What is the shadow as it should be. Shine
Short term plan conducting an open lesson in physics in 8 "B" according to the program
University of Cambridge physics teacher Kuspakova R.T.
Coming together is a beginning. Sticking together is progress. Working together is a success.
Henry Ford.
It is not enough to have a good mind, the main thing is to use it correctly.
Rene Descartes.
04/16/16 Subject physics Class 8 "B"
Lesson topic:
Shine. Sources of light. The star is the sun. The law of rectilinear light propagation. Shade and partial shade. Solar and Lunar eclipses.
Duisembaev B.M. and other Physics and Astronomy: Textbook for 8th grade. General education school 2nd ed. revised / B.M. Duisembaev, G.Z.Bayzhasarova, A.A. Mendetbekova. - Almaty; Publishing house "Mektep", 2008.-256 p .; silt
Objectives:
The purpose of the lesson:
to familiarize students with natural and artificial light sources; explain the law of rectilinear light propagation; explain the nature of solar and lunar eclipses.Encourage students to overcome difficulties in the process mental activity, cultivate an interest in physics.
Learning outcomes:
Everybody knows what is light, shadow, partial shade, eclipses.Most can useon practicebasic knowledge of light phenomena. Some are capable to analyze the differences in the formation of shadows and penumbra, eclipses.Be able to describe physical phenomena based on knowledge. Be able to formulate complete and competent answers and questions.Learning new concepts, teaching to work in a group, the ability to listen to opinions, ask questions on the topic.
Key ideas:
group mutual education will allow students to get closer, teach them the ability to hear and listen to the interlocutor, be more tolerant of each other, increase educational and cognitive motivation, improve the psychological climate in the classroom; the ability to conduct a dialogue will teach you to argue your point of view; activating students' critical thinking will allow them to solve the problems posed to them, develop research skills, relying on their own and indirect experience, will increase the efficiency of assimilation and actualization of knowledge, which will make it possible to transfer students to a mode of self-development.
Time
Strategy
Resources
Lesson content
Teacher activity: what will I do?
Activities
pupils
Org.
moment. (2 minutes)
Greeting, dividing into 2 groups(according to the inscription on candy wrappers), and presentation of the expert council
Greet
each other- Cross your arms over your chest (Arabs).
To create a collaborative environment, he uses the Compliments strategy.
Compliment the neighbor on the right and thank the neighbor on the left for something.
Introductory part (10min)
ICT,
group work,
KM,
ODO,
Internet resources.
Textbook
physics grade 8,
physics reference book,posters,
cell Phones.
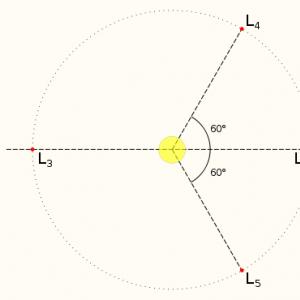
Before you start learning new topic need to analyze the results test work, answer the questions that have arisen about the work, sort out the most frequently made mistakes.I . Learning new material Outline of presentation of new material: 1. Light as visible radiation. 2.Natural and artificial light sources. 3.Beam and beam. 4.The law of rectilinear light propagation. five.Shade and partial shade. 6.Solar and lunar eclipses. In a short introductory talk, I will tell the students about the meaning of light in human cognition of the world around him. Thanks to the organ of vision, a person sees the world, communicates with the environment, can work and rest. Labor productivity depends on how objects are illuminated. Plants cannot develop normally without sufficient lighting. Knowledge of the laws of light phenomena allows one to design various optical devices that are widely used in human practice. The best illustration of the significance of light phenomena in human life is the "minute" experiment: invite the students to close their eyes for one minute and imagine "life in darkness" !!! What is light? All bodies are made of atoms (or molecules). But just as there is no sound in a guitar string, there is no light in an atom. The state of an atom when its energy is minimal is called normal (or unexcited). In this state, the atom does not emit energy. Any other state of an atom with an energy different from the minimum is calledexcited. An atom can be in an excited state for 10 3 from. The transition of an atom from an excited state to a normal state is accompanied by radiation electromagnetic waves. Light is electromagnetic radiationperceived by the eye by visual sensation. Question:-What is the difference between the radiation of an iron or a boiler and the radiation of an electric incandescent lamp?Light source are called bodies that can emit light. Any luminous body consists of a huge number of "elementary" emitters. Thus, the optical radiation of light sources is a set of emissions from individual atoms and molecules. "Demonstrating to students various sources of light (a burning match, a candle, a luminous bulb), the teacher