How are ferns different from mosses?
Mosses and ferns, according to the classification of plants, are included in the group higher spore plants... These are one of the most ancient representatives of the plant world of the Earth. In some periods of history, mosses and ferns dominated all plants, covering all areas of our planet. Later, angiosperms and gymnosperms began to prevail.
Mosses or mossy - this is the department of higher plants, which includes more than 100 families, 700 genera and about 10 thousand species. The age of these plants is counted from the Carboniferous period. There are three classes: anthocerotic, leafy and hepatic mosses. The most representative group is leafy or true mosses.
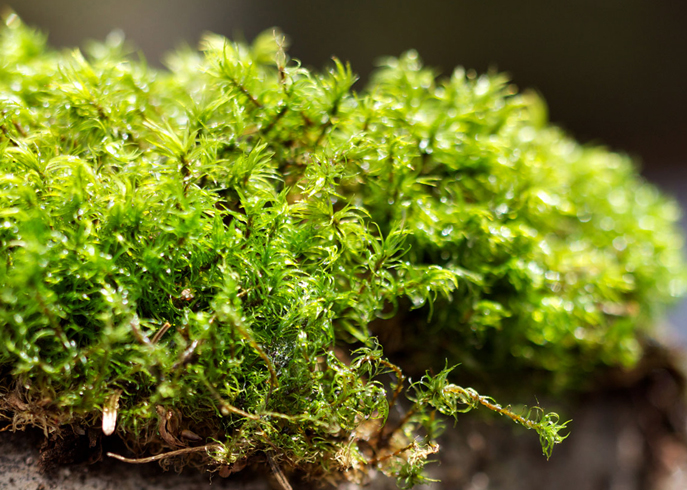

Today these mosses are known under the well-known names of sphagnum and cuckoo flax. Moss is often called moss, which deer eat in the tundra, although in reality it is not moss, but a “nickname” for some species of lichens. The branch of botany that studies bryophytes is called bryology.

The fern is one of the oldest surviving plants. The appearance of ferns is noted in the Devonian period (about 400 million years ago). Ferns are very diverse in shape (herbaceous, woody), sizes, cycles of existence. Despite the fact that in appearance all ferns are outwardly similar to each other, in nature there are more than 10,000 species of this plant. Let's consider the main differences between ferns and mosses.

Plant age
Ferns appeared on Earth somewhat earlier than mosses. At the junction of the Paleozoic and Mesozoic eras, the entire land was covered with giant tracts of fern forests. Mosses appeared at the end of the Devonian geological period, but did not develop to a biomass comparable to that of ferns.
The basis of minerals
Ferns, after dying off and long-term storage processes and chemical transformations in the earth, formed huge reserves of minerals: gas, coal, oil.
Mosses became the basis for the formation of peat, which is mined in peatlands. Peat is used as an organic fertilizer and a raw material for the production of paints, varnishes, acids, alcohol, wax, and plastics.
Separation of sexes
Ferns are monoecious plants with male (stamens) and female (pistils) flowers on the same plant. Mosses are representatives of dioecious plants in which female and male flowers are located on different plants. Ferns can reproduce by spores and vegetatively (rhizomes, frond, buds, aflebia). In addition, ferns are also characterized by sexual reproduction as part of their life cycle.

Differences between leaves
If mosses have, although microscopic, but ordinary leaves, then ferns have a leaf-like organ called frond.
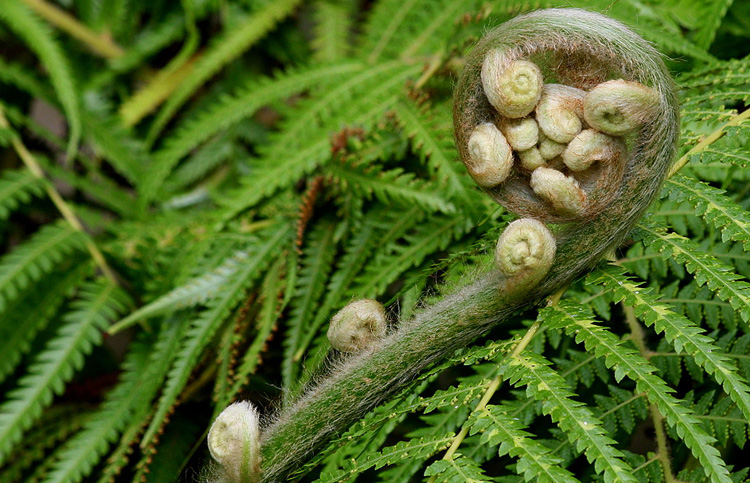

