Ural is the "stone belt" of the Russian land. Ural - a stone belt of the Russian land Urals a stone belt of the Russian land presentation
Ural - stone belt Russian land .

He is the Asian mainland
Came on a stone threshold
He knows the mammoth skeleton
In frozen soils. Downpours, winds
It has been sharpened for millions of years
So that the edges sparkle in a line.
Iron, nickel, chrome ores
I will touch with a word, I will find a rhyme for them.
No wonder the emerald stone in the mines
Green eye looks into the darkness.
The ridge will confuse the path of moose,
Ripe blueberries will start to regale,
Shines between the pines of the river Sosva,
The glacier will reach the bright cloud,
He will look into the lakes, he will enter the verse like this.
He smelled of forests and flowers
And bitter factory smoke.
S. Schipachev

Ural is a mountainous country,
stretching from victory
cut of the Kara Sea to
steppes of Kazakhstan from the north
more than 2000 km to the south, with
west to east - from 50

Continuation of the Ural Mountains
in the north are the islands
Novaya Zemlya and Vaigach, and on
south of the Mugodzhar mountains.

Ural is natural
border between Europe

called Riphean.
"Stone belt of the Russian land",
"Stone", "Earth belt" - so on-
called the Urals until the 18th century.

The name "Ural" appears from
from the 18th century In the works of the Russian historian
rik and geographer Vasily Nikiti-
cha Tatishcheva ("ur" in Mansi,
and "ure" in Even means

The Ural Mountains rise
ridges near the eyes
low-rise ridges and ridges
zhey dressed in taiga.

The highest point of the Urals
some mountains - Mount Narodnaya

Mountains consist of several
drink that run parallel
but to each other in the meridian
direction. The ridges are divided
longitudinal intermontane ponies
the paths through which the rivers flow.
Transverse valleys dismember
these chains into separate ridges and

History of development Ural.

- People settled in the Urals and moved gradually along the mountain steppes to the edge of the glacier.
- The ancient population of the Urals - the ancestors of the Udmurts, Komi, Khanty and others in the era of primitiveness created a rich and unique culture.

- The first people spoke the language of the modern peoples of the Khanty and Mansi. In the steppes of the Southern Urals, as well as in the territory Chelyabinsk region Abashev tribes lived.

bashkir village
- The main population of the Southern Urals in IX – XI centuries were the Bashkirs.
- From the second half XVI century Bashkiria became a vassal of the Muscovite state.
- The first Bashkir villages began to appear.

Cossacks
- AT XVI in. on the river In the Urals, free people appear who create a "Cossack republic" here.
- AT XVII in. Orenburg Cossacks formed in the Southern Urals.

Building fortresses
- In 1730-1750. near the area of present-day Miass, the first Russian settlements arose: Chebarkulskaya, Kundravinskaya, Uiskaya.
- The task of the government was to build fortresses in the Southern Trans-Urals, which led to an influx of peasants and service people.

The ancient inhabitants of the Urals
there were Bashkirs, Udmurts, Komi,
Khanty, Mansi, local Tatars.

The first settlements of the Russians
curled in the Urals in the upper reaches of the Ka-
we, their inhabitants, were engaged in hunting
that and fishing. In the XI century. on-
garden people Kalinnikovs-
we created the first salt-
varni in the village of Sol-Kama
(modern Solikamsk).

18th century - century of development of the mining plant -
Russian industry of the Urals.
The study of natural resources
Ural, deals with their description
at this time, V.N. Tatishchev. He justified
new the need for construction
you large industrial
ntra Ural and chose for him a me-
one hundred. So Catherine was founded

Geological research
of the Urals is actively
were born in the 19th century in I.V. Mushka-
tov, A.E. Fersman and others.

Mining industry
the Urals studied and
could improve
scientist D.I. Mendeleev.

About the fabulous wealth of the Urals
spoke brightly and colorfully
their tales about the mistress of Mednaya
mountains P.P. Bazhov.

"Ural! reference edge powers,
Her earner and blacksmith,
The same age as our ancient
And the glory of the current creator "
(A. Tvardovsky)

Natural resources Ural.

The Ural strikes with the wealth of its
bowels Ural is called a pantry
countries. About 1000 found here
various minerals and taken into account
over 10 thousand p/i deposits.
In terms of reserves of platinum, asbestos,
precious stones, potassium salts
The Urals owns one of the
places in the world.