informs that there arenatural andartificial sources of light. Natural light sources are the Sun, stars, atmospheric charges, as well as luminous objects of the animal and plant world (fireflies, rot, etc.) Artificial light sources, depending on what process is the basis for obtaining radiation, are divided intothermal andluminescent. - Give examples of natural and artificial light sources.Since light is electromagnetic radiation and all the properties of electromagnetic waves are inherent in it, then all optical problems can be solved on the basis of wave representations. However, this requires the use of a very cumbersome mathematical apparatus. However, when solving problems of constructing images in mirrors and lenses and when calculating optical devices, scientists use geometric methods. These methods make up the contentgeometric optics, which is otherwise calledradial optics. The basic concepts of geometric optics arebeam and beam. Moreover, these concepts cannot be identified. A beam of light can be observed, and the beam can only be drawn on paper: -cylindrical or conical channels within which light propagates are calledlight beams ; - ray is called a geometric line indicating the direction of transfer of light energy. Now the differences of these physical concepts with such their figurative-literary "analogues" as "rays of the Sun", "a ray of light fell on the table", "Katerina is a ray of light in the dark kingdom" and so on are obvious. There are no infinitely narrow beams of light; the light beam always has a finite width. The beam is, as it were, the axis of the beam, and not the beam itself.Geometric optics is based on three laws: a) the law of rectilinear light propagation; b) the law of light reflection; c) the law of refraction of light.Light in a homogeneous medium propagates rectilinearly - this is how the law of rectilinear propagation of light is formulated. What examples can you give to confirm the rectilinear propagation of light?Optically homogeneous an environment in which light travels at a constant speed is considered. If there are two media in which light travels at different speeds, then the medium where light travels at a lower speed is calledoptically denser, and an environment where light travels with a higher speed -optically less dense. Shade and partial shade. The straightness of light propagation is confirmed by the formationshadows. If you take a small light source, a screen and place an opaque object between them, then a dark image of its outlines will appear on the screen - a shadow.A shadow is an area of \u200b\u200bspace that does not receive light energy from a light source. - Why is the formation of a shadow proof of the straightness of light propagation? In the experiment, we did not take into account the size of the light source. A light source that is small compared to the distance to the screen is calledpoint light source. If we take a larger light source, then a penumbra is also formed around the shadow on the screen.Penumbra is an area of \u200b\u200bspace into which light energy from a light source partially falls. Solar and lunar eclipses are explained by the formation of shadows and penumbra.With a solar eclipse the full shadow of the moon falls on the earth. From this place on the Earth, the Sun is not visible. When the Moon, revolving around the Earth, falls into its shadow, thenmoon eclipse. At the end of the lesson, you can talk about the practical use of the law of rectilinear propagation of light (construction, laying roads, determining the height of objects, and so on).
Students' answers,
work in groups,
result
1 min
Fizminutka
Basics
part (15min)
View the PPT presentation.Watching video
We pose the problem: Group work: Snowball strategy - the teacher invites students to prepare speeches on the following questions:
1 group "Sun": What is light? What bodies serve as light sources? What is the difference between the radiation of an iron or a boiler and the radiation of an electric incandescent lamp? The star is the sun. The law of rectilinear light propagation.
2.group "Moon": What is meant in physics by the terms ray, beam of light, point source of light? Shade and partial shade. Solar and Lunar Eclipses. Give examples.
Individual work: Self-test knowledge
Test:
1. Light radiation ....?
A. ... makes different bodies visible;
B. Perceived by the eye; Radiates a heated body.
2 ... Light sources are
A. ... only natural. ... only artificial.
B. ... natural and artificial
3 ... What is a point light source?
A. Luminous body of small size.
B. source, the size of which is much less than the distance to it.
B. Very weakly luminous body.
4 ... How does light propagate in a homogeneous environment?
A. straightforward. B. curvilinear.
B. On any line connecting the source and the subject.
5 ... How light sources are subdivided
A. natural and artificial
B. mechanical. thermal
6. Is the source of visible light?
A) Heated electric kettle
B) TV antenna. C) Welding arc
7 ... Does it emit light among the listed sources?