A frond is a set of branches located in one plane, also called a flat flower. Another term is used to designate this organ - pre-run. As a result of evolution, the ferns did not have time to divide the frond into a separate leaf and stem. However, the leaf blade was almost formed; it remained only to take a step towards combining these plates into a leaf. Plants that evolved further this way became gymnosperms.
The purpose of the leaves
Moss leaves are only capable of producing chlorophyll. Photosynthesis occurs in fern leaves, that is, chlorophyll is also produced, and in addition to this, spores are deposited. Photosynthesis in mosses is slow and can occur even under snow, if the temperature in winter is close to zero degrees, then the moss remains evergreen.

Rhizomes
Roots are absent in mosses. This role is played by rhizoids - filamentous formations of single-row cells (similar in appearance to root hairs), which are able to attach to a source of water and nutrition. In ferns, the length of the rhizome can reach a length of 30 cm. In addition to the main rhizome, there are additional adventitious roots, processes from the rhizome.
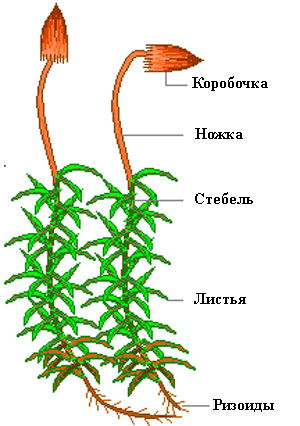
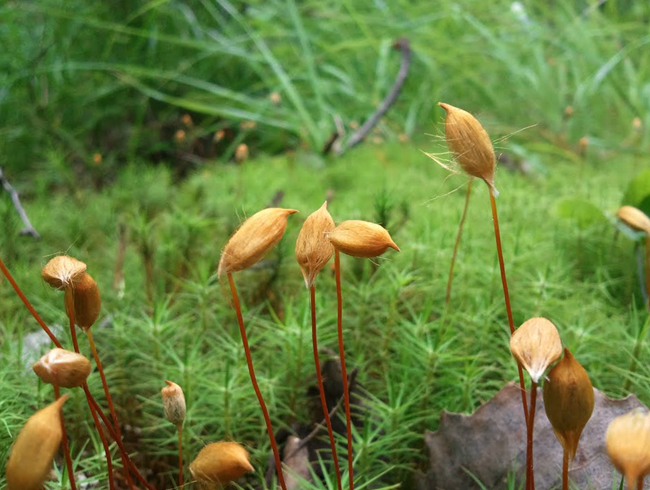
Moss cuckoo flax - structure
Differentiation of tissues
Ferns have well-formed bundles of conductive tissue, and parenchymal tissue is located between these bundles. The nutrients dissolved in water move along the conductive tissues. The main functions of parenchymal tissues: photosynthesis, storage of nutrients, air transport. No such division into tissue types was found in mosses.
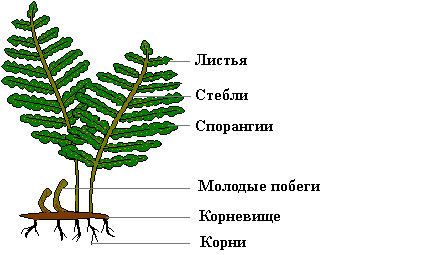
Difference of life cycles
In the life cycle of a fern, sporophyte prevails over gametophyte, and in mosses, gametophyte prevails over sporophyte. Moreover, if in mosses the gametophyte is an adult plant, then in ferns it is a separate plant, which is called an outgrowth.
Ploidy
According to this characteristic, ferns are diploid, and mosses are haploid. That is, in the nuclei of moss cells there is a single set of chromosomes, and in the nuclei of fern cells there is a double set.
Dispute location
The location of the spores in mosses is in the capsule, which is “attached” to the leg. In ferns, spores are found on the back of the frond.
Impact on the environment
Mosses accumulate water very efficiently, which in some cases leads to waterlogging of forest areas.
Evolution perspective
Mosses are at an evolutionary dead end, since their reproduction is impossible without water.