Map work.
1. Between what tectonic structures
is the Ural
2. What structure separates the Urals from the Russian Plateau?
3. What minerals are complex in the region
howling deflection of the Urals?

Ancient mountains of the Urals,
formed in the Paleozoic
during the Mesozoic and Paleo-
gene were almost full
tew are destroyed. In the Neogene
Quaternary time current
tonic movements under-
taken to different heights
separate blocks of the Urals.
Thus, folded
blocky Ural mountains

Ural fold system
Russian platform
West Siberian plate

Stages of the origin of the Ural Mountains.
Stage 1.
Archean and Proterozoic era .
Stage 2. Palaeozoic. (Hercynian folding)
Stage 3. Mesozoic era.
4 stage . Cenozoic era.

After that, the mountains were again subjected to
destruction as a result of
ness of external forces - weathering,
activity of rivers and ice. As a result-
those at the surface turned out to be internal
part of the folds, where intense
mineral formation processes were going on,
various ores arose.

As a result of weathering
education is taking place
kurums, trogs, circuses,
caves, caravans


Cis-Urals
Zauralye
central band

Relief and geological structure
Salekhard
Saber (1497)
Solikamsk
Chelyabinsk


hercynian
folding
ore
useful
fossils
Mid-altitude
and low
the mountains
sedimentary
useful
fossils
hills
Cis-Urals
edge of Russian
platforms
edge
West Siberian
slabs, break
ore useful
fossils
Zauralye

The main wealth of the Urals is ores,
moreover, complex ores, for example
measures, iron ores with admixture
titanium, vanadium, nickel, chromium.
Copper ores with an admixture of zinc,
gold, silver.
Most ore deposits
is located on the eastern slope
not where igneous predominates

Magnitogorsk
Vysokogorskoe
Krasnouralskoe
Large ore deposits
Kachkanarskoe
Khalilovskoe
Bakalskoye

The Urals are rich in deposits of color
ny metals.
Copper ore is mined at Krasno-
Ural, Gaisk and other deposits
deniya. In the north of the Urals were found
dens are large deposits of bok-
bauxite and manganese.

A lot of nickel is mined in the Urals
and chrome. The oldest place is gold
production in Russia – Berezovskoe
deposit near Yekaterinbur-

From non-metallic minerals follow-
em note the huge deposits
asbestos ("mountain flax") - price-
the most refractory material
la. Bazhenovskoye field
asbestos is one of the largest

The Urals have long been famous for all kinds of
ny precious and ornamental
with stones. Known Ural
gems: amethyst, smoky
topaz, green emerald,

sapphires, clear mountain
crystal, alexandrite, etc.
All these gems are mined
are mined mainly for
exact slope.

On the western slope of the Vish-
ry found high-
nye diamonds.

Ornamental stones of the Urals.
jasper
coil
malachite

In the Cis-Urals, Permian salt deposits
nye thicknesses of the marginal deflection
hold large reserves of potash
salt, rock salt, gypsum
(Verkhnekamskoe, Sol-Iletskoe,
Usolskoye deposit).

There are many construction projects in the Urals
materials - limestone, granite,
cement raw materials. Is in the Urals
also oil (Ishimbay and others) and
coal.


In addition to minerals
resources Ural is rich in forest
resources. Especially a lot
forests in the Northern Urals.

false Ural?
2. Determine what differences exist
yut in climatic conditions:
a) Northern and Southern Urals
b) Cis-Urals and Trans-Urals.

1. What water basins do the Ural rivers belong to?
2. What parts of the Urals are well provided with water resources?

river Chusovaya
Insufficient supply of water
resources of the Middle Urals.
The main rivers of the Urals: Chusovaya,
White, Ural, Kama.

R. Serebryanka
Waterfall on the river Zhigolan

The harsh beauty of the Polar and Se-
faithful Urals, exotic islands
dances, karst caves
him and the South Urals attracted
There are many tourists in these areas.
But recreational resources
insufficiently developed.

Nomenclature:
- Relief: Southern Urals, Middle Urals, Northern Urals,
polar Urals, Polar Urals, Pai-Khoi Ridge, Narodnaya town, Konstantin-
nov Kamen, city of Telpoziz, city of Denezhkin Kamen, city of Konzhakovsky
Stone, Kachkanar, Yamantau, Magnitnaya, Payer.
- Minerals .
- Rivers : Pike, Northern Sosva, Kosva, Tagil, Chusovaya, Ufa,
Yuryuzan, Ural, Belaya, Samara.
K.k. pp. 12-13, atlas p.42-43

photo gallery Ural mountains









Repetition Repetition 1. Why are the Caucasus young mountains? 2. Prove that these are young mountains 3. Why do the western parts of Ciscaucasia receive more precipitation than the eastern ones? 4. What is the name of the resorts of the Caucasus, which have mineral springs? 5. In the central part of the Caucasus, glaciers occupy a large area, although the territory receives a large amount of total solar radiation during the year. How do you explain it? What is the difference between local winds - foehn and bora?