A) Bonfire; B) Radiator; C) Sun.
8. What is the shadow?
A) An area of \u200b\u200bspace where light does not fall due to rectilinear propagation.
B). Dark place behind the subject
C) Unlit place
9. What is partial shade? What should be the source.
A) The place where half of the light falls. Long.
B) A place where there is light, but it is not enough.
C) An area of \u200b\u200bspace where there is both shadow and light. Point.
10. Which line is called a ray of light?
A) The line emanating from the light source
B A line, the will of which energy is propagated from a light source.
C) The line along which light from the source enters the eye.
Check correct answers appear on click
2.In
3. B
4.In
5.A
6.In
7.A
8.B
9B
Students are watching a presentation
discussion of the presentation,
work with the tutorial.
Group work: Snowball Strategy:
Students write down their thoughts and opinions individually.
(discuss their positions and reach a compromise on this issue and write down the result).
Create a poster by inscribing concepts according to the theme.
At the end of the discussions, students defend the work of the group, where they set out their understanding of the topic, generalize, substantiate their point of view, demonstrate the ability to argue their opinion; assessment skills.
Protection of posters.
Group work, self-regulation.
Students take tests.
Self-esteem
0 errors - 5
1-2 errors - 4
3-4 errors - 3
5-6 errors - 2
I'll finish
reader
part (8min)
We solve quality problems.
1. How can the light sources be positioned so that during the operation the shadow of the surgeon's hands does not cover the operation site?
Answer : Place several lamps overhead
2. Why don't objects give shadow on a cloudy day?
Answer : Subjects are lit by diffused light, the illumination from all sides is the same.
3. Can solar and lunar eclipses be observed from any point on the Earth's surface?
Answer : Lunar yes. Solar no.
4. Can a cyclist pass his shadow?
Answer : Yes, if a shadow is formed on a wall parallel to which the cyclist is traveling and the light source is moving faster than the cyclist in the same direction.
5. How does the size of the penumbra depend on the size of the light source?
Answer : The larger the source, the greater the partial shade.
6. Under what condition should the body produce a sharp shadow without penumbra on the screen?
Answer : If the light source is much smaller than the body.
Guys! In conclusion, I want to say. The physicist sees what everyone sees: objects and phenomena. He, like everyone else, admires the beauty and grandeur of the world, but behind this beauty available to all, another beauty of laws in the infinite variety of things and events opens up to him.
Love, children, physics!
She is always, everywhere.
Will help you in the skill,
Both in life and in work!
Lesson summary (3min)
Summing up the lesson,
assessment,
mutual appreciation
Strategy "Two stars and a wish" - students give 2 stars and write down for what, express one wish, which, in their opinion, will improve this work.
A word to the expert council
Reflection " Starry sky»
Home. Back.
(2 minutes)
§61.62, 63
Grateful secondary school
Public lesson in physics in 8 "B" class on the topic
Prepared by the physics teacher Kuspakova R.T.
aktobe
2015-2016 academic year
When illuminated by a light source, the dimensions of which are comparable to both the dimensions of the body and the distance between the source and the body. The penumbra is the periphery (outer part) of the shaded area. In the penumbra, only part of the light source is visible. In this it differs both from a full shadow, in which the source is not visible at all, and from full light: in the light it is completely visible.
Penumbra (the outer part of the shadow) from a celestial body can be observed, for example, during a partial eclipse of the Sun, when the observation point falls into the penumbra formed by the Moon in a stream of sunlight.
In the visual arts, in particular in photography, penumbra is understood not so much as space, but as a part of the body surface as an element of chiaroscuro - a weak shadow, a gradation of chiaroscuro on the surface of an object, occupying an intermediate position between light and deep shadow. Penumbra occurs when an object is illuminated by multiple light sources on a surface facing the light source at a slight angle.
In everyday speech, penumbra can be called any thin (weak, transparent, pale shadow) that occurs in low light.
Literature
- Yastold-Govorko V.A. Penumbra // Yastold-Govorko V.A. Photography and processing. Shooting, formulas, terms, recipes. Ed. 4th, abbr. M., Art, 1977.
