process of oxygen consumption by blood cells.
Specialists should also calibrate the analyzer in a timely manner and take samples only with dry heparin syringes, which are electrolytically balanced and do not affect the acidity of the sample.
Test results
As is already clear, the partial pressure of oxygen in the air can have a noticeable effect on the human body, but the level of gas pressure in the blood can be disturbed for other reasons. To determine them correctly, decoding should be trusted only by an experienced specialist who is able to take into account all the features of each patient.
In any case, hypoxia will be indicated by a decrease in the level of oxygen pressure. A change in blood pH, as well as carbon dioxide pressure or a change in bicarbonate levels, may indicate acidosis or alkalosis.
Acidosis is a process of acidification of the blood and is characterized by an increase in carbon dioxide pressure, a decrease in blood pH and bicarbonates. In the latter case, the diagnosis will be announced as metabolic acidosis.

Alkalosis is an increase in the alkalinity of the blood. It will be indicated by an increased pressure of carbon dioxide, an increase in the number of bicarbonates, and, consequently, a change in the pH level of the blood.
Conclusion
The performance of the body is affected not only by high-quality nutrition and physical activity. Each person gets used to certain climatic conditions of life in which he feels as comfortable as possible. Their change provokes not only poor health, but also a complete change in certain blood parameters. To determine the diagnosis from them, you should carefully select a specialist and monitor compliance with all norms for taking tests.