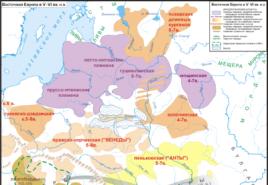
Ural The length of the Ural Mountains from south to north is 2 thousand kilometers, and from west to east from 50 to 150 kilometers. The Ural Mountains stretch from the coast of the Arctic Kara Sea to the steppes of Kazakhstan. In the east - the West Siberian Plain, in the west - the Russian Plain In ancient times, the Ural Mountains were called the Riphean Mountains, and until the 18th century, the "stone belt" (translated from Turkic, "Ural" means belt). The Ural Mountains are relatively low: only a few peaks reach a height of 1.5 thousand meters above sea level, and the highest of them (Mount Narodnaya) is 1895 meters. 1. Direction and extent 2. The borders of the Urals 3. The height of the mountains 4. How does it affect the nature of the Urals, its length from north to south for 2000 km?

The Urals The Urals are separated from the Russian platform by the Pre-Ural trough, which consists of sedimentary rocks (clay, sand, gypsum, limestone). The Ural Mountains were formed in PZ, but in MZ they were almost completely destroyed. Separate parts of the Urals rose during the KZ (Neogene). But even these folded-blocky Ural Mountains were destroyed as a result of external forces (weathering and erosion). Find Mineral deposits: -iron ores: Magnitogorsk, Kachkanarskoye, Khalilovskoye -Copper ores: Krasnouralskoye, Gayskoye, Sibaevskoye - gold: Berezovskoye -Asbestos: Bazhenovskoye -Oil: Ishimbay -Coal: Pechorsky, Kizelovsky


Urals Urals Mineral resources Western slope Eastern slope is gentle Geological structure igneous, metamorphic steep sedimentary Oil, gas, coal, phosphorites, potassium salts Iron, copper, nickel, manganese ores, gold, graphite, bauxite, asbestos







1. The climate of the Urals is diverse. Why? 2. Determine the average temperatures of January and July in the Northern (Polar) and Southern Urals. 3. Why does the western slopes of the mountains receive more precipitation than the eastern ones? 5. How do climatic conditions change with altitude? 4. In what climatic zone and region are the Ural Mountains located?

Climate of the Urals Climate of the Urals Despite their relatively low altitude, the Ural Mountains have a significant effect on climatic conditions. They are the boundary between different climatic zones: the temperate continental climate of the East European plain and continental climate of Western Siberia. Atlantic air masses reach the western slope of the Urals, trying to overcome it, rise higher and cool. As a result, more precipitation falls in the western part of the Urals than in the eastern part (approximately 1.5-2 times). The temperature regime also has its own characteristics. In the western part of the Urals, winters are more snowy and, accordingly, milder. In the east, snow falls less, and frosts reach ºС.

Ural Waters of the Urals The Ural Mountains are the watershed of the rivers flowing through the West Siberian Plain and the Russian Plain. In the Urals, rivers originate, so they are shallow. Name the rivers. Pechora Shchuchya, Northern Sosva, Tavda, Tura, Iset, Mias Kama, Belaya, Ufa, Chusovaya Which ocean basins are rivers? How to provide the industrial cities of the Urals with water? Construction of ponds and reservoirs There are few lakes in the Urals, they are tectonic, karst in origin
 Homework Homework Paragraph 32, On contour map select 5 parts of the Urals 2. Mark the highest points of the Urals 3. Mark the minerals of the Cis-Urals and Trans-Urals. To give comparative characteristic Southern and Polar Urals.
Homework Homework Paragraph 32, On contour map select 5 parts of the Urals 2. Mark the highest points of the Urals 3. Mark the minerals of the Cis-Urals and Trans-Urals. To give comparative characteristic Southern and Polar Urals.