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
Synonyms:See what "Penumbra" is in other dictionaries:
Penumbra ... Spelling dictionary-reference
The space between the areas of full shadow and full light that forms behind an opaque body when it is illuminated by a light source with large angular dimensions (Fig.). In the area of \u200b\u200bP., only part of the source is visible (in the shadow, the source is not visible at all). ... ... Physical encyclopedia
PENDANT, half-shade, about half-shade, half-shade, wives. Thin shade, very dimly lit place. "A distant threshing floor is slightly noticeable in partial shade." A.K. Tolstoy. Ushakov's explanatory dictionary. D.N. Ushakov. 1935 1940 ... Ushakov's Explanatory Dictionary
PENONTANE, and, about partial shade, in partial shade and in partial shade, pl. and, to her and to her, wives. Weak transparent shadow. In partial shade of foliage. Ozhegov's Explanatory Dictionary. S.I. Ozhegov, N.Yu. Shvedova. 1949 1992 ... Ozhegov's Explanatory Dictionary
Noun., Number of synonyms: 2 shade (34) chiaroscuro (3) ASIS synonym dictionary. V.N. Trishin. 2013 ... Synonym dictionary
penumbra - penumbra, genus. penumbra, offer. about partial shade, partial shade and partial shade; pl. penumbra, genus. penumbra and obsolete penumbra ... Dictionary of pronunciation and stress difficulties in modern Russian
The space between full shadow and full light areas. It is formed behind an opaque body when it is illuminated by a light source, the dimensions of which are comparable both with the dimensions of the body and with the distance between the source and the body (Fig.). In the area of… … Great Soviet Encyclopedia
penumbra - pusšešėlis statusas T sritis fizika atitikmenys: angl. half shade; partial shadow; penumbra vok. Halbschatten, m; Penumbra, f rus. penumbra, f pranc. pénombre, f ... Fizikos terminų žodynas
G. 1. Thin, pale shadow. 2. The dimly lit space between full shadow and full of light. Efremova's explanatory dictionary. T.F. Efremova. 2000 ... Modern dictionary Russian language Efremova
Penumbra, penumbra, penumbra, penumbra, penumbra, penumbra, penumbra, penumbra, penumbra, penumbra, penumbra, penumbra, penumbra 2. penumbra, penumbra, penumbra, penumbra, penumbra, penumbra, penumbra, penumbra, penumbra, penumbra ... ... Word forms
The light has to get into our eyes so that we can see something. If we close our eyes or enter a dark room, we will not see anything. We can perceive the visual world only with the help of our eyes.
A light source is a body that emits light - the sun, lamp, candle, etc.
Our eye also perceives light from those bodies that are illuminated by some source of light. All bodies are capable of reflecting light to a greater or lesser extent. 
Shadow
Light travels in a straight line. The beam of light is especially visible if there are dust particles or water droplets in the air that reflect the light.
If a ray of light falls on an opaque object, then an unlit spot, called a shadow, appears behind it. Depending on how far the subject is from the light source, the amount of shadow can vary. 
If we illuminate the subject with two lamps that stand side by side, then two shadows appear, partially overlapping one another.
Places that are not illuminated by any source are called direct shadows. Unlike direct shadow, partial shade is formed by superimposing shadow and light. 
The sun constantly illuminates the moon. Since the Moon makes a full revolution around the Earth in 28 days, we can observe the degree of illumination of the Moon's surface over time. 
On a new moon, the Moon is between the Sun and the Earth in such a way that its illuminated part is not visible to us.
The moon is growing and we see more and more illuminated part of the surface. On a full moon, we observe the fully illuminated surface of the moon.
When the Moon decreases, the illuminated part visible from the Earth slowly disappears, until the Moon turns into a thin crescent.
Once every 1.5 years, the trajectory of the Moon crosses the trajectory of the Earth, so the Moon falls into the shadow cast by the Earth. 
It is then that the Moon is not illuminated by the Sun, and we do not see it. This is called a lunar eclipse. 
Approximately once every 2.5 years, the Moon is located between the Sun and the Earth. At this moment, one can observe incomplete solar eclipse... If you are on Earth in the place where the Moon casts a shadow, the diameter of which is about 260 km, then you can see a total eclipse of the Sun. But this phenomenon is very rare and repeats itself no more often than once every 200 years.