slide 2
Repetition
- Why are the Caucasus young mountains?
- Prove that these are young mountains
- Why do the western parts of Ciscaucasia receive more precipitation than the eastern ones?
- What is the name of the resorts of the Caucasus, which have mineral springs?
- In the central part of the Caucasus, glaciers occupy a large area, although the territory receives a large amount of total solar radiation during the year. How do you explain it?
- What is the difference between local winds - foehn and bora?
slide 3
Ural
Ural! The supporting edge of the state,
Her earner and blacksmith,
The same age as our ancient glory
And the glory of the current creator
(A.T. Tvardovsky)
The Urals has long been considered a natural border separating two parts of the world - Europe and Asia.
slide 4
Ural - geological structure
The Ural Mountains are located between various tectonic structures, which explains their formation.
slide 5
Geographical position
- The length of the Ural Mountains from south to north is 2 thousand kilometers, and from west to east from 50 to 150 kilometers.
- The Ural Mountains stretch from the coast of the Arctic Kara Sea to the steppes of Kazakhstan. In the east - the West Siberian Plain, in the west - the Russian Plain
- In ancient times, the mountains of the Urals were called Riphean, and until the 18th century they were called “stone belt” (translated from Turkic, “Ural” means belt).
- The Ural Mountains are relatively low: only a few peaks reach a height of 1.5 thousand meters above sea level, and the highest of them (Mount Narodnaya) is 1895 meters.
- Direction and extent
- Ural borders
- Mountain height
- How does it affect the nature of the Urals, its length from north to south for 2000 km?
slide 6
Geological structure
- The Urals are separated from the Russian platform by the Cis-Ural trough, which consists of sedimentary rocks (clay, sand, gypsum, limestone).
- The Ural Mountains were formed in PZ, but in MZ they were almost completely destroyed.
- Separate parts of the Urals rose during the KZ (Neogene). But even these folded-blocky Ural Mountains were destroyed as a result of external forces (weathering and erosion).
Find Mineral Deposits:
- Iron ore: Magnitogorsk, Kachkanarskoe, Khalilovskoe
- Copper ores: Krasnouralskoye, Gayskoye, Sibaevskoye
- Gold: Berezovskoe
- Asbestos: Bazhenovskoye
- Oil: Ishimbay
- Coal: Pechorsky, Kizelovsky
Slide 7
Ural
Slide 8
Slide 9
Natural resources of the Urals
The Ural Mountains are rich in mineral resources. This is a real treasure trove of minerals.
- Asbestos
- Diamonds
Slide 10
slide 11
Natural resources of the Urals
- Amethyst
- Emerald
slide 12
- Amethyst. “Warm edge” is a special way of processing a gem, when each edge coming from the center of the stone plays with rays.
- Rhodonite - translated from Greek means "rose"
slide 13
- Pomegranate
- Topaz
- Alexandrite
Slide 14
- Coil
- cat eye
- Eye of the Tiger
- Aquamarine
- Lapis lazuli
- Olivine
slide 15
Climate
- The climate of the Urals is varied. Why?
- Determine the average temperatures of January and July in the Northern (Polar) and Southern Urals.
- Why does the western slopes of mountains receive more precipitation than the eastern slopes?
- How do climatic conditions change with height?
- In what climate zone and region are the Ural Mountains located?
slide 16
Ural climate
- Despite their rather small height, the Ural Mountains have a rather significant effect on climatic conditions.
- They are the boundary between different climatic zones: the temperate continental climate of the East European Plain and the continental climate of Western Siberia.
- Atlantic air masses reach the western slope of the Urals, trying to overcome it, rise higher and cool. As a result, more precipitation falls in the western part of the Urals than in the eastern part (approximately 1.5-2 times). The temperature regime also has its own characteristics. In the western part of the Urals, winters are more snowy and, accordingly, milder. In the east, snow falls less, and frosts reach 45-50 ºС.
Slide 17
Ural waters
The Ural Mountains are the watershed of the rivers flowing along the West Siberian Plain and along the Russian Plain. In the Urals, rivers originate, so they are shallow.
, Competition "Presentation for the lesson"
Class: 8
Presentation for the lesson
Back forward
Attention! The slide preview is for informational purposes only and may not represent the full extent of the presentation. If you are interested in this work, please download the full version.
Lesson Objectives:
- Educational- to acquaint students with the uniqueness of the PTK Ural and compare it with the Caucasus.
- Educational– continue developing the ability to determine geographical location; to improve the generalized cartographic method of reading conventional signs.
- Educational- generate interest in the topic being studied; ecological thinking; cultivate respect for the environment.
Lesson type: a lesson in improving knowledge, skills and abilities, learning new material.
Type of lesson: lesson-journey using a computer.
Forms and methods of the lesson: individual work, pair work, heuristic conversation, messages
Means of education: atlases, slides, computer, interactive whiteboard.
Concepts: Ural, names of minerals and rocks.
Nomenclature: Deposits of iron ore - Magnitogorsk, Kachkanorskoe, copper ores - Krasnouralskoe, Gaiskoe, gold - Berezovskoe, asbestos - Bazhenovskoye, salt - Verkhnekamskoe, Sol-Iletskoe, oil - Ishembaisky.
Lesson plan:
1. Organizational moment.
2. Verification homework.
3. Learning a new topic:
3.1 Geographic location
3.2. Relief, geological development
3.3. Climate
3.4. Inland waters
3.5. Natural resources
4. Consolidation and withdrawal.
5. Homework.
DURING THE CLASSES
1. Organizational moment
2. Checking homework on the topic “Caucasus”
3. Learning a new topic
There is already a link in your chain of knowledge about the Caucasus Mountains (Slide 2 - image of the chain). Let's continue exploring the mountains. “Only mountains can be better than mountains ...” - the epigraph of today's lesson. Topic: "The Urals - the stone belt of the Russian land." The purpose of the lesson: To get acquainted with the uniqueness of the PTK of the Urals and compare it with the Caucasus (Slide 3 - the topic of the lesson).
Let's recall the plan for characterizing the study of the PTK and fill in the information about the Caucasus in the table. Working with an interactive whiteboard (Slide 4)
Teacher: Guys, what do you know about the Urals? (Mountain country, length 2000 km, border between Europe and Asia)(Slide 5).
– And today we will continue to fill the link with new knowledge.
1. The name of the mountain
Teacher: Ancient authors called these mountains Rifian, “Stone”, “Earth Belt”, “Stone Belt of the Russian Land” - this is how the Urals were called until the 18th century. The name Ural first appears in the works of the Russian historian and geographer Vasily Nikitich Tatishchev and replaces all previous names. What does this word mean: “Ur” in Mansi, and “ure” in Evenki means “mountain”, in Turkic “belt” (students write in notebooks). The Ural, which has a length of 2000 km, is not only a mountain, but a whole mountainous country, a mountain belt.
2. We determine the geographical position of the Ural Mountains. To do this, recall the plan for determining the geographical location. (Students work with atlases and an interactive map)
- In what direction are the Ural Mountains stretched?
- How can the nature of the Urals be affected by its elongation for ... km.
- Determine on the map 5 peaks of the Urals and its height? (Slide 7)
3. Relief and geological development. The Urals is located between two tectonic structures: Russian ... and West Siberian ...
The Ural was formed in the ancient Paleozoic - in the Hercynian period, in the Mesozoic it was almost completely destroyed. In the Neogene - Quaternary time, individual blocks were raised. Then again weathering. The destruction of the mountains revealed rich mineral deposits, made them available for development.
(Teacher's story)(Slide 8)
4. The climate of the Urals is diverse. Why?
Map task:
1. Determine the average January temperature in the north of the Urals.
2. Average temperature in the south of the Urals.
3. Average July temperature in the north of the Urals.
4. The average temperature in the south of the Urals (slide 8)
Practical work of students on maps of the atlas(Slide 9)
- The mountains are stretched for 2000 km. in the meridional direction and the northern part of the Urals is located beyond the Arctic Circle and receives much less solar radiation than the southern
- Differences in moistening of the western and eastern slopes.
- In any mountains, climatic conditions change with height.
5. Inland waters
The Ural is a watershed of current rivers, along the West Siberian Plain and along the Russian Plain. Find on the map the rivers flowing from the Ural Mountains.
Students mark major rivers and lakes on a contour map.(Slide 10).
Messages-presentations about the Chusovaya River, lakes Turgoyak and Zyuratkul are heard.
6. Natural resources of the Urals
Soviet poet Alexander Tvardovsky wrote:
Ural! The supporting edge of the state,
Her earner and blacksmith,
The same age as our ancient glory
And glory to the current creator ...
4. Brainstorm: Why did this particular region receive such a high title: “The stronghold of the state, its miner and blacksmith?” (Students' opinions are heard)
The Urals is the underground pantry of the country, about one thousand varieties of minerals have been found here and over 12 thousand mineral deposits have been taken into account.
The main wealth of the Urals is ores, and complex ones, with an admixture of titanium, vanadium, nickel, chromium, and copper ores with an admixture of zinc, gold, silver.
The Northern Urals are rich in forest resources, the Southern Urals are rich in soil, agro-climatic, but there is not enough water resources. The Urals are rich in recreational resources. (Slide 13)
Tourists are attracted not only by beautiful places, picturesque lakes, but also by the only Ilmensky mineralogical reserve. (student presentation)
5. Conclusions. Return to the purpose of the lesson. Checking the table "Comparative characteristics of the Caucasus and the Urals." (Slide 14)
6. Reflection. The journey is over. Did you like it? What have you learned?
7. Homework (slide 15)
Tikhonov Vladimir
The presentation material can be used in the lessons of the world around this topic. The presentation tells about the location of the Ural Mountains, their structure, rivers and lakes, climate, wildlife, natural resources.
Download:
Preview:
To use the preview of presentations, create a Google account (account) and sign in: https://accounts.google.com
Slides captions:
URAL - STONE BELT OF RUSSIA Lesson on OM for a 4B grade student high school No. 605 St. Petersburg Tikhonov Vladimir (teacher Bushuev V.Yu.)
"Ural" in Bashkir - belt There is a Bashkir tale about a giant who wore a belt with deep pockets. He hid all his wealth in them. The belt was huge. Once a giant stretched it, and the belt lay across the whole earth, from the cold Kara Sea in the north to the sandy shores of the southern Caspian Sea. This is how the Ural Range was formed.
The stone belt of the Urals stretches for more than 2500 km from the shores of the Arctic Ocean in the north to the semi-desert regions of Kazakhstan in the south. The Ural stretches between the East European and West Siberian plains, is located at the junction of Europe and Asia and is the border between these regions.
The Ural Mountains are divided into five parts: Polar Urals Subpolar Urals Northern Urals Middle Urals Southern Urals
The Polar Ural is the northernmost part of the Ural Mountains. The area is about 25,000 km². It is separated from the Subpolar Urals by the Khulga River. An active branch of the Northern Railway. Polar Ural
The Subpolar Urals is a mountain system in Russia, stretching from the headwaters of the Lyapin (Khulga) River in the north to Mount Telposiz ("The Nest of the Winds") (altitude about 1617 m) in the south. Subpolar Urals
Lakes of the Subpolar Urals mountain lakes mostly glacial type. 499 reservoirs are located at an altitude of 500 to 1000 m above sea level - the deepest (28 m) is Lake Torgovoe.
Lakes of the Subpolar Urals Above 1000 m there are only 68 lakes, and among them the deepest (38 m) is Lake Mansi. The water in the lakes is very clean, transparent, colorless, slightly mineralized.
The Northern Urals stretches from Kosvinsky Kamen to the banks of the Shchugor River. The Northern Urals The Northern Urals is one of the most remote and inaccessible regions of the Urals. Bear Corner - this is the name of one of its peaks.
The massifs of the Middle Urals are much lower, usually not higher than 600-800 m. There are relatively few lakes, but here are the sources of the Pechora and Ural rivers. Middle Ural
The name "South Ural" is also accepted as the unofficial name of the Chelyabinsk region. The Southern Ural is the widest southern part of the Ural Mountains. Southern Urals
Rivers Rivers belong to the basins of the Arctic Ocean: Pechora, Usa, Tobol, Iset, Tura, Lozva, Northern Sosva; and the Caspian Sea: Kama, Chusovaya, Belaya, Ural.
The climate of the Urals is typical mountainous; rainfall is unevenly distributed. The climate is very diverse, as all zones possess. Ural climate
Fauna A couple of centuries ago, the animal world was richer than it is now. Plowing, hunting, deforestation have displaced and destroyed the habitats of many animals. Wild horses, saigas disappeared
bustard bustards
Herds of deer migrated deep into the tundra. But rodents (hamsters, field mice) spread on the plowed lands
Forests are inhabited by predators: brown bears, wolves, foxes, wolverines, sables, ermines, lynxes
Ungulates are found in them: roe deer, elk, deer
Countless treasures lie in the Ural mountains And the “Mistress of the Copper Mountain” guards them
The Mistress of the Copper Mountain lives in the underground halls of the Ural gems if she wants to - she will turn into a green lizard, she will cry - the emeralds are dripping.
Natural resources cobalt potash salt rock salt gold platinum gems forest resources asbestos zinc copper ores iron ores